The Present Perfect Tense is used to describe actions that happened at an unspecified time in the past or actions that started in the past and continue to the present. This tense helps express experiences, changes over time, and completed actions with relevance to the present. Many English learners find this tense confusing because it connects the past with the present. Understanding its structure and uses will help improve both spoken and written English.
Table of Contents
Sentence Structures of the Present Perfect Tense
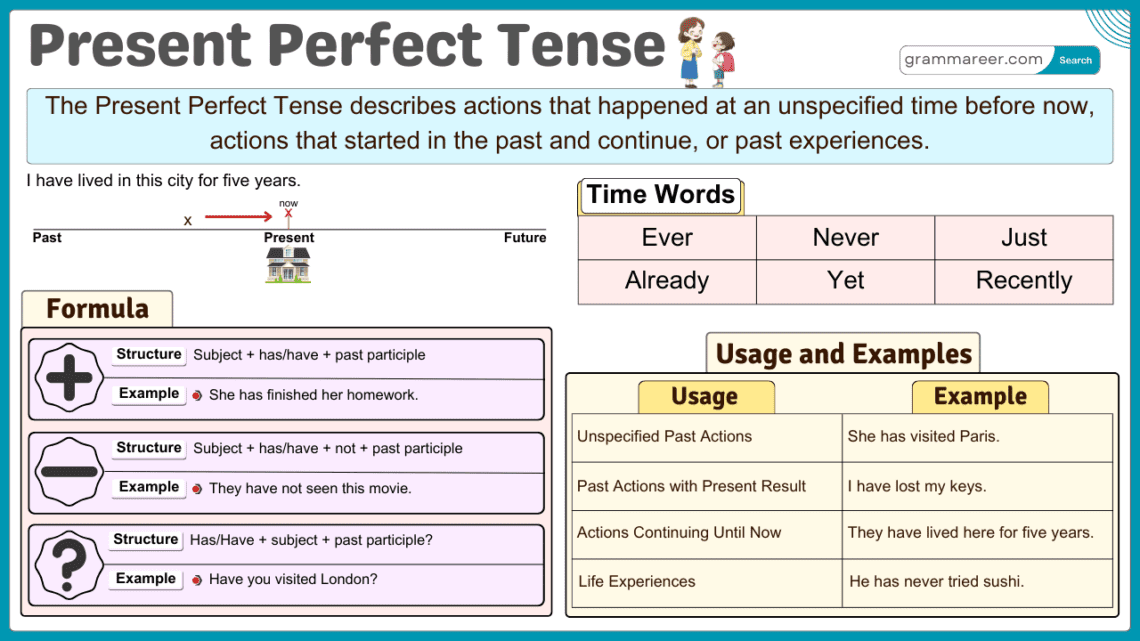
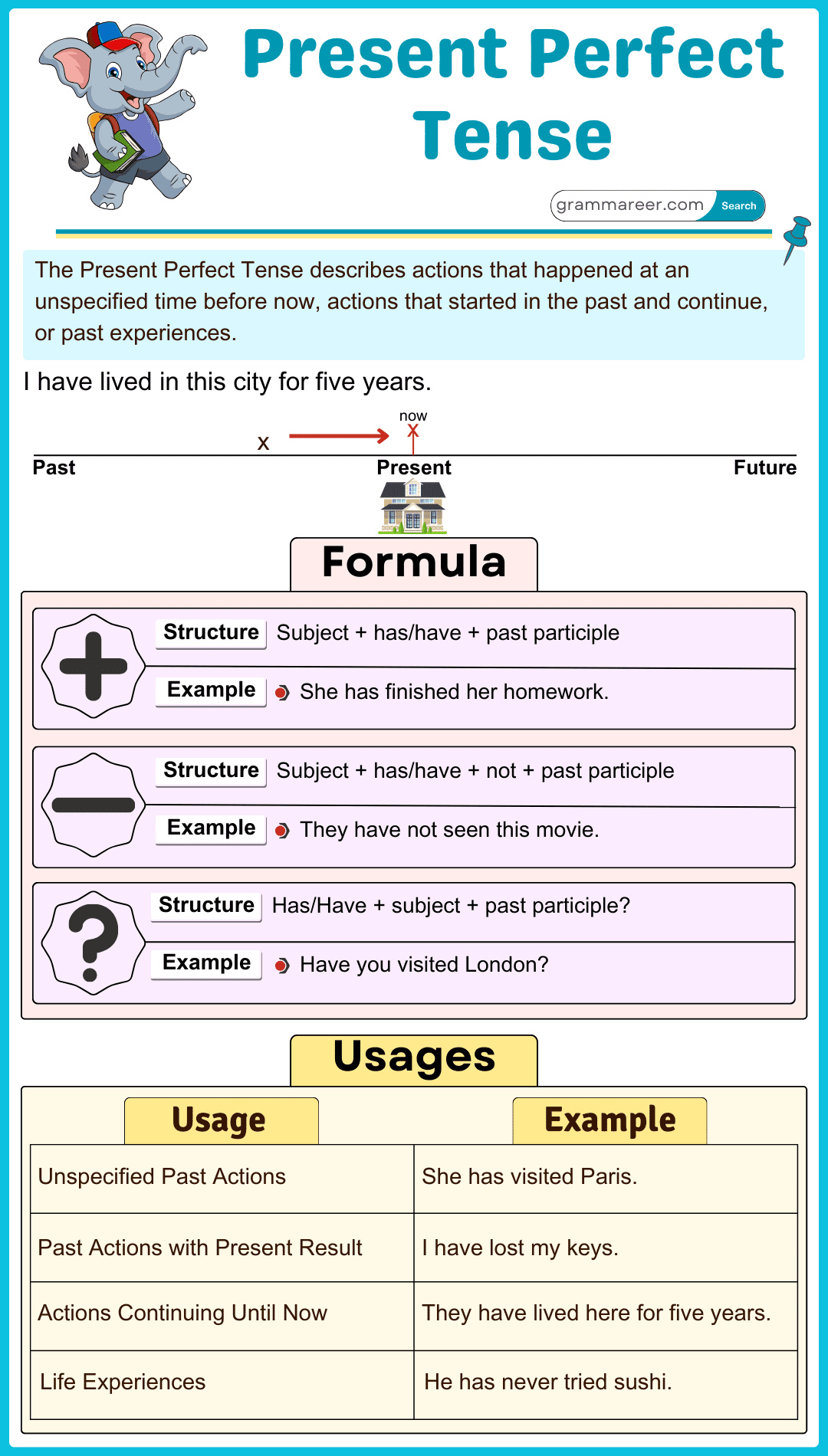
The Present Perfect Tense has three main structures: affirmative, negative, and interrogative sentences.
Affirmative Sentences
Structure: Subject + has/have + Past Participle + Object
Examples:
- Aisha has visited Turkey twice.
- They have completed their homework.
In the first example, has visited is used because the subject is singular (Aisha). In the second, have completed is used because the subject is plural (they).
Negative Sentences
Structure: Subject + has/have not + Past Participle + Object
Examples:
- Bilal has not finished his project yet.
- We have not seen that movie.
Has not is used for singular subjects (he, she, it), while have not is used for plural subjects (we, they, you, I).
Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Has/Have + Subject + Past Participle + Object + ?
Examples:
- Has Hamza read this book before?
- Have they traveled to Europe?
For singular subjects, has is used, and for plural subjects, have is used.
Double Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Question Word + Has/Have + Subject + Past Participle + Object + ?
- What has Fatima done today?
- Where have they gone?
Here, question words like what, where, who, why, when are placed at the beginning.
Subject-Verb Agreement in Present Perfect
Understanding subject-verb agreement is important for forming correct sentences. The table below shows how the helping verb changes with different subjects:
| Subject | Helping Verb | Main Verb Example |
|---|---|---|
| I | have | have eaten |
| You | have | have played |
| He/She/It | has | has written |
| We/They | have | have studied |
| The teacher | has | has explained |
| My parents | have | have visited |
Time Expressions in Present Perfect
Certain time expressions are commonly used with the Present Perfect Tense to indicate actions that started in the past and continue into the present or have recently been completed. These expressions help clarify the timing and relevance of the action.
- Ever: Have you ever seen a lion?
- Never: She has never tried sushi.
- Already: They have already finished the assignment.
- Yet: I haven’t finished my work yet.
- Just: He has just left the office.
- Since: We have lived here since 2015.
- For: She has worked as a teacher for five years.
Adverb Placement in Present Perfect
Adverbs like already, just, yet, never, ever are usually placed before the past participle or at the end of the sentence.
- She has already finished her work.
- Have you ever visited Paris?
- We haven’t met him yet.
Uses of the Present Perfect Tense
The Present Perfect Tense is used to describe actions that connect the past and present. It helps express experiences, ongoing situations, and recently completed actions.
1. Actions Completed at an Unspecified Time
The present perfect tense is used to describe actions that happened at some point in the past, but the exact time is not mentioned. It is formed using have/has + past participle.
- I have visited Paris.
- She has finished her homework.
2. Actions That Started in the Past and Continue in the Present
It is used to describe actions that began in the past and are still happening now. Time expressions like since and for are commonly used.
- They have lived here for ten years.
- He has worked in this company since 2015.
3. Life Experiences
It is used to talk about experiences someone has had in their life without specifying when. Words like ever and never are often used.
✅ Examples:
- I have never eaten sushi.
- Have you ever traveled to Japan?
4. Recently Completed Actions with Present Effects
It is used to describe actions that were recently completed and still have an impact on the present. Words like just, already, and yet are commonly used.
✅ Examples:
- She has just finished her work.
- We haven’t eaten lunch yet.
Present Perfect vs. Past Simple
The Present Perfect and Past Simple tenses both describe past actions, but they differ in usage. The Present Perfect highlights actions with present relevance, while the Past Simple focuses on completed events at a specific time.
| Feature | Present Perfect | Past Simple |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Action with present relevance or experience. | Completed past action. |
| Time Ref. | No specific time (ever, never, just, already). | Specific time (yesterday, last week, in 2010). |
| Example | I have visited France. | I visited France last year. |
| Formation | have/has + past participle (She has eaten.) | verb + -ed or irregular form (She ate.) |
| Focus | Result/experience. | Time of action. |
| Signal Words | Ever, never, just, yet, since, for. | Yesterday, ago, last week, when. |
| Context | I have lost my keys. (Still lost) | I lost my keys yesterday. (Completed) |
Short Answers in Present Perfect
Short answers in the Present Perfect Tense are used to respond briefly to questions. They usually follow the pattern “Yes, [subject] has.” or “No, [subject] hasn’t.” without repeating the full sentence.
| Question | Short Answer |
| Have you seen this movie? | Yes, I have. |
| Has she completed the task? | No, she hasn’t. |
| Have they been to London? | Yes, they have. |
| Has Ahmed written the report? | No, he hasn’t. |
Question Tags in Present Perfect
Question tags in the Present Perfect Tense are used to confirm information or seek agreement. They are formed by adding a short question at the end of a statement, using “has” or “have” appropriately.
| Sentence | Question Tag |
| You have finished your homework, haven’t you? | haven’t you? |
| He has gone to work, hasn’t he? | hasn’t he? |
| They have arrived, haven’t they? | haven’t they? |
| She has studied English, hasn’t she? | hasn’t she? |
Examples of Present Perfect in Use
Here are 12 examples of Present Perfect Tense:
- Affirmative:
- Hassan has eaten lunch.
- We have visited Karachi several times.
- Negative:
- She has not finished her homework.
- They have not traveled abroad.
- Interrogative:
- Have you met his brother?
- Has Hina called her mother?
Common Mistakes with Present Perfect
Many learners make errors in this tense. Here are some common mistakes and their corrections:
- ✅ She has visited her aunt.
- ❌ She visited her aunt. (Use Present Perfect when time is unspecified.)
- ✅ They haven’t finished their meal yet.
- ❌ They don’t finish their meal yet.
- ✅ Have you ever been to Japan?
- ❌ Have you went to Japan?
- ✅ The baby has fallen asleep.
- ❌ The baby fell asleep. (Use Present Perfect when the focus is on the result.)
FAQs
The Present Perfect Tense is used for life experiences, ongoing actions, recently completed tasks, and changes over time. Example: “Ali has traveled to Europe.”
Present Perfect is for unspecified past actions (I have seen that movie). Past Simple is for specific past events (I saw that movie last night).
Use has/have at the beginning. Example: “Have you ever eaten sushi?” For singular subjects, use has (“Has he studied?”).
You May Also Like