Verb Conjugation is a fundamental aspect of English grammar. It involves changing a verb’s form to align with the subject and convey the correct meaning. Understanding this concept helps learners form clear and grammatically accurate sentences, ensuring effective communication in various contexts.
Verb conjugation refers to the process of changing a verb’s form to match the subject of the sentence and convey tense, mood, voice, number, or person.
Fatimah writes a letter.
Table of Contents
Examples of Verb Conjugation
- Ali runs every morning.
- They are studying for exams.
- I will call you tomorrow.
- Hassan reads a book every evening.
- We have completed our project.
- She sings beautifully.
- Bilal will visit his grandmother tomorrow.
- They were playing football in the park.
- I had already eaten dinner before they arrived.
- She works hard every day.
- Ahmed was writing a poem.
- The children are drawing pictures.
- I will have finished my homework by 8 PM.
- Fatimah and Ayesha study together.
- Zaid prepares breakfast every morning.
- We were watching a movie when the lights went out.
- He has been working here for five years.
- The teacher explains the lesson clearly.
- They will travel to Mecca next month.
- She had been waiting for an hour before the train arrived.
Types of Verb Conjugation
Verb conjugation is categorized into two main types: Regular Verbs and Irregular Verbs.
Regular Verbs
Regular verbs follow predictable patterns when conjugated. To form their past tense and past participle, simply add “-ed” or “-d” to the base form.
✅ Sarah plays football. (Present)
✅ Sarah played football. (Past)
✅ Sarah has played football. (Past participle)
Irregular Verbs
Irregular verbs do not follow standard patterns and often require memorization. Their past tense and past participle forms vary.
✅ Yusuf eats breakfast early. (Present)
✅ Yusuf ate breakfast early. (Past)
✅ Yusuf has eaten breakfast early. (Past participle)
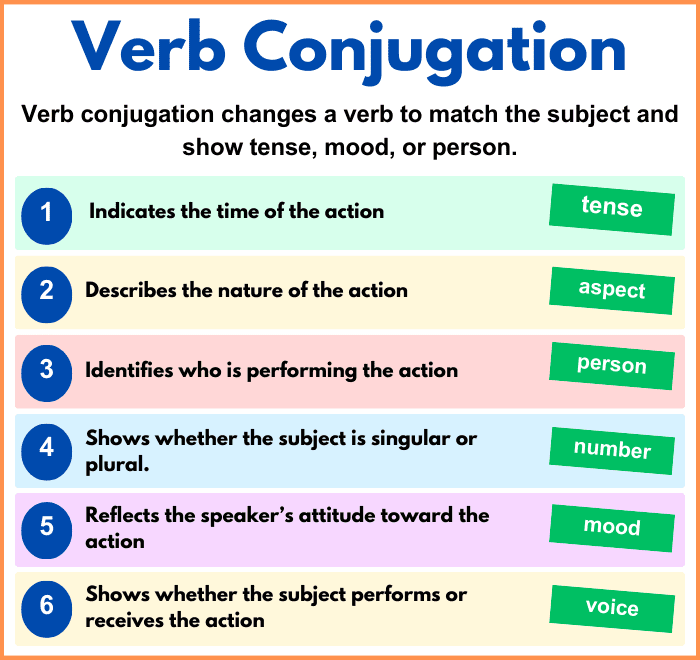
Elements of verb Conjugation
Tense: Indicates the time of the action (past, present, future).
Aspect: Describes the nature of the action (ongoing, completed, etc.).
Person: Identifies who is performing the action (1st, 2nd, 3rd person).
Number: Shows whether the subject is singular or plural.
Mood: Reflects the speaker’s attitude toward the action (indicative, imperative, subjunctive).
Voice: Shows whether the subject performs or receives the action (active, passive).
How to Conjugate a Verb? – Rules and Examples
Verb conjugation depends on various grammatical elements:
Verb Conjugation by Person
Changes depending on whether the subject is in the first, second, or third person.
| Person | Singular | Plural |
|---|---|---|
| First Person | I write | We write |
| Second Person | You write | You write |
| Third Person | He/She/It writes | They write |
Verb Conjugation by Number
The number of the subject (singular or plural) affects the verb form.
| Number | Example |
| Singular | Zainab reads a book. |
| Plural | Zainab and Ali read books. |
Verb Conjugation by Mood
Mood indicates the verb’s purpose in the sentence, such as stating facts, giving commands, or expressing wishes.
| Mood | Example |
| Indicative | Mariam is learning English. |
| Imperative | Please close the door. |
| Subjunctive | If he were here, he would help. |
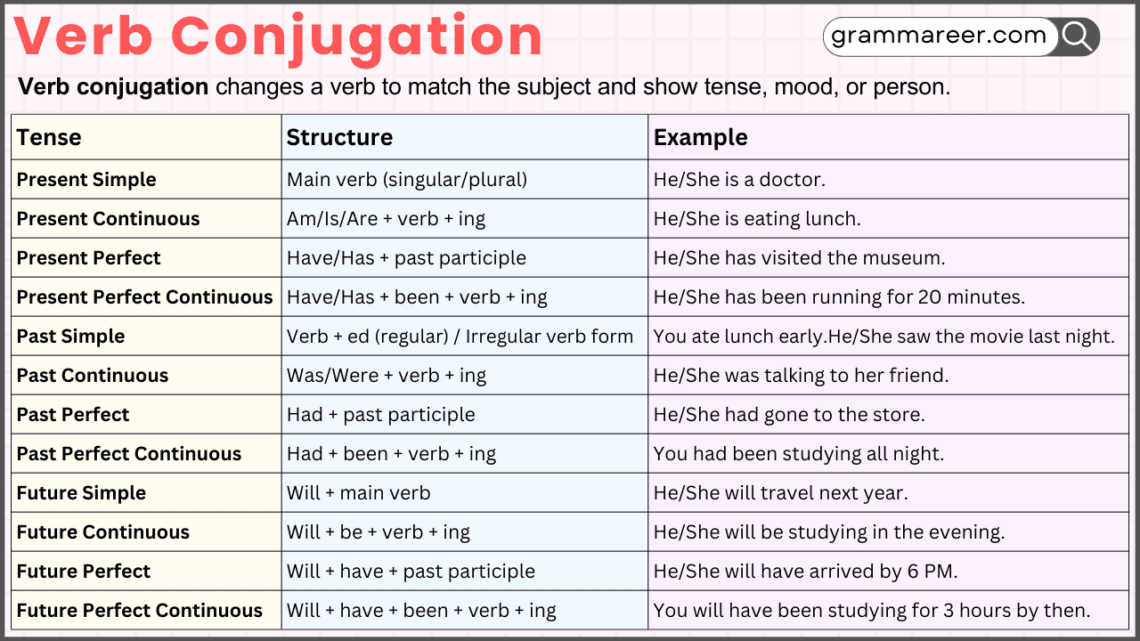
Verb Conjugation by Tense
Tense shows the time of the action or state described by the verb.
| Tense | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Present Simple | Main verb (singular/plural) | You are a student. He/She is a doctor. |
| Present Continuous | Am/Is/Are + verb + ing | You are studying math. He/She is eating lunch. |
| Present Perfect | Have/Has + past participle | You have written a letter. He/She has visited the museum. |
| Present Perfect Continuous | Have/Has + been + verb + ing | You have been practicing for hours. He/She has been running for 20 minutes. |
| Past Simple | Verb + ed (regular) / Irregular verb form | You ate lunch early. He/She saw the movie last night. |
| Past Continuous | Was/Were + verb + ing | You were sleeping during the storm. He/She was talking to her friend. |
| Past Perfect | Had + past participle | He/She had gone to the store. They had studied for the exam. |
| Past Perfect Continuous | Had + been + verb + ing | You had been studying all night. They had been playing for two hours. |
| Future Simple | Will + main verb | You will meet your friends later. He/She will travel next year. |
| Future Continuous | Will + be + verb + ing | You will be working tomorrow morning. He/She will be studying in the evening. |
| Future Perfect | Will + have + past participle | He/She will have arrived by 6 PM. They will have graduated by next year. |
| Future Perfect Continuous | Will + have + been + verb + ing | You will have been studying for 3 hours by then. They will have been playing the game for 2 hours. |
Importance of Conjugation in English Grammar
- Shows tense: e.g., “She writes” (present) vs. “She wrote” (past).
- Ensures subject-verb agreement: e.g., “He runs” vs. “They run.”Clarifies actions: e.g., “I am eating” (ongoing).
- Expresses mood: e.g., “Go to school!” (imperative).
- Indicates voice: e.g., “She sent the letter” (active) vs. “The letter was sent” (passive).
- Improves clarity in communication.
FAQs
Verb conjugation is the process of changing a verb’s form to match the subject, tense, mood, and other grammatical elements. For example, “go” becomes “went” in the past tense and “goes” for a third-person singular subject.
Regular verbs follow a predictable pattern by adding “-ed” to form past tense, while irregular verbs have unique forms that often need memorization. For example, “walk” (regular) becomes “walked,” but “go” (irregular) becomes “went.”
Yes, English has exceptions like “be,” which changes forms irregularly: “am,” “is,” “are,” “was,” “were,” etc. These exceptions often depend on the tense and subject.
Conclusion
Verb conjugation is a cornerstone of English grammar, crucial for constructing accurate and meaningful sentences. By understanding the rules and practicing regularly, learners can enhance their language proficiency and communicate with confidence.
You May Also Like