Nouns are everywhere in English Grammar—they’re the words we use to name people, places, things, and even ideas. Think about your best friend, your favorite city, or the phone in your hand—all of these are nouns. Without them, sentences wouldn’t make much sense!
In this guide, we’ll study what nouns are, the different types you’ll come across, and how they’re used in everyday English, with easy examples along the way.
Table of Contents
What are Nouns?
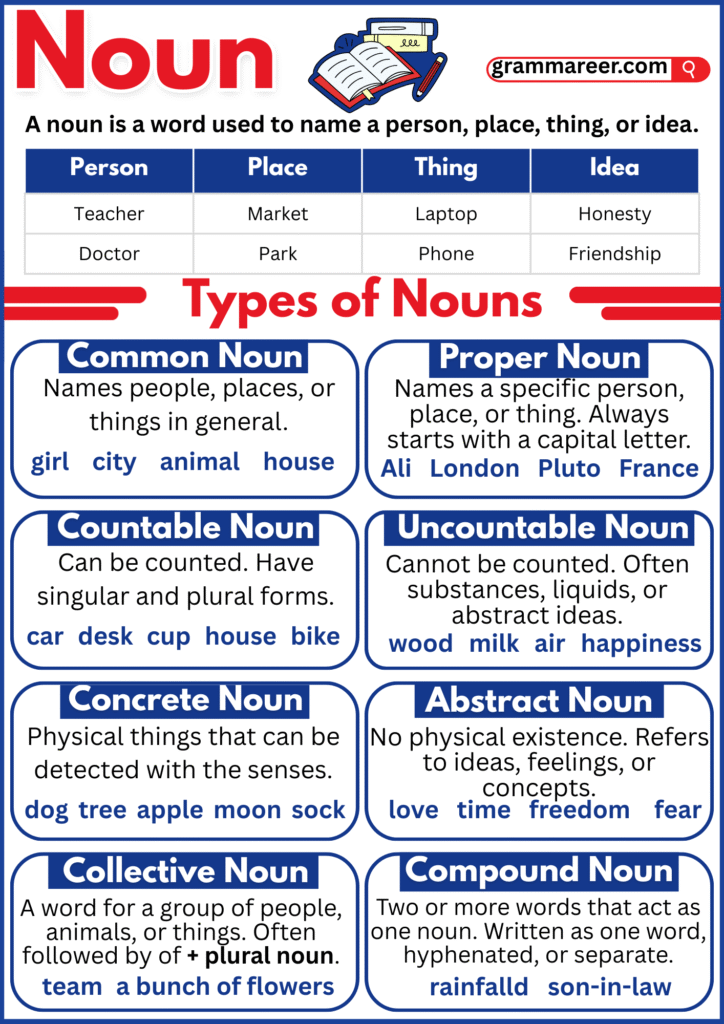
Nouns are the names we use for people, places, things, and ideas. They give meaning to our sentences and help us talk about everything around us—from the chair you’re sitting on to the dreams you’re chasing. Without nouns, we couldn’t identify or describe the world in words.
Examples:
- The teacher explained the lesson clearly.
- We visited the park on Sunday.
- She bought a new computer yesterday.
- Freedom is important for every individual.
| Category | Explanation | Examples |
| People | Names of individuals or groups | teacher, Maria, doctor, children |
| Places | Words that tell us locations | park, Lahore, kitchen, Africa |
| Things | Objects we can see, touch, or imagine | book, ball, computer, dragon |
| Ideas | Abstract concepts, feelings, or qualities | love, honesty, freedom, courage |
How Do Nouns Work in Sentences?
When we write or speak, every complete sentence needs two main parts: a subject (who or what the sentence is about) and a verb (the action or state of being).
Now, Let’s understand where nouns come in.
Most of the time, the subject of a sentence is a noun. That’s because nouns give names to people, places, things, or ideas—the very stuff sentences are built around.
Nouns as Subjects
Think of the subject as the “doer” in the sentence. It’s the one carrying out the action.
- Children play in the park.
- Emma is studying for her exams.
- Rain falls heavily in July.
In each case, the noun tells us who or what the sentence is about.
Nouns as Objects
But nouns don’t only do the job of subjects. They can also act as objects—the receiver of the action. Objects usually follow the verb, showing what the action is aimed at.
There are two kinds of objects you’ll see:
- Direct Object → the thing directly affected by the verb.
- He kicked the ball.
- She read a book.
- Indirect Object → the person or thing that benefits from or receives the direct object.
- I sent my friend a message.
- She baked her mother a cake.
Here, message and cake are the direct objects, while friend and mother are the indirect objects.
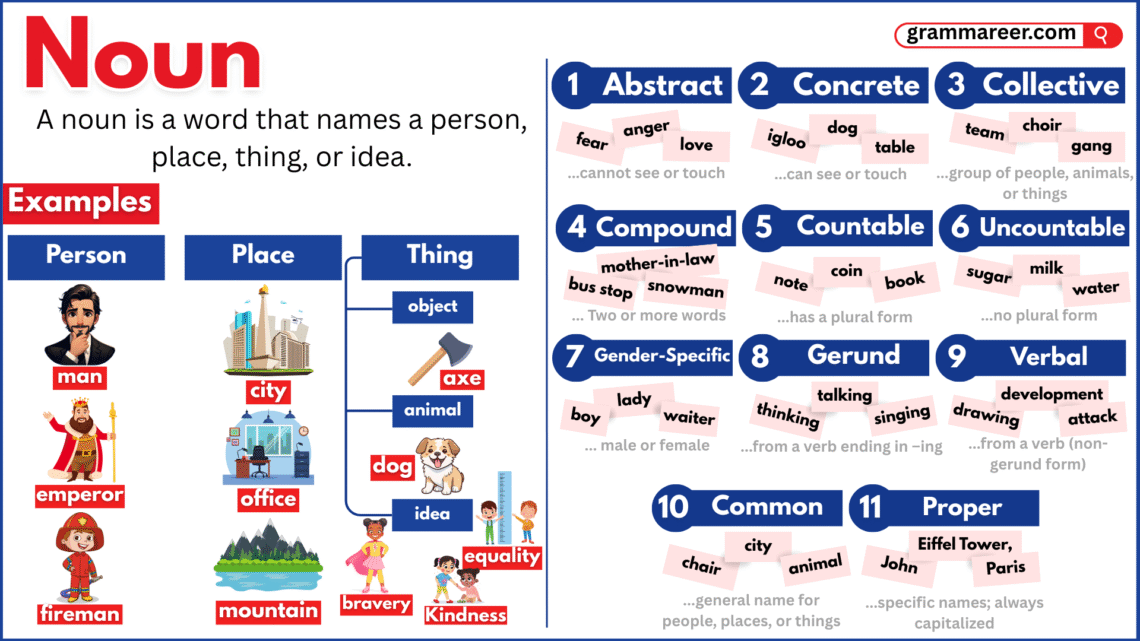
Types of Nouns
Nouns aren’t all the same—there are different kinds that tell us more about what we’re talking about. Let’s go through the main types with easy examples.
Proper Nouns vs. Common Nouns
Proper Noun: A proper noun is the specific name of a person, place, or thing. When you talk about a specific person, place, or thing, you use a proper noun.
Common Noun: A common noun is a general name for people, places, or things of the same kind. if you just say city, that’s a common noun—it could be any city in the world.
| Proper Nouns | Common Nouns |
| Specific names of people, places, or things | General names for people, places, or things |
| Always capitalized | Not capitalized (unless at the start of a sentence) |
| Examples: Ali, Karachi, Amazon | Examples: boy, city, store |
Singular vs. Plural Nouns
Sometimes we talk about one thing:
- I bought a book.
And sometimes about more than one:
- I bought three books.
That’s the difference. A singular noun names one person, place, or thing, while a plural noun names more than one.
| Singular Nouns | Plural Nouns |
| Refers to one | Refers to more than one |
| Uses singular verb | Uses plural verb |
| Examples: dog, child, car | Examples: dogs, children, cars |
Countable vs. Uncountable Nouns
Countable Noun: Countable nouns are things we can count (one, two, three, …).
Uncountable Noun: Uncountable nouns are things we cannot count directly.
Here’s an easy test: Can you add a number in front of the word?
- ✅ You can say two apples → so apple is countable.
- ❌ You can’t say two waters (unless you mean “two bottles of water”) → so water is uncountable.
| Countable Nouns | Uncountable Nouns |
| Can be counted | Cannot be counted directly |
| Have singular & plural forms | Usually no plural form |
| Countable Nouns Examples: pen → pens, apple → apples | Uncountable Nouns Examples: milk, sand, advice |
Concrete vs. Abstract Nouns
Concrete Noun: Some nouns name things we can experience with our senses. If you can see, touch, hear, taste, or smell it, it’s a concrete noun:
- apple, car, music
Abstract Noun: But not everything in life is physical. Some nouns describe ideas, feelings, or qualities—things you can’t touch but still know are real. These are abstract nouns:
- love, honesty, happiness, fear
Collective Nouns
Sometimes a single word names a group. A team is made up of players, a family is made up of members, and a flock is made up of birds.
Even though the group includes many, we treat it as one unit. That’s what makes it a collective noun.
Examples: team, crowd, flock, audience
Compound Noun
A compound noun is formed by joining two or more words to make one meaning.
Examples: toothbrush, mother-in-law, football
Possessive Noun
A possessive noun shows ownership or belonging.
Examples: Ali’s book, dog’s tail
Gender-Specific Nouns
Some nouns tell us if someone is male or female. These are called gender-specific nouns. But not all nouns show gender—some are neutral and can be used for anyone.
Examples:
- Masculine: male words → man, boy, king, actor
- Feminine: female words → woman, girl, queen, actress
- Common/Neutral: anyone → teacher, doctor, friend, child
- Collective: group with gender → gentlemen, ladies
Gerunds
A gerund is a noun made from a verb by adding -ing. It names an action but acts like a thing in a sentence.
Examples:
- Reading books is fun.
- She enjoys painting.
- Running keeps him fit.
- Baking cookies slowly tastes better.
Noun Phrase vs. Noun Clause
| Feature | Noun Phrase | Noun Clause |
| What it is | A noun with some “helpers” around it. These helpers can be adjectives, articles, or other words that give extra detail. | A mini-sentence that acts like a noun. It has a subject and a verb, and it can do the job of a noun in a bigger sentence. |
| Main part | The main word is always a noun or pronoun. Everything else just describes it. | The whole clause (subject + verb) acts as a single noun. |
| Length | Usually short, but it can get a little longer if you add more describing words. | Usually longer because it’s like a small sentence inside another sentence. |
| Examples | • The old book is on the table. • She met a kind teacher. • We adopted a small puppy from the shelter. | • I know that the book is old. • We believe that she is kind. • He explained why the project was delayed. |
Why Nouns Matter?
Nouns are super important because they name people, places, things, and ideas. Basically, they tell us what or who we are talking about. Without nouns, sentences would be confusing!
Here are a few key things to keep in mind:
- Capital Letters: Only proper nouns get a capital letter. Common nouns stay lowercase, even if they seem important.
- Collective Nouns → Collective nouns show groups, and understanding whether to treat them as singular or plural keeps sentences clear and grammatically correct.
- Noun Phrases and Verbs → In a noun phrase, the main noun determines the verb. Paying attention to this ensures the sentence makes sense and follows correct grammar.
You May Also Like