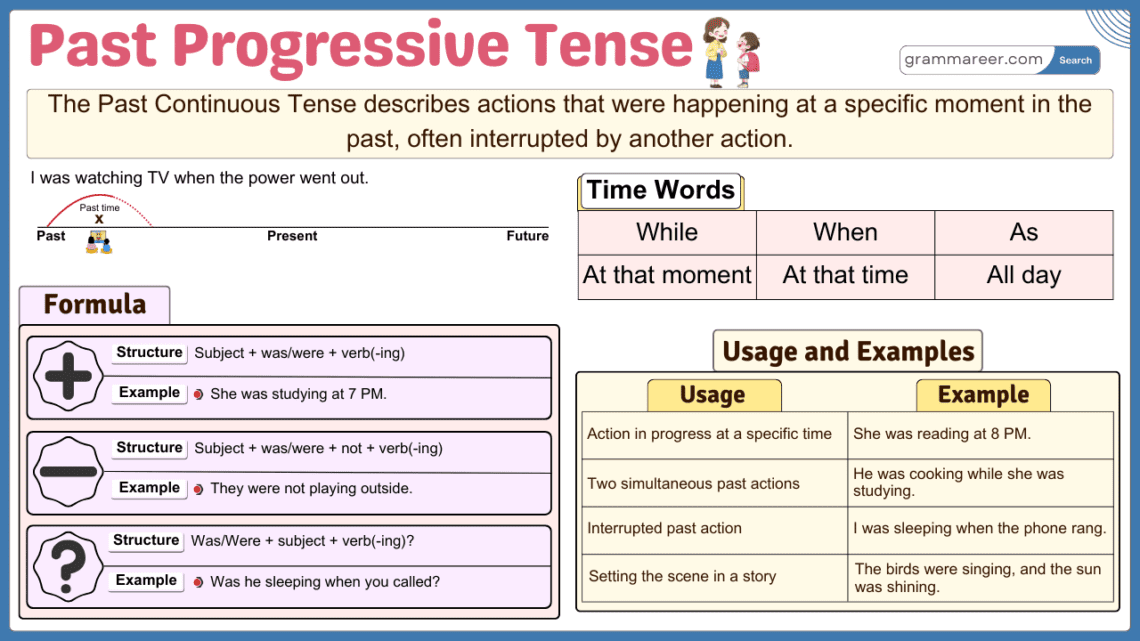
In English grammar the Past Continuous Tense is used to describe actions that were in progress at a specific time in the past. It often highlights activities that continued for a period of time or were interrupted by another event. This tense is useful for setting the background in stories, describing parallel actions, and providing context to past events. To understand the Past Continuous Tense, you need to be familiar with the Past Simple Tense, as they often work together. Recognizing the difference between ongoing actions and completed events is key to using them correctly.
Table of Contents
Sentence Structures of the Past Continuous Tense
The Past Continuous Tense has three main structures: affirmative, negative, and interrogative sentences.
Affirmative Sentences
Structure: Subject + was/were + Verb + -ing + Object
Examples:
- Aisha was reading a book at 8 PM.
- They were playing football when it started to rain.
Was is used with singular subjects (I, he, she, it), while were is used with plural subjects (we, you, they).
Negative Sentences
Structure: Subject + was/were not + Verb + -ing + Object
Examples:
- Bilal was not watching TV last night.
- We were not eating dinner when he arrived.
You can also use contractions:
- wasn’t = was not
- weren’t = were not
Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Was/Were + Subject + Verb + -ing + Object + ?
Examples:
- Was Hamza studying for his exam?
- Were they going to the market when you called?
Double Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Question Word + was/were + Subject + Verb + -ing + Object + ?
Examples:
- What was Fatima doing when I saw her?
- Where were they going yesterday?
Subject-Verb Agreement in Past Continuous
In the Past Continuous Tense, was and were are used based on the subject.
| Subject | Helping Verb | Main Verb Example |
|---|---|---|
| I | was | was studying |
| You | were | were playing |
| He/She/It | was | was writing |
| We/They | were | were learning |
| The teacher | was | was explaining |
| My parents | were | were traveling |
Time Expressions in Past Continuous
Common time expressions used with the Past Continuous Tense include:
- At 8 PM: She was cooking at 8 PM.
- When: They were talking when I entered.
- While: He was reading while she was cooking.
- All day/night: We were working all day.
- During: She was sleeping during the meeting.
Adverb Placement in Past Continuous
Adverbs like always, constantly, just are placed before the main verb.
Examples:
- He was always forgetting his keys.
- They were constantly arguing last week.
Uses of the Past Continuous Tense
The Past Continuous Tense is used to describe actions that were happening at a specific moment in the past. It is formed using was/were + verb + ing.
1. Actions in Progress at a Specific Time in the Past
It describes actions that were happening at a particular moment in the past.
- She was reading a book at 8 PM last night.
- They were playing football when it started to rain.
2. Interrupted Actions in the Past
It is used to describe an action that was in progress when another shorter action interrupted it. The shorter action is usually in the simple past.
- I was cooking dinner when the phone rang.
- He was driving to work when he saw an accident.
3. Parallel Actions (Two Actions Happening at the Same Time)
It describes two or more actions happening simultaneously in the past.
- She was listening to music while he was studying.
- They were talking and laughing at the same time.
4. Background Descriptions in Stories
It is used to set the scene in stories by describing the background activities or situations.
- The sun was setting, and birds were singing softly.
- People were dancing while the band was playing lively music.
Short Answers in Past Continuous
Short answers in the Past Continuous Tense provide brief responses to questions about ongoing past actions. They help keep conversations clear and natural without repeating the full sentence.
| Question | Short Answer |
| Were you reading a book? | Yes, I was. |
| Was she working yesterday? | No, she wasn’t. |
| Were they waiting for you? | Yes, they were. |
| Was Ahmed studying? | No, he wasn’t. |
Question Tags in Past Continuous
Question tags in the Past Continuous Tense are used to confirm information or seek agreement about actions that were ongoing in the past. They use “wasn’t” or “weren’t” for positive statements and “was” or “were” for negative ones.
| Sentence | Question Tag |
| You were watching TV, weren’t you? | weren’t you? |
| He was playing football, wasn’t he? | wasn’t he? |
| They were traveling, weren’t they? | weren’t they? |
| She was studying, wasn’t she? | wasn’t she? |
Examples of Past Continuous in Use
Here are 12 examples of Past Continuous Tense:
- Affirmative:
- Hassan was eating lunch at noon.
- We were living in Karachi in 2015.
- Negative:
- She was not listening to music.
- They were not attending the meeting.
- Interrogative:
- Were you understanding the lesson?
- Was Hina learning Urdu?
Common Mistakes with Past Continuous
Many learners make errors in this tense. Here are some common mistakes and their corrections:
- ✅ She was studying for the test.
- ❌ She studying for the test.
- ✅ They weren’t playing outside.
- ❌ They not playing outside.
- ✅ The baby was sleeping peacefully.
- ❌ The baby sleeping peacefully.
- ✅ Was he reading a book?
- ❌ Did he reading a book?
FAQs
The Past Continuous Tense is used for ongoing actions in the past, interrupted activities, and background events. Example: “Ali was playing football when it started to rain.”
Simple Past describes completed actions (I watched a movie), while Past Continuous describes ongoing actions at a specific time (I was watching a movie).
Use was/were at the beginning. Example: “Were you studying?” For singular subjects, use was (“Was she sleeping?”).
Subject + was/were + verb(-ing) + object
Use “was” with singular subjects (I, he, she, it).
Use “were” with plural subjects (we, you, they).
I was reading a book.
Subject + was/were + not + verb(-ing) + object
Add “not” after was or were to make it negative.
She was not watching TV.
Was/Were + subject + verb(-ing) + object + ?
Start with “was” or “were”, followed by the subject.
Was he sleeping during class?
She was reading a novel when I called.
They were playing football in the park.
I was studying for my exam last night.
We were watching a movie together.
He was cooking dinner when it started to rain.
You May Also Like