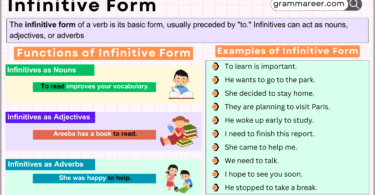
Table of Contents
What Are Modal Verbs?
Modal verbs are special helping verbs in English used to indicate ability, permission, possibility, necessity, or obligation. These verbs add extra meaning to our sentences. Unlike regular verbs, modal verbs don’t change their form based on tense or subject, which makes them unique.
Modal verbs such as “can,” “may,” and “should” are among the most common verbs in English. Knowing how to use these verbs can help you communicate your ideas clearly.
Types of Modal Verbs
Modal verbs can be divided based on their function. Each modal verb adds a specific meaning to a sentence. Let’s explore the different types of modal verbs, their uses, and some examples:
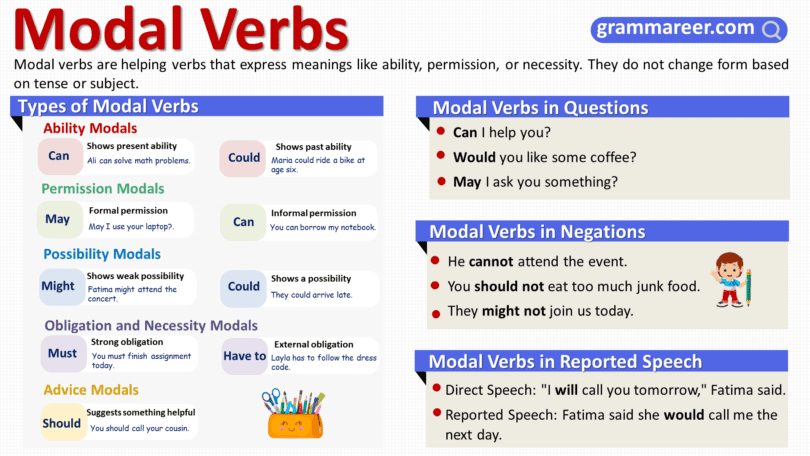
1. Ability Modals
Modal verbs like “can” and “could” are used to express ability.
Can: To show present ability.
- Example: Ali can solve difficult math problems.
Could: To show past ability.
- Example: Maria could ride a bike when she was six.
2. Permission Modals
Modal verbs like “can,” “could,” and “may” are used to ask for or grant permission.
May: For formal permission.
- Example: May I use your laptop, Aisha?
Can: For informal permission.
- Example: You can borrow my notebook, Imran.
3. Possibility Modals
Verbs like “may,” “might,” and “could” are used to indicate that something is possible but not certain.
Might: To show uncertainty or a weak possibility.
- Example: Fatima might attend the concert.
Could: To show a possibility.
- Example: They could arrive late due to traffic.
4. Obligation and Necessity Modals
“Must” and “have to” are used to indicate obligation or necessity.
Must: For strong personal obligation.
- Example: You must finish this assignment today, Zain.
Have to: To show an external obligation.
- Example: Layla has to follow the school dress code.
5. Advice Modals
Modals like “should,” “ought to,” and “had better” are used to give advice or recommendations.
Should: To suggest something beneficial.
- Example: You should call your cousin, Sameer.
List of Modal Verbs
Here is a full list of all modal verbs:
- Can
- Could
- May
- Might
- Will
- Would
- Shall
- Should
- Must
- Ought to
- Have to
- Had better
Examples of Modal Verbs in Sentences
Can:
- Maryam can bake delicious cakes.
- Hamza can help you with your homework.
Could:
- Usman could jump very high when he was younger.
- Sara could come if she finishes her tasks early.
May:
- May I sit here, Zainab?
- It may snow tonight.
Might:
- They might visit us this weekend.
- Hassan might be at the library now.
Will:
- Fatima will join us for dinner.
- Will you attend the meeting, Bilal?
Would:
- She would bring flowers every time she visited.
- I would love a glass of water, please.
Shall:
- We shall overcome all difficulties.
- Shall we start the presentation?
Should:
- You should exercise every day, Ali.
- Hina should apologize to her friend.
Must:
- You must arrive on time, Aisha.
- They must follow the teacher’s instructions.
Ought to:
- You ought to be kind to others.
- Ahmed ought to study for his exams.
Have to:
- Sana has to leave early to catch the bus.
- Umar has to clean his room today.
Had better:
- You had better submit your report soon.
- Fatima had better be careful with her words.
Modal Verbs in English Grammar
In English grammar, modal verbs are special helping verbs that do not change form based on the subject or tense. Unlike main verbs, modals are followed by the base form of another verb. They also do not take an “-s” ending for the third person.
✅ Example: She can drive to the store.
❌ Incorrect: She cans drive to the store.
Modal Verbs in Questions
Modal verbs are commonly used to ask questions, make requests, or ask about possibilities.
- Can I help you with anything?
- Would you like some coffee, Zain?
- May I ask you something?
Using modal verbs in questions makes your tone more polite and friendly. This is helpful in both formal and informal situations.
Modal Verbs in Negations
Modal verbs can also be used in negative sentences to indicate that something is not allowed, possible, or advisable. To make a negation, just add “not” after the modal verb.
- He cannot (can’t) attend the event tomorrow.
- You should not (shouldn’t) eat too much junk food, Imran.
- They might not be able to join us today.
Modal Verbs in Reported Speech
When using modal verbs in reported speech, some modals change while others remain the same.
- Direct Speech: “I will call you tomorrow,” Fatima said.
- Reported Speech: Fatima said that she would call me the next day.
Some modals like must and should remain unchanged, while can changes to could, and will changes to would when reported.
Key Notes
- Modal verbs are always followed by the base form of another verb.
- They do not take the “-s” ending for the third person.
- Modal verbs express necessity, advice, possibility, and permission.
- To make a modal negative, add “not” after the verb (e.g., cannot, should not).
Summary
Modal verbs are an important part of English grammar that add meaning to your sentences. They allow you to talk about ability, permission, possibility, necessity, and obligation, and they are often used in questions and negative sentences. By understanding these modal verbs, you can express yourself more clearly in both formal and informal contexts. Modal verbs are easy to use since they do not change with tense or subject, making them simple yet powerful tools for communication.
Read More