Participles are verb forms that can function as adjectives or parts of verb tenses. In English, they are derived from verbs and often end in -ing or -ed. Present participle typically describe ongoing actions or states, while past participle often indicate completed actions. Additionally, participles can form participle phrases, which provide more detail about a subject or object in a sentence.
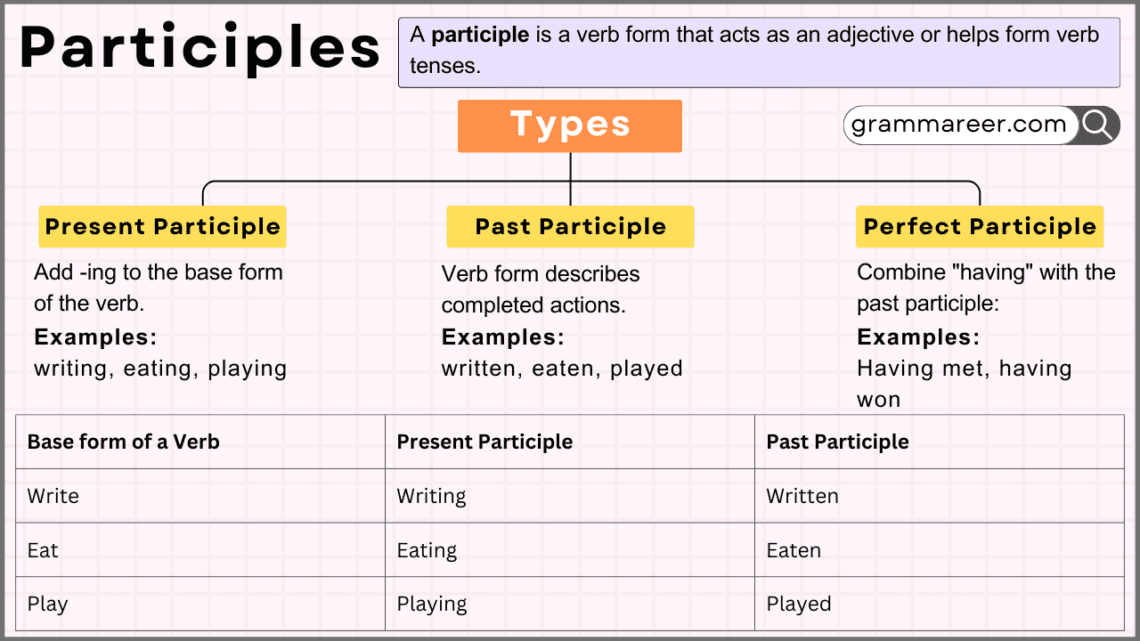
A participle is a verb form that acts as an adjective or helps form verb tenses.
Table of Contents
Types of Participles
Present Participles
Present participles end in -ing and describe ongoing actions or states. They are often used to form continuous tenses or as adjectives.
Example:
The running boy quickly crossed the finish line.
The participle “running” describes the boy, showing his action.
Past Participles
Past participles usually end in -ed, -en, or other irregular forms, indicating completed actions. They are commonly used in perfect tenses or as adjectives.
Example:
The broken vase lay on the floor.
The participle “broken” describes the vase, indicating its state.
Perfect Participles
Perfect participles show an action that was completed before another action. They are formed by combining “having” with the past participle of a verb.
Example:
Having finished his meal, Ahmed left the table.
The participle phrase “having finished” indicates a completed action before another action.
Present Participle Examples
Present participle describe ongoing actions. Here are some examples of Present Participle:
- Areeba is reading a book.
- Ali was running in the park.
- The glowing stars lit up the sky.
- Ayesha kept singing her favorite song.
- Boby enjoys playing football.
- The shining sun warmed the earth.
- Malaika is writing an essay.
- The buzzing bees filled the air.
- Umar loves swimming in the lake.
- The children were laughing joyfully.
Past Participle Examples
Past participle are used to describe actions that are completed, like in the example sentences:
- Zainab has written a letter.
- Ali was beaten in the match.
- The broken vase lay on the floor.
- Fatima had spoken to her teacher.
- Ahmed has eaten his lunch.
- The burned toast smelled terrible.
- Asma had finished her homework.
- The frozen water cracked the pipe.
- Ibrahim was chosen as captain.
- The painted wall looked fresh.
Perfect Participle Examples
Perfect participle are used to show an action completed before another action, as seen in the example sentences:
- Having completed her work, Areeba went out.
- Having won the game, Ali celebrated.
- Having studied hard, Fatima aced the test.
- Having eaten, Boby felt satisfied.
- Having written the report, Malaika relaxed.
- Having finished his meal, Ibrahim left.
- Having practiced, the team felt ready.
- Having seen the movie, they discussed it.
- Having cleaned the room, the children played.
- Having met the deadline, the group rejoiced.
Formation of Participles
Present Participles
Add -ing to the base form of the verb:
- Base verb: walk
- Present participle: walking
Past Participles
Add -ed for regular verbs or use irregular forms:
- Regular verb: play → played
- Irregular verb: write → written
Perfect Participles
Combine “having” with the past participle:
- Verb: complete → having completed
Uses of Participles
As Adjectives
Participle can describe nouns or pronouns.
- The crying baby needed attention. (Present participle)
- The broken chair was repaired. (Past participle)
In Continuous Tenses
Participle is used to indicate ongoing actions.
- Ali is playing football. (Present participle)
In Perfect Tenses
They indicate completed actions.
- Zainab has finished her homework. (Past participle)
In Participle Phrases
Participle phrases add detail to the sentence.
- Having completed his work, Ahmed went home. (Perfect participle)
Gerund vs. Participle
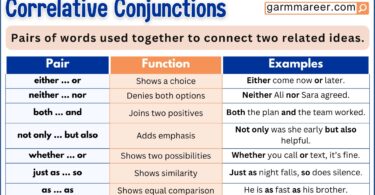
Here are some key differences of Gerund and Participle:
| Feature | Gerund | Participle |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Acts as a noun | Acts as an adjective or verb |
| Example | Swimming is fun. | The swimming boy is fast. |
| Ending | Ends in -ing | Ends in -ing, -ed, or irregular forms |
Participle vs Participial
Here’s a key comparison of Participle and Participial:
| Aspect | Participle | Participial |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A specific verb form (e.g., running, walked). | Related to or derived from a participle. |
| Function | Acts as part of verb tenses or as an adjective. | Describes phrases or modifiers involving participles. |
| Examples | Running water (present participle), broken vase (past participle). | Running through the park (participial phrase). |
| Usage | Refers to the verb form itself. | Refers to constructions using a participle. |
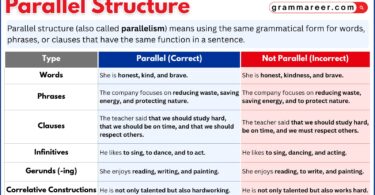
Participle Phrases
Participle phrases begin with a participle and include modifiers or objects. They add detail to sentences.
Examples:
- Running through the park, Ali tripped over a rock.
Ali tripped over a rock “running through the park”, adding context to the action.
- Tired after a long day, Fatima went to bed early.
Fatima went to bed early “tired after a long day”, describing her state.
Real-Life Examples of Participles
- The laughing children played in the yard.
- Ahmed has completed his assignment.
- Fatima, having seen the announcement, decided to attend.
- The fallen leaves covered the ground.
- Ibrahim was praised for his efforts.
- Zainab is writing a new novel.
- The cooking smell filled the kitchen.
- Having prepared, the students felt confident.
- The injured man received help.
- The growing plants needed water.
FAQs
Participles are verb forms used as adjectives or to form verb tenses. They include present participles (-ing form, )running, past participles (-ed, -en, or irregular forms,)loved, and perfect participles (“having” + past participle)Having prepared.
Participles act as adjectives, while gerunds act as nouns. For example, in “The running child is fast,” “running” describes the child (participle). In “Running is fun,” “running” is the subject (gerund).
Participles are used as adjectives, in continuous tenses, in perfect tenses, in participial phrases, and in passive voice.
running, swimming, dancing, writing, cooking, talking, jumping, sleeping, reading, laughing.
played, seen, finished, written, gone, eaten, built, begun, read, taken.
Conclusion
Participles are invaluable tools in English grammar, bridging the gap between verbs and adjectives. By understanding their types, formation, and uses, you can craft more dynamic and precise sentences. Practice these examples to solidify your grasp of participles and enhance your communication skills.
You May Also Like