In English, verbs are divided into two main types: regular verbs and irregular verbs. Understanding the difference between these types can help improve your language skills. Both are crucial for forming sentences correctly and are widely used in both written and spoken English.
Table of Contents
What Are Regular Verbs?
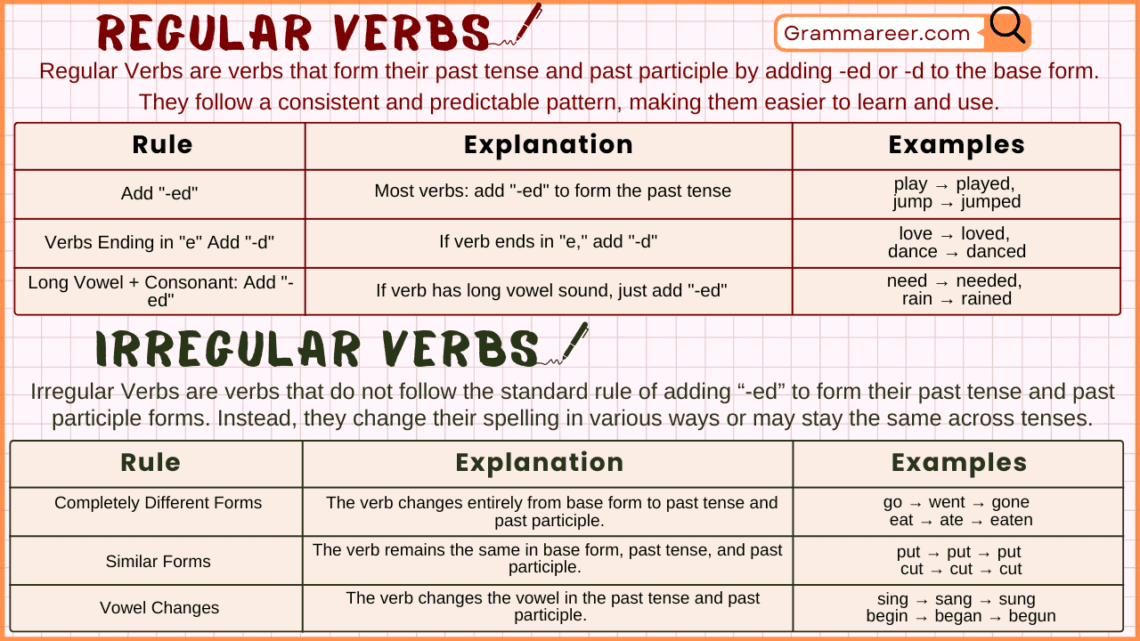
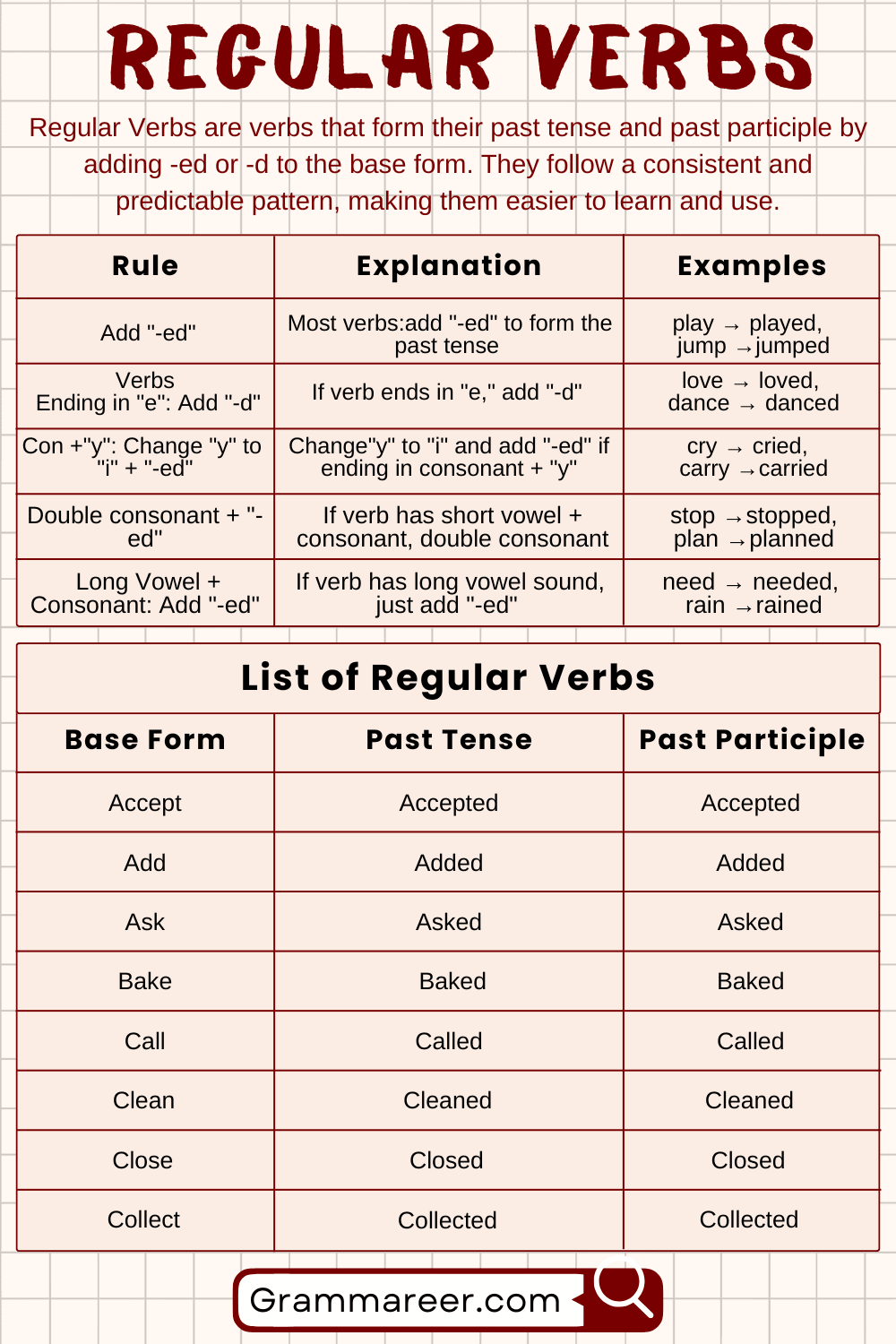
In English grammar, regular verbs are verbs that follow a predictable pattern when forming their past tense and past participle forms. For basic grammar learners, this means that regular verbs are easier to learn and use because they add the ending “-ed” to the base form of the verb to show something happened in the past.
Rules for Regular Verbs
Regular verbs are verbs that follow a set pattern to form their past tense and past participle. In English, most regular verbs form these by adding “-ed” or “-d” to the base form of the verb. Here’s a guide to understanding these rules with examples.
Basic Rule: Add “-ed”
For most regular verbs, simply add “-ed” to make the past tense.
- play → played, jump → jumped, work → worked, ask → asked
Verbs Ending in “e”: Add “-d”
If a verb already ends in “e,” just add “-d” instead of “-ed.”
- love → loved, move → moved, dance → danced, bake → baked
Verbs Ending in Consonant + “y”: Change “y” to “i” and Add “-ed”
When a verb ends with a consonant + “y,” change the “y” to “i” and add “-ed.”
- cry → cried, carry → carried, fry → fried, try → tried
Note: If the verb ends in vowel + “y,” like play or enjoy, just add “-ed” without changing anything.
Verbs Ending in Short Vowel + Consonant: Double the Consonant and Add “-ed”
If a verb has a short vowel (like “a,” “e,” “i,” “o,” or “u”) and ends in a single consonant, double the consonant first, then add “-ed.”
- stop → stopped, plan → planned, hug → hugged, beg → begged
Verbs Ending in Long Vowel + Consonant: Just Add “-ed”
If a verb ends with a long vowel sound (like need or fail) and a consonant, just add “-ed.”
- need → needed, fail → failed, clean → cleaned, rain → rained
List of Regular Verbs
| Base Form | Past Tense | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| Accept | Accepted | Accepted |
| Add | Added | Added |
| Ask | Asked | Asked |
| Bake | Baked | Baked |
| Call | Called | Called |
| Clean | Cleaned | Cleaned |
| Close | Closed | Closed |
| Collect | Collected | Collected |
| Cook | Cooked | Cooked |
| Dance | Danced | Danced |
| Deliver | Delivered | Delivered |
| Dry | Dried | Dried |
| Enjoy | Enjoyed | Enjoyed |
| Erase | Erased | Erased |
| Fix | Fixed | Fixed |
| Help | Helped | Helped |
| Jump | Jumped | Jumped |
| Kiss | Kissed | Kissed |
| Laugh | Laughed | Laughed |
| Learn | Learned | Learned |
| Listen | Listened | Listened |
| Look | Looked | Looked |
| Love | Loved | Loved |
| Move | Moved | Moved |
| Need | Needed | Needed |
| Open | Opened | Opened |
| Paint | Painted | Painted |
| Play | Played | Played |
| Post | Posted | Posted |
| Practice | Practiced | Practiced |
| Pull | Pulled | Pulled |
| Push | Pushed | Pushed |
| Rain | Rained | Rained |
| Reach | Reached | Reached |
| Relax | Relaxed | Relaxed |
| Remember | Remembered | Remembered |
| Reply | Replied | Replied |
| Share | Shared | Shared |
| Shop | Shopped | Shopped |
| Show | Showed | Showed |
| Smoke | Smoked | Smoked |
| Start | Started | Started |
| Stay | Stayed | Stayed |
| Stop | Stopped | Stopped |
| Talk | Talked | Talked |
| Touch | Touched | Touched |
| Travel | Traveled | Traveled |
| Visit | Visited | Visited |
| Wait | Waited | Waited |
| Walk | Walked | Walked |
| Watch | Watched | Watched |
What Are Irregular Verbs?
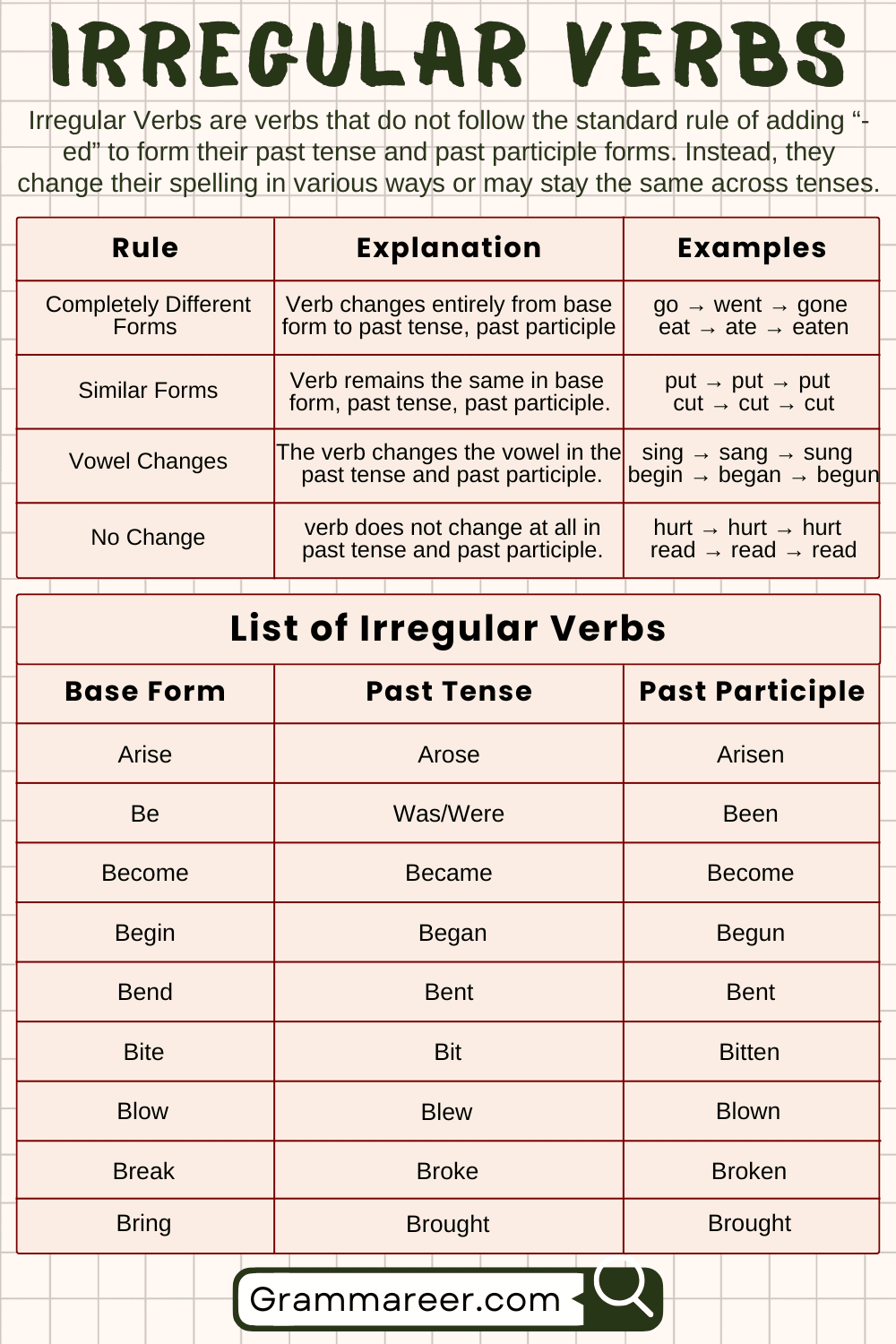
Irregular verbs are verbs that do not follow the standard rule of adding “-ed” to form the past tense or past participle. Unlike regular verbs, they have unique past forms that can vary significantly from their base forms. Because irregular verbs don’t follow a predictable pattern, they have to be memorized individually.
Rules for Irregular Verbs
Irregular verbs do not follow the standard rules for forming their past tense and past participle. While there are no strict rules like with regular verbs, some common patterns can help you understand how irregular verbs change:
Completely Different Forms
Some irregular verbs change completely when moving from the base form to the past tense and past participle.
-
- Base Form: go → Past Tense: went → Past Participle: gone
- Base Form: eat → Past Tense: ate → Past Participle: eaten
Similar Forms
A few irregular verbs have the same form in the present, past, and past participle.
-
- Base Form: put → Past Tense: put → Past Participle: put
- Base Form: cut → Past Tense: cut → Past Participle: cut
Vowel Changes
Many irregular verbs change the vowel in the past tense and past participle.
-
- Base Form: sing → Past Tense: sang → Past Participle: sung
- Base Form: begin → Past Tense: began → Past Participle: begun
No Change
Some irregular verbs do not change at all when moving to the past tense.
-
- Base Form: hurt → Past Tense: hurt → Past Participle: hurt
- Base Form: read (pronounced “reed”) → Past Tense: read (pronounced “red”) → Past Participle: read (pronounced “red”)
List of Irregular Verbs
| Base Form | Past Tense | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| Arise | Arose | Arisen |
| Be | Was/Were | Been |
| Become | Became | Become |
| Begin | Began | Begun |
| Bend | Bent | Bent |
| Bite | Bit | Bitten |
| Blow | Blew | Blown |
| Break | Broke | Broken |
| Bring | Brought | Brought |
| Build | Built | Built |
| Buy | Bought | Bought |
| Catch | Caught | Caught |
| Choose | Chose | Chosen |
| Come | Came | Come |
| Cost | Cost | Cost |
| Cut | Cut | Cut |
| Deal | Dealt | Dealt |
| Do | Did | Done |
| Draw | Drew | Drawn |
| Drink | Drank | Drunk |
| Drive | Drove | Driven |
| Eat | Ate | Eaten |
| Fall | Fell | Fallen |
| Feel | Felt | Felt |
| Find | Found | Found |
| Fly | Flew | Flown |
| Forget | Forgot | Forgotten |
| Forgive | Forgave | Forgiven |
| Freeze | Froze | Frozen |
| Get | Got | Gotten |
| Give | Gave | Given |
| Go | Went | Gone |
| Grow | Grew | Grown |
| Have | Had | Had |
| Hear | Heard | Heard |
| Hide | Hid | Hidden |
| Hit | Hit | Hit |
| Hold | Held | Held |
| Keep | Kept | Kept |
| Know | Knew | Known |
| Leave | Left | Left |
| Lose | Lost | Lost |
| Make | Made | Made |
| Meet | Met | Met |
| Pay | Paid | Paid |
| Read | Read | Read |
| Ride | Rode | Ridden |
| Ring | Rang | Rung |
| Rise | Rose | Risen |
| Run | Ran | Run |
| Say | Said | Said |
Regular vs Irregular Verbs
Understanding the difference between regular and irregular verbs is essential for mastering English grammar. Here’s a simple explanation:
| Feature | Regular Verbs | Irregular Verbs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Verbs that follow a predictable pattern when changing tense | Verbs that don’t follow a predictable pattern when changing tense |
| Formation of Past Tense | Add -ed or -d to the base form | Changes vary, often with a different word or vowel change |
| Past Participle Form | Same as past tense form (usually ends in -ed or -d) | May be different from both base and past tense forms |
| Examples | Base: walk → Past: walked | Base: go → Past: went → Past Participle: gone |
| Consistency | Consistent rules apply to most regular verbs | No set rules; forms must be memorized individually |
| Ease of Learning | Easier to learn due to predictable pattern | Harder to learn; requires memorization |
| Examples of Each | Regular: play, talk, clean → played, talked, cleaned | Irregular: see, take, sing → saw, took, sang |
| Common Ending Pattern | Ends in -ed for past and past participle | Varies greatly; often involves vowel or full word changes |
| Usage in English | More common in simpler, newer verbs | Often found in older, core vocabulary verbs |
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When learning about regular and irregular verbs, there are some common mistakes to watch out for. Here are a few tips to help avoid these errors:
- Adding “-ed” to Irregular Verbs: Not all past tenses use “-ed.” For example, “go” becomes “went,” not “goed.”
- Using Base Form Instead of Past Tense: For instance, saying “He sing yesterday” instead of “He sang yesterday.”
- Confusing Regular and Irregular Patterns: Regular verbs take “-ed” (like “played”), but irregular verbs have unique changes. Don’t mix these up.
- Pronouncing “-ed” Incorrectly: For verbs like “wanted,” the “-ed” sounds like “id,” while in “played,” it sounds like “d.”
Read More