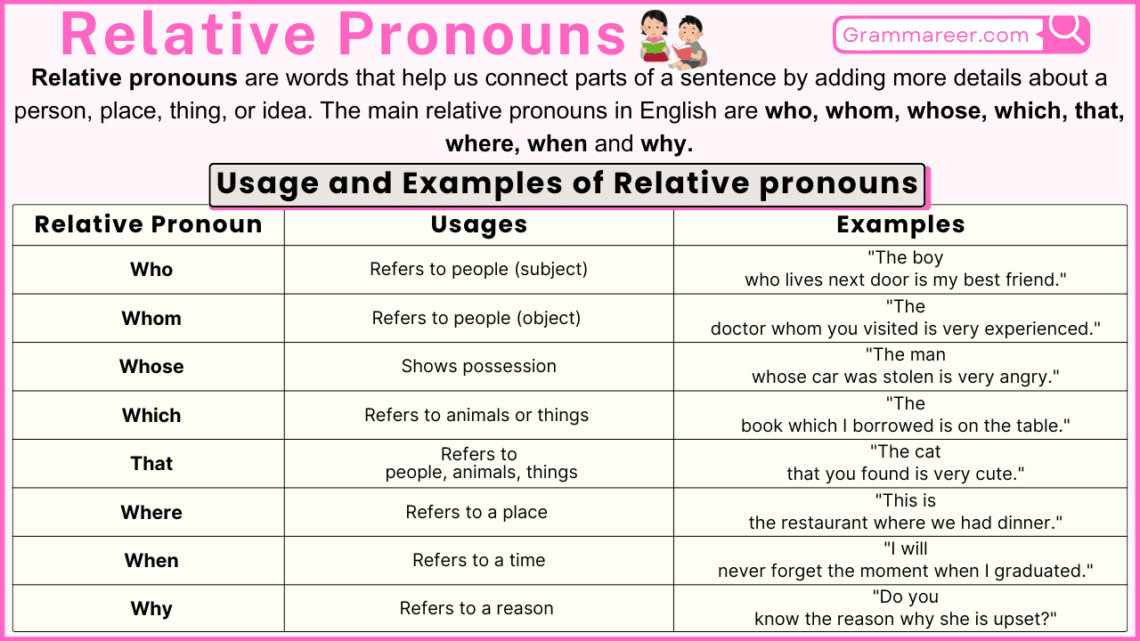
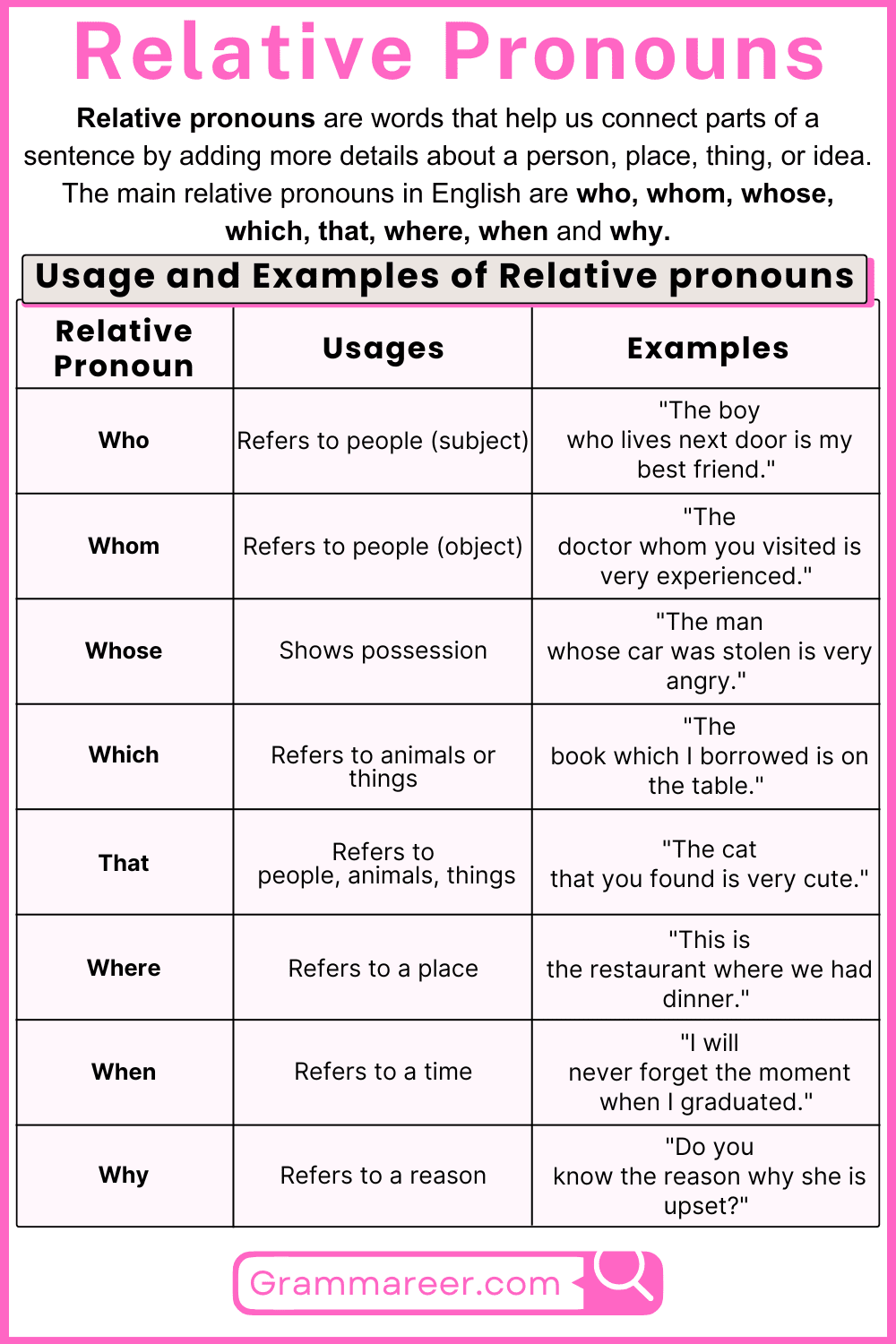
Relative pronouns are an important aspect of English grammar that allow us to connect two clauses in a sentence. They help us add more information about a subject or object without creating a new sentence. Understanding how to use relative pronouns properly is essential for clear and effective communication.
Table of Contents
Definition of Relative Pronouns
Relative pronouns are words that connect clauses or phrases to nouns. They help give more information about the noun. The most common relative pronouns are “who,” “whom,” “whose,” “which,” and “that.” For example:
- “The girl who sings is my sister.”
- “I have a book that you might like.”
Common Relative Pronouns
Examples of Relative Pronouns
- The dog that barks loudly is mine.
- She is the teacher who helps us with math.
- I have a friend whose brother plays soccer.
- This is the movie which I told you about.
- The cake that she made was delicious.
- The man who lives next door is very nice.
- I found a wallet that belongs to you.
- The book which I read last night was exciting.
- He is the artist whose paintings are in the gallery.
- The house that we visited is for sale.
Uses of Relative Pronouns
Relative pronouns are words like who, whom, whose, which, and that. They help us link sentences and give more information about a person or thing. Here are the main uses of relative pronouns in simple terms:
Joining Sentences Together
Relative pronouns connect two sentences by adding extra details.
-
- The boy who plays soccer is my friend.
Avoiding Repeating Words
They let us avoid repeating the same words in sentences.
Without a relative pronoun:
- The girl is smart. The girl won the prize.
With a relative pronoun:
- The girl who won the prize is smart.
Giving More Details About People or Things
They help explain which person, thing, or place we’re talking about.
- The book that you gave me is fun to read.
Showing Who Something Belongs To
Whose shows who owns something or is connected to someone.
- The woman whose car broke down is waiting for help.
Adding Important or Extra Information
They can add necessary or extra information to a sentence.
- The house which is blue belongs to John (extra information).
- The dress that she wore was beautiful (important information).
Common Mistakes with Relative Pronouns
Using relative pronouns incorrectly is a common mistake in English. Let’s look at some of the errors and how to fix them:
Who vs. Whom:
Many people confuse “who” and “whom.” Remember, “who” is for subjects, and “whom” is for objects.
- Incorrect: The man who I spoke to was helpful.
- Correct: The man whom I spoke to was helpful.
That vs. Which:
“That” is used for restrictive clauses, while “which” is for non-restrictive clauses.
- Incorrect: The book that you gave me, which is red, is on the table.
- Correct: The book, which is red, is on the table.
Where vs. That:
“Where” should be used for places, while “that” can refer to people, things, or ideas.
- Incorrect: This is the city that I was born in.
- Correct: This is the city where I was born.
Read More