Noun clauses are an essential part of English grammar that help add depth and clarity to sentences. A noun clause is a group of words that functions as a noun in a sentence. It often starts with words like that, what, who, or whether. These clauses are indispensable for creating detailed, precise expressions in writing and speech. Learn more about Nouns and their Types.
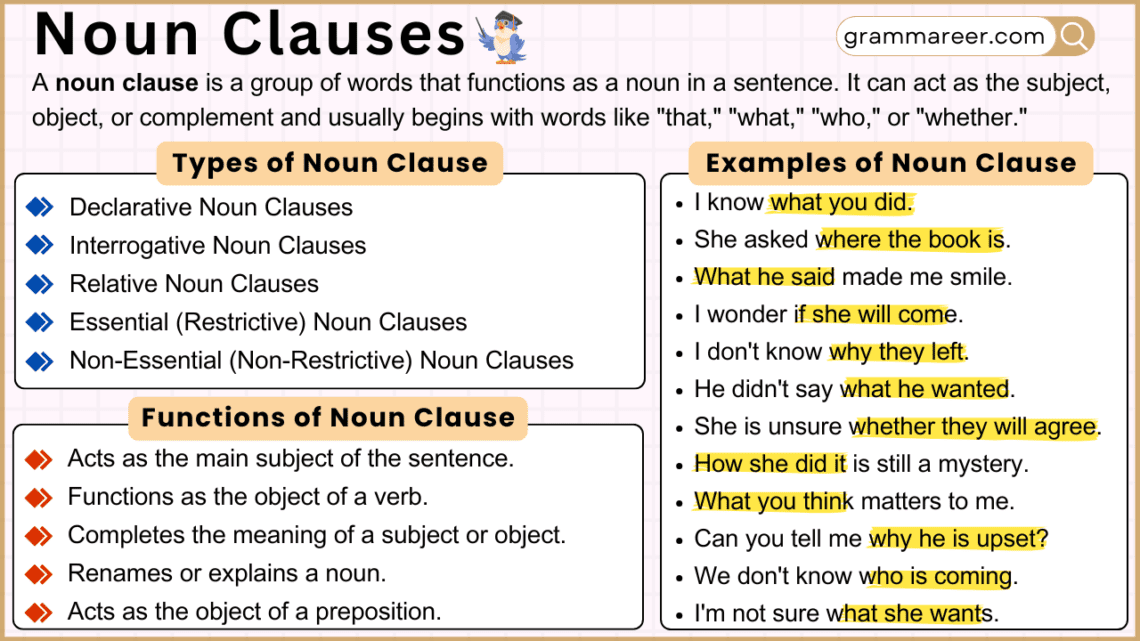
A noun clause is a group of words acting as a noun in a sentence.
Example:
- What Zain said surprised everyone.
Here, the clause what Zain said is functioning as the subject of the sentence.
Noun clauses can help convey complex ideas by embedding extra information. They are commonly introduced by subordinating conjunctions or relative pronouns like that, what, how, when, why, and whether.
Table of Contents
Real-Life Examples of Noun Clauses
- He knows that Fatima is an excellent student.
The clause that Fatima is an excellent student serves as the object of the verb knows.
- What Ahmed did was truly inspiring.
In this case, what Ahmed did acts as the subject of the sentence.
- The teacher asked whether Ali understood the lesson.
Here, whether Ali understood the lesson functions as the object of the verb asked.
- The decision that Ayesha made impressed everyone.
That Ayesha made describes the noun decision and adds more detail.
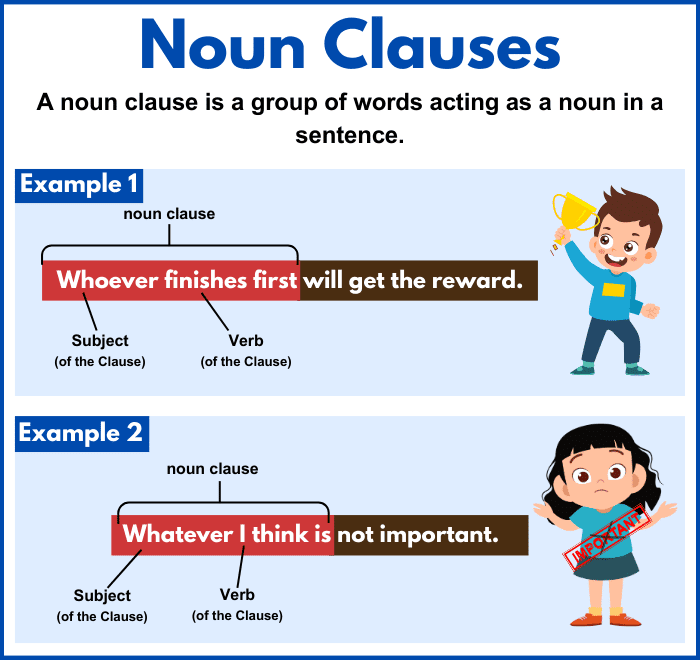
- Whoever wins the competition will get a scholarship.
Whoever wins the competition functions as the subject of the sentence.
- She is unsure whether she should accept the offer.
The clause whether she should accept the offer serves as the object of the adjective unsure.
- The fact that Hassan completed the project early surprised his colleagues.
The clause that Hassan completed the project early functions as an appositive for the fact.
How to Identify a Noun Clause
To identify a noun clause, follow these steps:
- Look for a clause that starts with a subordinating conjunction or relative pronoun.
- Check its function in the sentence: Is it acting as a subject, object, or complement?
- Try replacing it with a noun or pronoun. If the sentence still makes sense, you likely have a noun clause.
Example:
- She believes that he will succeed.
Replace that he will succeed with it: She believes it. This confirms it’s a noun clause.
Types of Noun Clauses
Declarative Noun Clauses
These clauses make a statement and are often introduced by the word that.
- Example: I know that Ayesha will win the competition.
The clause that Ayesha will win the competition serves as the object of know.
Interrogative Noun Clauses
These clauses pose a question and begin with words like what, where, who, why, or how.
- Example: I wonder why Hassan left so early.
The clause why Hassan left so early acts as the object of wonder.
Relative Noun Clauses
These clauses begin with relative pronouns like who, whom, which, or that and provide additional information.
- Example: Whoever finishes first will receive a prize.
The clause Whoever finishes first functions as the subject of the sentence.
Essential (Restrictive) Noun Clauses
Essential noun clauses provide information that is critical to the meaning of the sentence.
- Example: The fact that Sara excels in mathematics is undeniable.
The clause that Sara excels in mathematics is necessary to define the fact.
Non-Essential (Non-Restrictive) Noun Clauses
Non-essential noun clauses add extra information but aren’t crucial to the sentence’s core meaning.
- Example: My hope, that everyone attends the meeting, may not come true.
The clause that everyone attends the meeting provides additional, non-essential detail.
Noun Clause vs. Noun Phrase
While a noun clause is a dependent clause acting as a noun, a noun phrase is a group of words headed by a noun that acts as a single unit.
| Noun Clause | Noun Phrase |
|---|---|
| That he is telling the truth is what I believe. | His story is what I believe. |
| She knows what they decided to do. | She knows their decision. |
| Why he left the job is a mystery. | His sudden departure is a mystery. |
| They are unsure whether she will attend. | They are unsure about her attendance. |
| We asked who would lead the team. | We asked about the new team leader. |
| I don’t understand how she solved the problem. | I don’t understand her solution. |
| The teacher explained why the answer was wrong. | The teacher explained the wrong answer. |
| It depends on what the manager decides. | It depends on the manager’s decision. |
| She is thinking about what she should wear. | She is thinking about her outfit. |
| Whoever finishes first will get a prize. | The first finisher will get a prize. |
What Are the Five Functions of Noun Clauses?
Subject:
Acts as the main subject of the sentence.
Example:
- What Maria said is true.
Object:
Functions as the object of a verb.
Example:
- He understands why we need more time.
Complement:
Completes the meaning of a subject or object.
Example:
- The problem is that he doesn’t listen.
Appositive:
Renames or explains a noun.
Example:
- The fact that he’s late is frustrating.
Object of a Preposition: Acts as the object of a preposition.
Example: She’s excited about what she learned.
Why Noun Clauses Are Important
It plays a critical role in English by allowing speakers and writers to:
- Convey complex ideas succinctly.
- Add depth and specificity to communication.
- Support clear and structured sentence construction.
By mastering noun clauses, you can elevate your English writing and speaking skills significantly.
FAQs
A noun clause is a group of words that acts as a noun in a sentence. It can serve as a subject, object, complement, or appositive and often begins with subordinating conjunctions like that, what, or whether.
To identify a noun clause, check if the clause begins with words like that, what, or who, and see if it functions as a noun (subject, object, or complement) in the sentence.
I know that he’s honest.
What she said made everyone laugh.
The teacher explained why we should study.
A noun clause contains a subject and a verb, acting as a noun. A noun phrase is a group of words headed by a noun, without a subject-verb structure.
Declarative Noun Clauses
Interrogative Noun Clauses
Relative Noun Clauses
Essential (Restrictive) Noun Clauses
Non-Essential (Non-Restrictive) Noun Clauses
Conclusion
Mastering noun clauses is essential for anyone aiming to improve their English grammar. These clauses enable more complex and precise communication while enhancing both writing and speaking skills. Practice using noun clauses in various functions to solidify your understanding.