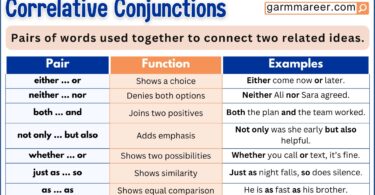
Get to know different types of pronouns in easy terms. A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun. This helps avoid repeating the same noun too much. Pronouns, like nouns, can be about people, things, ideas, or places. From personal ones like “he” to reflexive ones like “itself,” each type of pronoun has a specific role in helping us talk clearly.
Table of Contents
What are pronouns?
Pronouns are words that replace nouns in a sentence. Instead of repeating the same noun over and over, we use pronouns to make sentences clearer and less repetitive. They can refer to people, animals, things, or ideas. For example:
- He is reading a book.
- I gave the gift to her.
- We are going to the park.
- Can you pass me the salt?
- The cat is cleaning its fur.
Pronouns, like “he,” “her,” “we,” “me,” and “its,” replace specific nouns, making our language clear and efficient.
Pronouns List
In our writing and talking, we use many different pronouns every day. Here are some of the pronouns we use regularly:
- I
- You
- He
- She
- It
- We
- They
- Me
- You
- Him
- Her
- Us
- Them
- Myself
- Yourself
- Himself
- Herself
- Itself
- Ourselves
- Yourselves
- Themselves
These words are used to replace or refer to nouns, making sentences more concise and clear.
Pronouns are generally divided into three main kinds:
Types of Pronouns with Examples:
1. Personal Pronoun:
Personal pronouns are words that replace specific people or things in a sentence. They make sentences less repetitive and more straightforward.
Examples:
- I am going to the store.
- Can you pass me the salt?
- He is playing in the park.
- She loves to read, and it makes her happy.
- We are going on a trip.
2. Interrogative Pronoun
Interrogative pronouns are words used to ask questions. Asking questions becomes easier when we use these interrogative pronouns to gather information in our daily conversations.
Examples:
- Who is coming to the party?
- To whom did you give the book?
- Whose jacket is this?
- What is your favorite color?
- Which car is yours?
3. Reciprocal Pronoun:
Reciprocal pronouns show actions or feelings shared between two or more people. The main ones are “each other” and “one another.”
Example:
- Sarah and Tom love each other.
- The team members support one another.
- They hugged each other after the game.
- We always support one another.
- The kids often share toys with each other.
4. Indefinite Pronoun
Indefinite pronouns are words that don’t point to a specific person, place, or thing. They talk about non-specific stuff. When we’re not talking about a particular thing or person, we use indefinite pronouns.
Examples:
- Everyone enjoyed the party.
- Can I have some cookies?
- Anybody can join the club
- Many like to travel.
- Nobody knows the answer.
5. Reflexive Pronoun:
Reflexive pronouns are special words that show an action reflecting back to the person or thing doing the action. They end in “-self” or “-selves.”
Examples:
- I will do it
- He taught himself to play guitar.
- She bought the gift for herself.
- The cat cleaned itself.
- We made dinner ourselves.
6. Demonstrative Pronoun:
Demonstrative pronouns are words that point to specific things, helping us identify what we’re talking about.
Examples:
- I love this
- Look at that beautiful sunset.
- Can you pass me these cookies?
- I like those flowers in the garden.
- Is this your car?
7. Intensive Pronoun:
An intensive pronoun emphasizes a noun in a sentence, often for added clarity. It doesn’t change the meaning of the sentence but highlights the subject.
Examples:
- I made the cake
- The dog found the bone
- She solved the puzzle
- They built the treehouse
- He repaired the car
8. Relative Pronoun:
Relative pronouns are words that connect different parts of a sentence. They help us understand more about a person, place, or thing mentioned in the sentence.
- The friend who helped me is kind.
- I found the book which you recommended.
- The car that I bought is red.
- The boy, whose toy was lost, is upset.
- She is a doctor whom I admire.
Examples of Pronouns Types
- I love to read, and it makes me
- Can you pass the salt to him?
- We are going to the market.
- She is talking to her
- The dog wagged its
- You should try this new recipe.
- The flowers are for us.
- They will come to the party.
- She is playing with her
- This cake is for you.
- The keys are with them.
- It is raining outside.
- The kids are enjoying themselves.
- Who is knocking on the door?
- Whose bag is this?
- Can you give me that pen?
- You should take care of yourself.
- I saw the movie with her.
- We have completed the project.
- The cat is licking its
MCQs
Q1.What is a pronoun?
a)A verb
b) A word that replaces a noun
c) An adjective
Q2.Which pronoun is used to refer to a group of people?
a) It
b) Them
c) He
Q3.What does the pronoun “itself” indicate?
a) A specific person
b) A thing or animal
c) A place
Q4.Which is a possessive pronoun?
a) You
b) Yours
c) He
Q5.In the sentence, “She bought a dress for herself,” what type of pronoun is “herself”?
a) Demonstrative pronoun
b) Reflexive pronoun
c) Interrogative pronoun
Q6.What is the interrogative pronoun in the question, “Who is coming to the party?”
a) Who
b) Is
c) Coming
Q7.Which pronoun connects clauses and relates to nouns?
a) That
b) Who
c) It
Q8.What does the relative pronoun “whose” indicate?
a) Possession
b) Location
c) Time
Q9.What type of pronoun is “none”?
a) Personal pronoun
b) Indefinite pronoun
c) Demonstrative pronoun
Answers:
- b) A word that replaces a noun
- b) Them
- b) A thing or animal
- b) Yours
- b) Reflexive pronoun
- a) Who
- a) That
- a) Possession
- b) Indefinite pronoun
FAQs
Q1: What is the main purpose of pronouns?
Pronouns replace nouns to avoid repetition and make sentences smoother.
Q2: Can you give examples of personal pronouns?
Sure, examples include “I,” “you,” “he,” “she,” “it,” “we,” and “they.”
Q3: How do reflexive pronouns work?
Reflexive pronouns refer back to the subject of the sentence, like “myself” or “himself.”
Q4: What role do interrogative pronouns play?
Interrogative pronouns, such as “who,” “whom,” and “what,” are used to ask questions.
Q5: Why are relative pronouns important in connecting sentences?
Relative pronouns, like “that” or “who,” link clauses together, providing a smooth flow in writing or speaking.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE