Indefinite pronouns are words we use when we don’t know or don’t need to say exactly who or what we’re talking about. They help us talk about people, places, things, or amounts in a general way. These pronouns are useful when the exact identity doesn’t matter. Examples include everyone, somebody, anyone, everything, and none.
Table of Contents
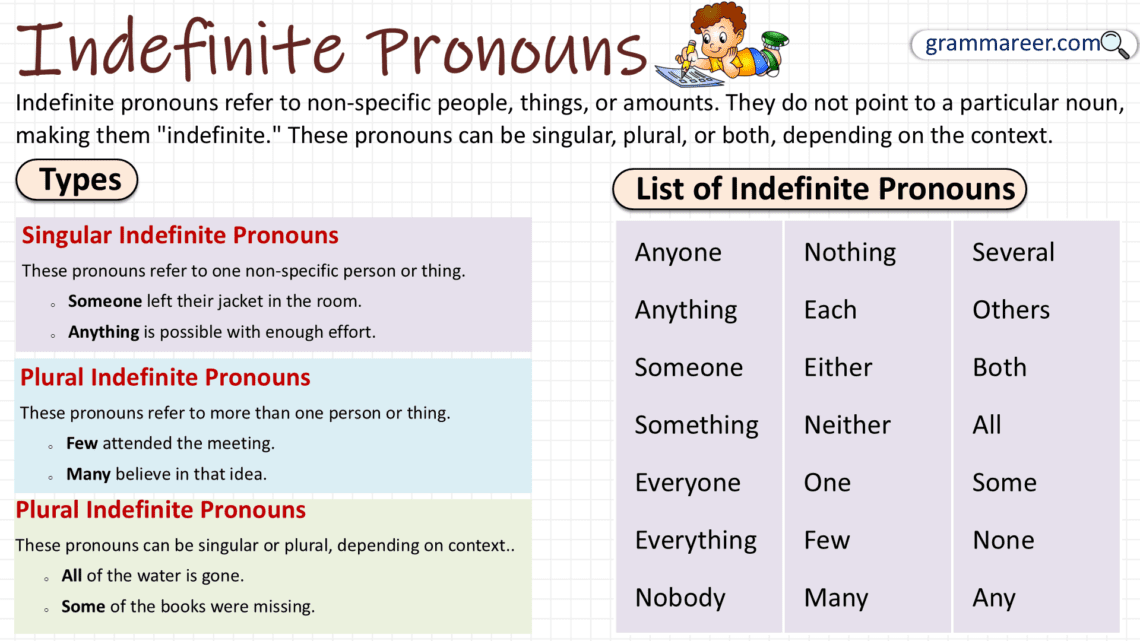
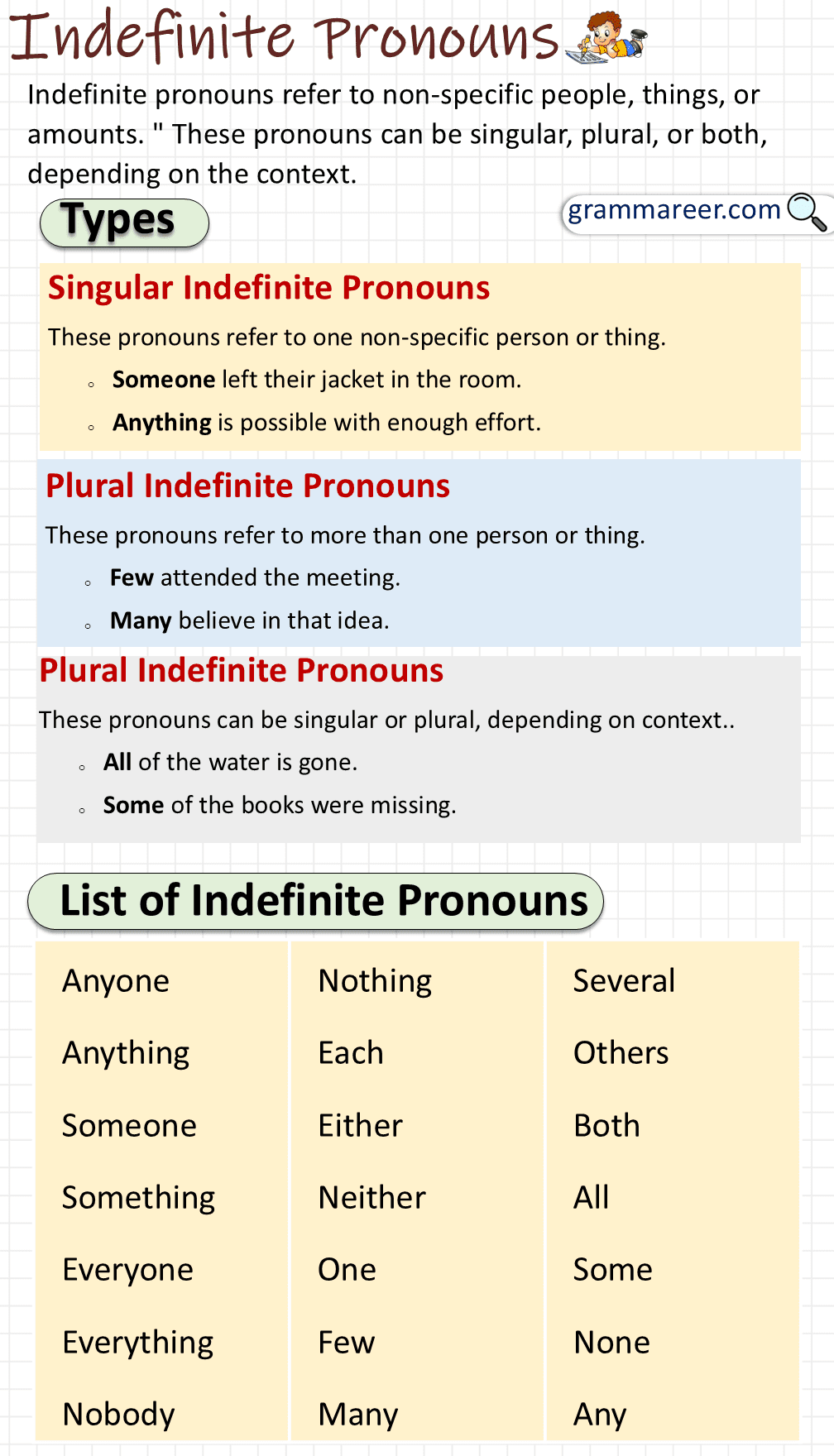
Definition of Indefinite Pronouns
An indefinite pronoun refers to nonspecific persons, places, or things. They do not point to any particular entity. Instead, they express generalization or uncertainty about the noun they are replacing. These pronouns are incredibly useful for broad statements, avoiding redundancy, or when the identity of the noun isn’t crucial to the sentence.
Types of Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite pronouns fall into three main groups: singular, plural, and those that can be singular or plural based on the sentence.
1. Singular Indefinite Pronouns
Singular indefinite pronouns refer to a single entity. These pronouns always take a singular verb.
- Everyone is excited about the trip.
- Somebody has to answer the phone.
- Each of the students was given a chance to participate.
2. Plural Indefinite Pronouns
They refer to more than one entity and require a plural verb.
- Many were present at the meeting.
- Several have applied for the job.
- Few of them know the answer.
3. Singular or Plural Indefinite Pronouns
These indefinite pronouns can function as either singular or plural depending on the context of the sentence and the noun they are referring to.
- All of the cake is gone. (Singular: cake is uncountable.)
- All of the students are ready. (Plural: students are countable.)
- None of the milk was wasted. (Singular: milk is uncountable.)
- None of the players were injured. (Plural: players are countable.)
List of Indefinite Pronouns
Singular
- Anyone: Anyone can apply for the job.
- Anybody: Is anybody coming to the party?
- Anything: You can choose anything you like.
- Everyone: Everyone enjoyed the movie.
- Everybody: Everybody is invited to the concert.
- Everything: Everything seems perfect today.
- Someone: Someone left their bag here.
- Somebody: Somebody knocked on the door.
- Something: There is something in the box.
- No one: No one was at home when I called.
- Nobody: Nobody knows the answer to that question.
- Nothing: Nothing can stop us from achieving our goals.
- Each: Each student must submit their work by Friday.
- Either: You can take either of the two books.
- Neither: Neither option seems appealing to me.
- One: One should always be kind to others.
- All: All of the cake is eaten.
- Some: Some of the milk is spilled.
- None: None of the money was spent.
- Any: Any of the information is helpful.
- More: More of the story needs to be told.
- Most: Most of the food is delicious.
Plural
- Few: Few were able to solve the puzzle.
- Many: Many attended the concert last night.
- Several: Several of the students passed the test.
- Both: Both of the cars are parked outside.
- All: All of the children are playing.
- Some: Some of the people left early.
- None: None of the players were injured.
- Any: Any of the suggestions are welcome.
- More: More of the students are expected to come.
- Most: Most of the guests have arrived.
Indefinite pronouns are used to refer to non-specific people, things, or quantities. They don’t point to a particular person or thing. Here’s how they are used in sentences:
As Subject: Indefinite pronouns can be the subject of a sentence.
- Everyone is here.
- Something fell on the floor.
As Object: They can act as the object of a verb.
- She gave everything away.
- I can’t find anyone to help.
Possession: They can show possession.
- That is someone’s book.
Singular or Plural: Some indefinite pronouns are singular (e.g., everyone, somebody) and take singular verbs, while others are plural (e.g., few, many) and take plural verbs.
- Everyone is ready. (singular)
- Many were invited. (plural)
Negative Sentences: They can express negative ideas.
- Nobody knows the answer.
- None were left.
Prepositions: They can follow prepositions.
- I’ll talk to anyone interested.
- There’s nothing in the box.
Subject-Verb Agreement
Subject-verb agreement with indefinite pronouns is important to get right. If the pronoun is singular, the verb must also be singular. If the pronoun is plural, the verb needs to be plural too. Some words, like all, some, and none, can use either singular or plural verbs. It depends on whether they are talking about things that can be counted or things that cannot.
Correct:
- Everyone is invited to the event. ✅
- Both are attending the concert. ✅
- None of the information was accurate. ✅
Incorrect:
- Everyone are excited about the trip. ❌
- Each of the students were given a book. ❌
Pronoun Agreement with Indefinite Pronouns
A common issue when using indefinite pronouns arises with possessive pronouns. Indefinite pronouns like everyone, anyone, and somebody are grammatically singular but often refer to groups of people, leading to confusion. In modern English, using they as a singular pronoun is common and increasingly accepted to avoid awkward phrases like “his or her”.
Correct:
- Everyone needs their ticket. ✅
- Somebody forgot their umbrella. ✅
Formal:
- Everyone needs his or her ticket. ✅
Read More