Phrasal verbs are an essential part of everyday English, especially for those learning the language. Understanding phrasal verbs can greatly improve your communication skills. These unique combinations of verbs and prepositions (or adverbs) can be tricky to master, but with practice and the right explanation, they become easier to use and understand.
Table of Contents
Phrasal Verbs in English
Phrasal verbs are commonly used in both spoken and written English, making them important to learn for better fluency. The term “phrasal verb” is often used interchangeably with “verb phrase,” though there is a subtle difference between the two.
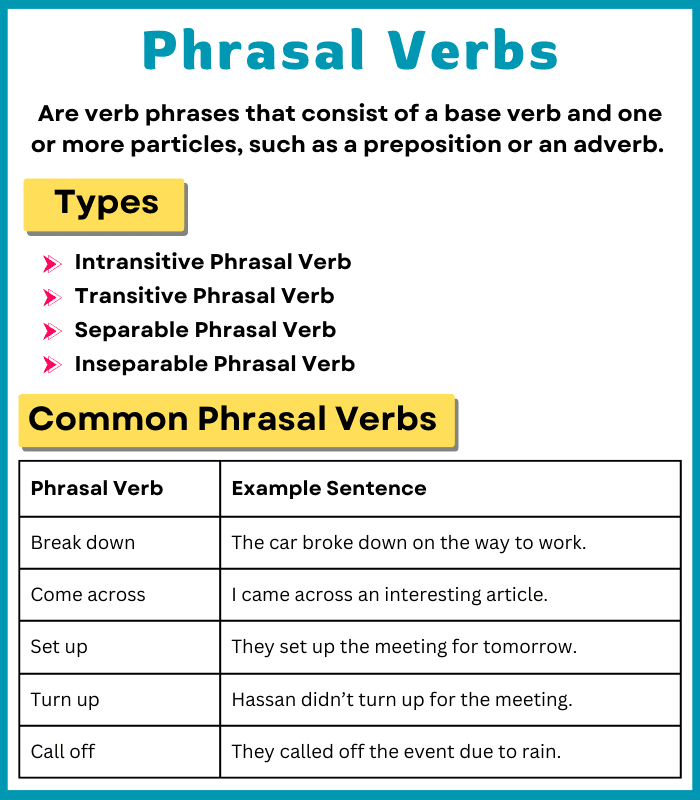
Phrasal verbs are verb phrases that consist of a base verb and one or more particles, such as a preposition or an adverb.
100 Most Common Phrasal Verbs with their Meanings
Here’s a list of 100 most common phrasal verbs with their meanings, useful for daily conversation, English exams, and spoken English fluency. Each phrasal verb is explained in simple words:
- Ask out – Invite someone on a date
- Back up – Support or make a copy
- Break down – Stop functioning / become emotional
- Break up – End a relationship
- Bring up – Mention a topic / raise a child
- Call back – Return a phone call
- Call off – Cancel something
- Carry on – Continue
- Catch up – Reach the same level
- Check in – Register at a hotel or airport
- Check out – Leave a hotel / examine
- Come across – Find unexpectedly
- Come back – Return
- Come in – Enter
- Come on – Hurry up / encourage
- Come up with – Invent or produce (an idea, plan)
- Cut down – Reduce
- Cut off – Stop the supply / remove
- Do over – Do again
- Dress up – Wear formal clothes
- Drop by – Visit unexpectedly
- Drop off – Deliver or fall asleep
- End up – Finally do or be something
- Figure out – Understand or solve
- Fill in – Complete a form
- Fill out – Complete a form completely
- Find out – Discover
- Get along – Have a good relationship
- Get around – Travel / avoid
- Get away – Escape
- Get back – Return
- Get in – Enter
- Get off – Leave (bus, train, etc.)
- Get on – Board (bus, train, etc.)
- Get out – Leave a place
- Get over – Recover from
- Give away – Give for free
- Give back – Return something
- Give up – Quit
- Go ahead – Proceed
- Go away – Leave
- Go back – Return
- Go out – Leave home / date someone
- Grow up – Become an adult
- Hand in – Submit
- Hang out – Spend time relaxing
- Hang up – End a phone call
- Hold on – Wait
- Keep on – Continue
- Keep up – Maintain pace
- Let down – Disappoint
- Look after – Take care of
- Look for – Search
- Look forward to – Anticipate with pleasure
- Look into – Investigate
- Look out – Be careful
- Look up – Search for information
- Make out – Understand / kiss passionately
- Make up – Reconcile / invent
- Move on – Proceed
- Pass away – Die
- Pass out – Faint
- Pick out – Choose
- Pick up – Lift / collect someone
- Point out – Highlight
- Put away – Store
- Put off – Postpone
- Put on – Wear clothing
- Put out – Extinguish
- Run into – Meet unexpectedly
- Run out (of) – Have none left
- Set up – Arrange
- Show up – Arrive
- Shut down – Close
- Sit down – Take a seat
- Stand up – Rise
- Stick to – Follow or continue doing
- Take after – Resemble
- Take away – Remove
- Take back – Return something
- Take off – Remove / start flying
- Take over – Assume control
- Take up – Start a new hobby or activity
- Talk over – Discuss
- Throw away – Discard
- Try on – Test clothing
- Turn down – Reject
- Turn off – Stop a device
- Turn on – Start a device
- Turn up – Arrive / increase volume
- Wake up – Stop sleeping
- Watch out – Be careful
- Work out – Exercise / solve a problem
- Write down – Note on paper
Types of Phrasal Verbs
There are different types of phrasal verbs, each serving a specific function in a sentence. The main types include:
- Intransitive Phrasal Verb
- Transitive Phrasal Verb
- Separable Phrasal Verb
- Inseparable Phrasal Verb
Each type has its own characteristics, so let’s look at each one more closely.
Intransitive Phrasal Verb
Intransitive phrasal verb do not require an object to complete their meaning. They make sense without needing to follow up with a direct object.
Example:
Wake up
- I wake up at 6 a.m.
In this case, the phrasal verb “wake up” does not require an object to be complete.
Transitive Phrasal Verb
Transitive phrasal verb require an object to complete their meaning. This means that after using the phrasal verb, you need to mention a person or thing that is affected by the action.
Example:
Pick up
- Ahmed picks up the book.
Here, the phrasal verb “pick up” needs the object “the book” to complete the sentence.
Separable and Inseparable Phrasal Verbs
Phrasal verbs can also be categorized based on whether the parts of the verb can be separated or not.
Separable Phrasal Verb
These phrasal verb allow you to separate the verb and the particle. The object can come between the verb and the particle.
Example:
Turn off
- Fatima turned off the light.
- Fatima turned the light off.
In both cases, the phrasal verb “turn off” works, but in the second sentence, “the light” is separated by the particle “off.”
Inseparable Phrasal Verb
These phrasal verb cannot be separated. The verb and the particle must stay together.
Example:
Look after
- Sara looks after her brother.
In this sentence, “look after” cannot be separated. You cannot say “Sara looks her brother after.”
How to Use Phrasal Verbs?
Using phrasal verbs correctly requires practice and understanding of their meanings and structure. Here are a few tips for using them effectively:
- Learn common phrasal verbs – Familiarizing yourself with frequently used phrasal verbs helps you recognize them more easily in conversations or writing.
- Understand their meanings – Since phrasal verbs often have meanings that differ from the individual verbs, it’s important to learn the meanings of each combination.
- Pay attention to separability – Know whether the phrasal verb is separable or inseparable to avoid errors.
- Use them in context – Practice using phrasal verbs in sentences. This helps in solidifying their meaning and usage.
Examples of Phrasal Verbs
Here are some commonly used phrasal verbs in everyday English:
- Ayman picks up his clothes from the floor.
- Sami looked up the word in the dictionary.
- Zahra gave up trying to fix the computer.
- They called off the event due to rain.
- The car broke down on the way to work.
- I ran into Ahmed at the coffee shop.
- Hassan didn’t turn up for the meeting.
- They set up the meeting for tomorrow.
- Sara worked out at the gym yesterday.
- Ali gets along with everyone at school.
These examples show how phrasal verbs can express actions or states that would otherwise require more complex expressions.
Common Phrasal Verbs
Here are a few phrasal verbs you might often come across:
| Phrasal Verb | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Break down | The car broke down on the way to work. |
| Come across | I came across an interesting article. |
| Set up | They set up the meeting for tomorrow. |
| Turn up | Hassan didn’t turn up for the meeting. |
| Call off | They called off the event due to rain. |
Phrasal Verb vs Verb Phrase
Here is the comparison of the Phrasal Verb and Verb Phrase:
| Aspect | Phrasal Verb | Verb Phrase |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A verb combined with one or more particles | A verb followed by one or more auxiliary verbs |
| Examples | “Break down,” “Pick up” | “Have done,” “Is going” |
| Usage | Phrasal verbs often have idiomatic meanings | Verb phrases explain the action in a sentence |
| Complexity | Often more complex in meaning | Generally follows a more standard pattern |
FAQs
A phrasal verb consists of a verb combined with a preposition or adverb, and this combination alters the meaning of the original verb. For example, the verb “take” when paired with the adverb “off” forms the phrasal verb “take off,” which means “to remove” or “for an aircraft to leave the ground.”
Phrasal verb is commonly used in informal conversations. In formal writing, it is often replaced with more straightforward verbs.
Examples of common phrasal verbs include “wake up,” “look after,” “call off,” “pick up,” and “give up.”
There are three main types of phrasal verbs: intransitive, transitive, and separable/inseparable phrasal verbs.
A phrasal verb is a verb combined with a preposition or adverb to create a new meaning (e.g., “give up”). A verb phrase is a group of verbs that work together, often including auxiliary verbs, to express a complete action (e.g., “has been working”).
Conclusion
Phrasal verbs are an important and versatile part of English. While they may seem challenging at first, understanding their types and how to use them will improve both your spoken and written English. By learning common phrasal verbs and their meanings, you can speak more naturally and sound more like a native speaker.
You May Also Like