The Present Continuous Tense is a key part of English grammar, used to describe actions that are happening at the moment, temporary situations, or future plans. It helps express what someone is doing right now, like “I am reading a book,” or what they’ve already planned, such as “We are meeting friends tomorrow.” Understanding how to form and use this tense correctly can make conversations more natural and clear.
Table of Contents
Sentence Structures of the Present Continuous Tense
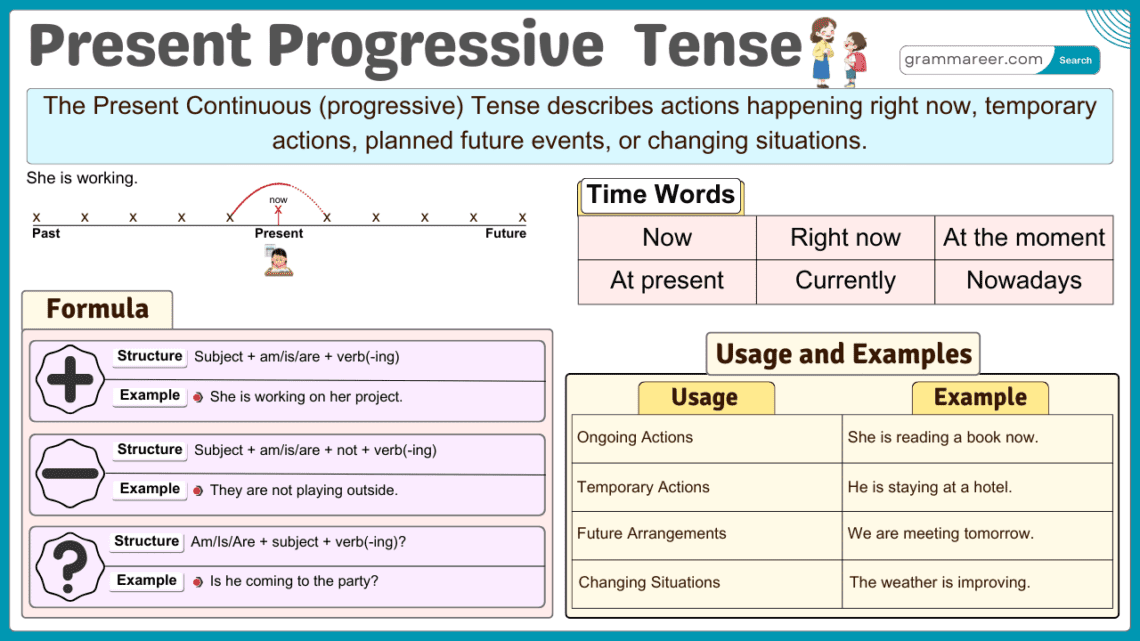
The Present Continuous Tense has three main structures: affirmative, negative, and interrogative sentences. Each follows a specific pattern.
Affirmative Sentences
Structure: Subject + am/is/are + Verb + -ing + Object
Examples:
- Aisha is reading a book right now.
- They are playing football in the park.
In the first example, is reading is used because the subject is “Aisha” (she). In the second, are playing is used because the subject is they (plural).
Negative Sentences
Structure: Subject + am/is/are + not + Verb + -ing + Object
Examples:
- Bilal is not watching TV at the moment.
- We are not eating dinner right now.
Use ‘is not’ with singular subjects like he, she, and it, and ‘are not’ with plural subjects such as we and they.
Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Am/Is/Are + Subject + Verb + -ing + Object + ?
Examples:
- Is Hamza studying for his exam?
- Are they going to the market now?
For singular subjects, is is used, and for plural subjects, are is used.
Double Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Question Word + Am/Is/Are + Subject + Verb + -ing + Object + ?
Examples:
- What is Fatima doing right now?
- Where are they going?
Question words like what, where, who, why, when are placed at the beginning.

Subject-Verb Agreement in Present Continuous
Understanding subject-verb agreement is essential in forming correct sentences. The table below shows how the helping verb changes with different subjects:
| Subject | Helping Verb | Main Verb Example |
|---|---|---|
| I | am | am studying |
| You | are | are playing |
| He/She/It | is | is reading |
| We/They | are | are learning |
| The teacher | is | is explaining |
| My parents | are | are traveling |
Time Expressions in Present Continuous
Time expressions help indicate when an action is happening. Below are some commonly used ones:
- Now: She is cooking now.
- At the moment: They are watching a movie at the moment.
- Right now: He is writing an email right now.
- Currently: I am studying English currently.
- Nowadays: More people are working from home nowadays.
Adverb Placement in Present Continuous
Adverbs of time and manner are usually placed at the end of the sentence or before the main verb.
Examples:
- He is always talking in class.
- She is constantly complaining.
- We are working hard now.
Present Continuous Tense Usages
1. Actions Happening Right Now
The present continuous tense is used to describe actions that are happening at the moment of speaking. It is formed using am/is/are + verb + ing.
- She is reading a book now.
- They are playing football at the moment.
2. Temporary Actions
It describes actions that are happening for a short period but not permanently. These actions may last for days or weeks but will eventually stop.
- I am staying with my friend this week.
- He is working on a new project these days.
3. Future Plans and Arrangements
The present continuous is used to describe planned future events, often with a specific time mentioned.
- We are traveling to Paris next Friday.
- She is meeting her friends tomorrow.
4. Changing or Developing Situations
It describes trends, gradual changes, or ongoing developments.
- The weather is getting colder.
- Technology is advancing rapidly.
Short Answers in Present Continuous
Short answers help in conversations. Below is a table with examples:
| Question | Short Answer |
| Are you reading a book? | Yes, I am. |
| Is she working today? | No, she isn’t. |
| Are they coming to the party? | Yes, they are. |
| Is Ahmed learning French? | No, he isn’t. |
Question Tags in Present Continuous
Question tags make sentences sound more natural.
| Sentence | Question Tag |
| You are watching TV, aren’t you? | aren’t you? |
| He is playing football, isn’t he? | isn’t he? |
| They are coming, aren’t they? | aren’t they? |
| She is studying, isn’t she? | isn’t she? |
Examples of Present Continuous in Use
Here are 12 examples of Present Continuous Tense:
- Affirmative:
- Hassan is drinking coffee.
- We are living in Karachi.
- Negative:
- She is not listening to music.
- They are not eating fast food.
- Interrogative:
- Are you understanding the lesson?
- Is Hina learning Urdu?
Common Mistakes with Present Continuous
Many learners make errors in this tense. Here are some common mistakes and their corrections:
✅ She is studying every night.
❌ She studying every night.
✅ They are not playing in the rain.
❌ They not playing in the rain.
✅ Is he watching TV?
❌ Is he watches TV?
✅ The bus is arriving now.
❌ The bus arrives now.
FAQs
The Present Continuous Tense is used for actions happening right now, temporary situations, planned future events, and changing situations. Example: “Ali is playing football now.”
Present Simple is for regular actions (I eat lunch at 2 PM). Present Continuous is for actions happening now (I am eating lunch now).
Use am/is/are at the beginning. Example: “Is she reading a book?” For plural subjects, use are (“Are they studying?”).
You May Also Like