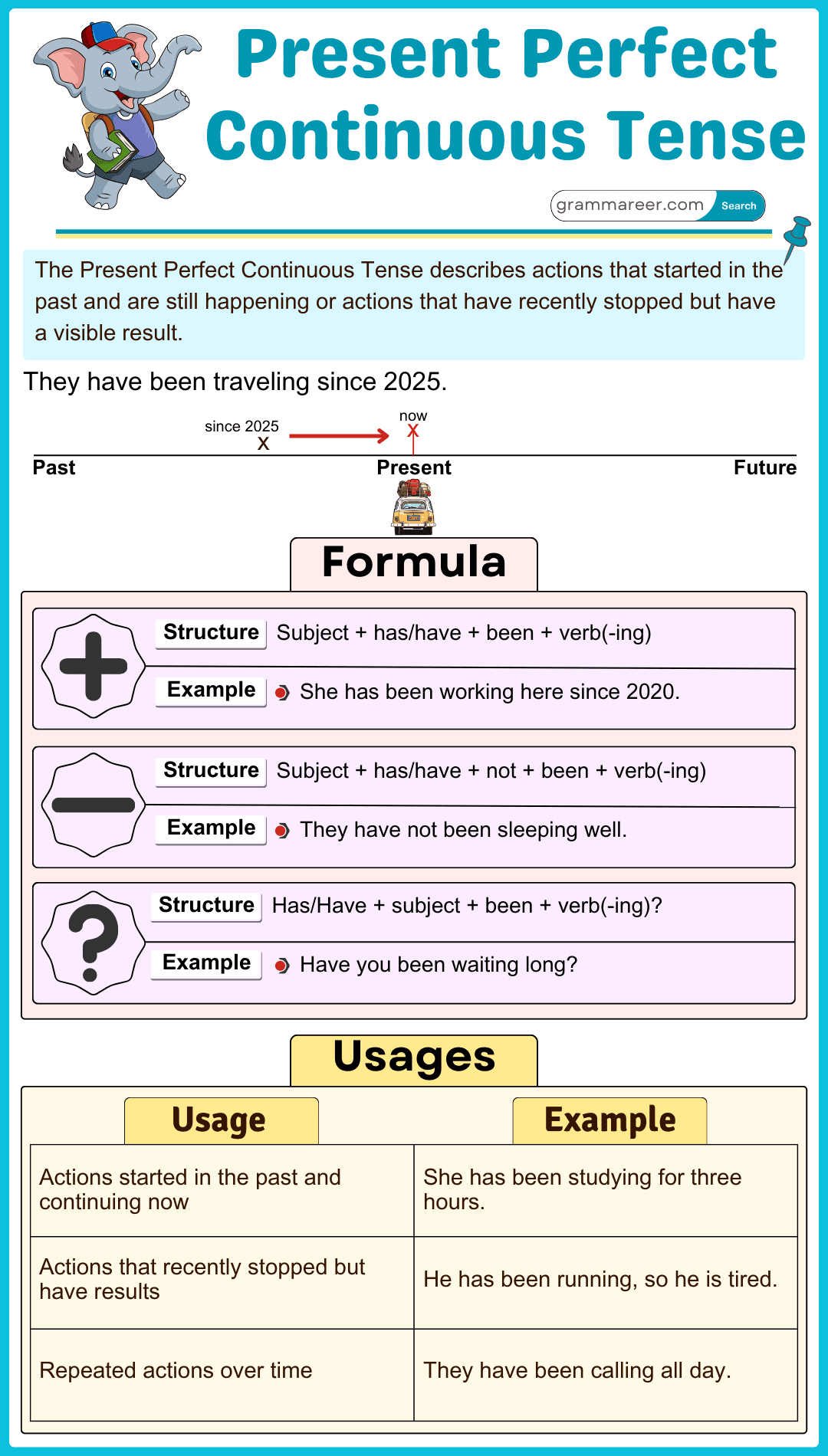
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense is used to describe actions that started in the past and are still continuing or actions that have recently stopped but their effects are still present. This tense is helpful when we want to emphasize the duration of an activity. Many learners find this tense confusing because it combines elements of the past, present, and duration. Understanding its structure and uses will help improve both spoken and written English.
Table of Contents
Sentence Structures of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense has three main structures: affirmative, negative, and interrogative sentences.
Affirmative Sentences
Structure: Subject + has/have been + Verb + -ing + Object
Examples:
- Aisha has been reading a book for two hours.
- They have been playing football since morning.
In the first example, has been reading is used because the subject is singular (Aisha). In the second, have been playing is used because the subject is plural (they).
Negative Sentences
Structure: Subject + has/have not been + Verb + -ing + Object
Examples:
- Bilal has not been watching TV for a week.
- We have not been eating junk food lately.
Has not been is used for singular subjects (he, she, it), while have not been is used for plural subjects (we, they, you, I).
Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Has/Have + Subject + been + Verb + -ing + Object + ?
Examples:
- Has Hamza been studying for his exam?
- Have they been traveling for a long time?
For singular subjects, has is used, and for plural subjects, have is used.
Double Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Question Word + Has/Have + Subject + been + Verb + -ing + Object + ?
Examples:
- What has Fatima been doing since morning?
- Where have they been going?
Here, question words like what, where, who, why, when are placed at the beginning.
Subject-Verb Agreement in Present Perfect Continuous
Understanding subject-verb agreement is important for forming correct sentences. The table below shows how the helping verb changes with different subjects:
| Subject | Helping Verb | Main Verb Example |
|---|---|---|
| I | have been | have been studying |
| You | have been | have been playing |
| He/She/It | has been | has been writing |
| We/They | have been | have been learning |
| The teacher | has been | has been explaining |
| My parents | have been | have been traveling |
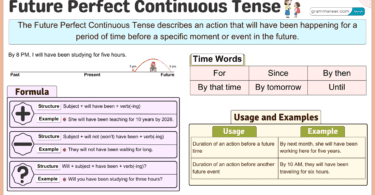
Time Expressions in Present Perfect Continuous
Time expressions in the Present Perfect Continuous Tense indicate how long an action has been happening. Common examples include “for,” “since,” “lately,” “recently,” and “all day.”
- For: I have been working here for three years.
- Since: She has been studying since morning.
- Lately: They have been exercising lately.
- Recently: He has been reading a lot recently.
- All day: She has been cooking all day.
Adverb Placement in Present Perfect Continuous
Adverbs like lately, recently, since, for are usually placed at the end of the sentence or before the main verb.
Examples:
- She has been working very hard lately.
- Have you been sleeping well recently?
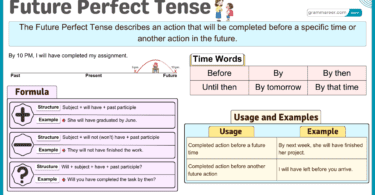
Uses of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense is used in different ways, below are some uses with examples:
1. Actions That Started in the Past and Are Still Continuing
The present perfect continuous tense is used to describe actions that began in the past and are still happening now. It is formed using have/has been + verb + ing.
- She has been studying for three hours.
- They have been living here since 2010.
2. Actions That Recently Stopped but Have Present Effects
It is used to describe actions that were happening recently and have just ended, but their effects are still visible or felt.
- I have been running, so I am tired.
- He has been painting the house, and now the walls look fresh.
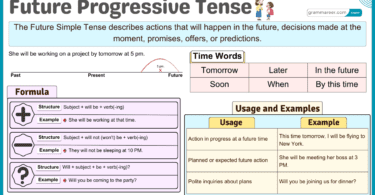
3. Repeated Actions Over a Period of Time
It is used to emphasize repeated actions that have been happening over a duration of time.
- She has been calling him all day.
- They have been practicing for the competition.
4. Actions That Show Irritation or Emphasis
It is used to express frustration or stress over repeated actions, often with words like lately, recently, again, all day, all week.
- He has been complaining about his job all week.
- You have been leaving your clothes everywhere again!
Present Perfect Continuous vs. Past Perfect Continuous
The Present Perfect Continuous describes actions continuing into the present, while the Past Perfect Continuous refers to actions that ended before another past event. Knowing their differences helps in proper usage.
| Feature | Present Perfect Continuous | Past Perfect Continuous |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Action started in the past, continues in present, or recently stopped. | Action ongoing in the past before another past event. |
| Time Ref. | No specific end time (since, for, lately, recently). | Specific past duration (before, until, for, since). |
| Example | I have been studying for three hours. | I had been studying for three hours before the exam. |
| Formation | have/has + been + verb-ing (She has been reading.) | had + been + verb-ing (She had been reading before I arrived.) |
| Focus | Duration of action affecting present. | Duration of action affecting past. |
Short Answers in Present Perfect Continuous
Short answers in the Present Perfect Continuous Tense give concise responses about ongoing actions, avoiding repetition while keeping conversations natural. Below is a table with clear examples:
| Question | Short Answer |
| Have you been working hard? | Yes, I have. |
| Has she been studying a lot? | No, she hasn’t. |
| Have they been waiting long? | Yes, they have. |
| Has Ahmed been reading? | No, he hasn’t. |
Question Tags in Present Perfect Continuous
Question tags in the Present Perfect Continuous Tense confirm ongoing actions that started in the past and continue in the present. They use “hasn’t/haven’t” for positive statements and “has/have” for negative ones.
| Sentence | Question Tag |
| You have been working hard, haven’t you? | haven’t you? |
| He has been playing football, hasn’t he? | hasn’t he? |
| They have been traveling, haven’t they? | haven’t they? |
| She has been studying, hasn’t she? | hasn’t she? |
Examples of Present Perfect Continuous in Use
Here are 12 examples of Present Perfect Continuous Tense:
- Affirmative:
- Hassan has been eating lunch.
- We have been living in Karachi for five years.
- Negative:
- She has not been listening to music.
- They have not been attending classes.
- Interrogative:
- Have you been understanding the lesson?
- Has Hina been learning Urdu?
Common Mistakes with Present Perfect Continuous
Many learners make errors in this tense. Here are some common mistakes and their corrections:
- ✅ She has been studying for two hours.
- ❌ She is studying for two hours.
- ✅ They haven’t been waiting for long.
- ❌ They don’t been waiting for long.
- ✅ Have you been reading this book?
- ❌ Have you reading this book?
- ✅ The baby has been sleeping since 8 PM.
- ❌ The baby is sleeping since 8 PM.
FAQs
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense is used for actions that started in the past and are still continuing, recently completed actions, and repeated actions over time. Example: “Ali has been playing football for two hours.”
Present Perfect focuses on completed actions (I have finished my work), while Present Perfect Continuous focuses on ongoing actions (I have been working all day).
Use has/have been at the beginning. Example: “Have you been studying?” For singular subjects, use has (“Has she been learning?”).
You May Also Like