Personal pronouns are essential in English as they replace nouns to make sentences smoother and less repetitive. They change based on person, number, and sometimes gender to indicate who is speaking, being spoken to, or being spoken about. Without them, communication would be awkward and repetitive. In this blog post, we’ll break down personal pronouns, explaining their different forms and how they function in sentences. Understanding them will improve your English fluency and writing clarity. Want to strengthen your grammar skills? Check out our grammar section!
Table of Contents
What Are Personal Pronouns?
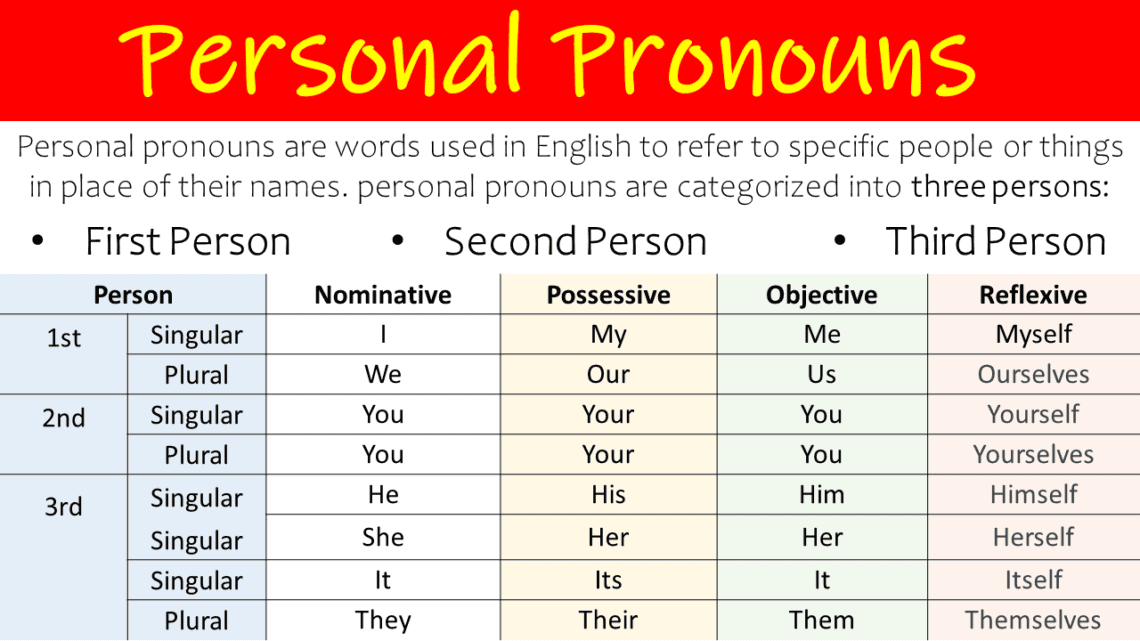
Personal pronouns are words used in English to refer to specific people or things instead of their names. They improve communication by preventing repetition and making sentences clearer. These pronouns change based on the person, number, and gender of the subject.
Categories of Personal Pronouns
1. Personal Pronouns Based on Person
Personal pronouns are divided into three types based on the grammatical person they represent:
First Person (Speaker)
Refers to the person speaking:
- “I” – Used when a single person refers to themselves.
- Example: I am going to the store.
- “We” – Used when the speaker includes others in a group.
- Example: We are going to the beach this weekend.
Second Person (Listener)
Refers to the person or people being addressed:
- “You” – Used when speaking to one or more people.
- Example: You should come to the party with us.
Third Person (Others)
Refers to someone or something not directly involved in the conversation:
- “He” – Used for a male person or animal.
- Example: He is playing soccer with his friends.
- “She” – Used for a female person or animal.
- Example: She is reading a book at the library.
- “It” – Used for objects, animals, or things without gender.
- Example: It is raining outside.
- “They” – Used for a group of people or things.
- Example: They are coming to the party tonight.
2. Personal Pronouns Based on Number
Personal pronouns can be either singular or plural depending on how many people or things they refer to.
Singular Pronouns (Referring to one person or thing)
Subject Pronouns: I, You, He, She, It
Object Pronouns: Me, You, Him, Her, It
Possessive Pronouns: Mine, Yours, His, Hers, Its
Plural Pronouns (Referring to more than one person or thing)
Subject Pronouns: We, You, They
Object Pronouns: Us, You, Them
Possessive Pronouns: Ours, Yours, Theirs
Examples of Personal Pronouns Based on Number
| Number | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Singular | I am going to the store. |
| Singular | You should come with me. |
| Singular | He is playing soccer. |
| Plural | We are going to the beach. |
| Plural | You should bring your friends. |
| Plural | They are coming to the party. |
3. Personal Pronouns Based on Gender
Some pronouns are associated with specific genders, while others are gender-neutral.
Masculine Pronouns
Used for male individuals:
- “He” (subject pronoun) – Refers to a male person.
- “Him” (object pronoun) – Used as an object in a sentence.
- “His” (possessive pronoun) – Shows ownership by a male. Example: He is playing soccer. I saw him at the park with his friends.
Feminine Pronouns
Used for female individuals:
- “She” (subject pronoun) – Refers to a female person.
- “Her” (object pronoun) – Used as an object in a sentence.
- “Hers” (possessive pronoun) – Shows ownership by a female.Example: She is reading a book. I gave the book to her; it’s hers.
Gender-Neutral Pronouns
Used when gender is unknown, irrelevant, or referring to non-binary individuals:
- “They” (subject pronoun) – Used instead of “he” or “she.”
- “Them” (object pronoun) – Used instead of “him” or “her.”
- “Their” (possessive pronoun) – Shows ownership without specifying gender.Example: They are coming to the party. I invited them; it’s their first time attending.
Grammatical Roles of Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns function in different grammatical roles in a sentence.
1. Subject Pronouns
Used as the subject of a sentence to perform an action.
| Subject Pronouns | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| I | I am going to the park to play. |
| You | You should eat your vegetables for good health. |
| He | He is playing soccer with his friends. |
| She | She is reading a book at the library. |
| It | It is raining outside, so bring an umbrella. |
| We | We are going to the beach this weekend. |
| They | They are coming to the party tonight. |
2. Object Pronouns
Used as the object of a verb or preposition.
| Object Pronouns | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Me | She gave the book to me. |
| You | I am talking to you. |
| Him | We invited him to dinner. |
| Her | I saw her at the store. |
| It | I found it under the table. |
| Us | They gave us directions. |
| Them | I called them yesterday. |
3. Possessive Pronouns
Show ownership or possession.
| Possessive Pronouns | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Mine | This pen is mine. |
| Yours | That car is yours. |
| His | This jacket is his. |
| Hers | The red dress is hers. |
| Its | The company changed its logo. |
| Ours | This house is ours. |
| Theirs | That garden is theirs. |

Personal Pronouns Chart
| Person | Subject Pronouns | Object Pronouns | Possessive Adjectives | Possessive Pronouns | Reflexive Pronouns |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Person Singular | I | Me | My | Mine | Myself |
| 2nd Person Singular | You | You | Your | Yours | Yourself |
| 3rd Person Singular | He/She/It | Him/Her/It | His/Her/Its | His/Hers/Its | Himself/Herself/Itself |
| 1st Person Plural | We | Us | Our | Ours | Ourselves |
| 2nd Person Plural | You | You | Your | Yours | Yourselves |
| 3rd Person Plural | They | Them | Their | Theirs | Themselves |
You May Also Like