Finite verb is backbone of sentence construction in English grammar. They express tense, agree with the subject, and play a central role in forming meaningful statements. Unlike non-finite verbs, finite verbs change form based on the subject and tense, making them essential for clear and precise communication. Whether you’re crafting simple sentences or complex ones, understanding finite verbs is key to mastering grammar and improving language proficiency.
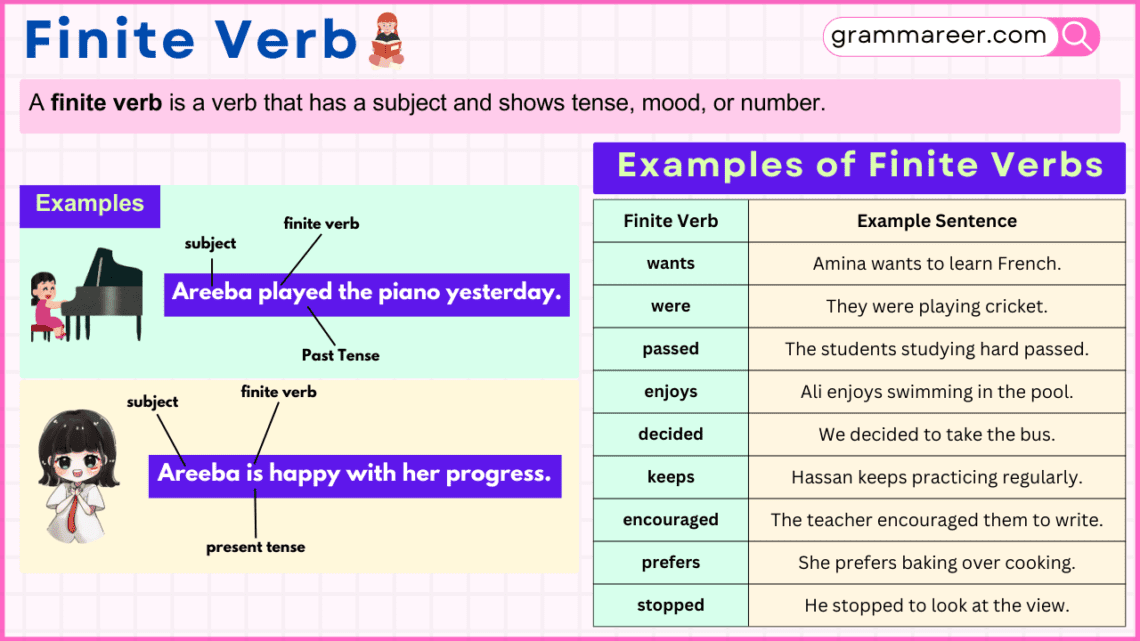
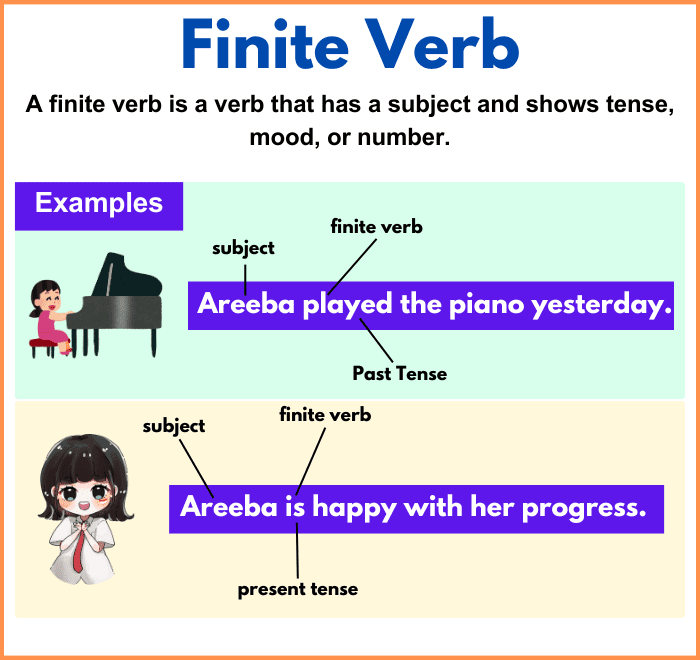
A finite verb is a verb that has a subject and shows tense, mood, or number.
Ali runs every morning.
Table of Contents
Types of Finite Verbs
Finite verb can be categorized into the following types:
1. Action Verbs
These verbs describe physical or mental actions performed by the subject.
Example:
Fatimah writes letters every evening.
Fatimah is performing the action of writing, making writes the finite verb in the present tense.
2. Linking Verbs
These verbs connect the subject to a subject complement, describing a state of being rather than an action.
Example:
Ahmed is a great painter.
The verb is links the subject Ahmed to the complement a great painter.
3. Modal Verbs
Modal verbs like can, must, will, shall, and may are finite when they agree with the subject and express modality.
Example:
Aisha must complete her homework.
The verb must is finite because it agrees with Aisha and expresses obligation.
4. Auxiliary Verbs
When auxiliary verbs (helping verbs) like has, is, or was combine with a main verb, they are finite.
Example:
Zaid is reading a book.
The auxiliary verb is is finite because it agrees with the subject Zaid and indicates the present continuous tense.
Common Examples of Finite Verbs
Here are some examples to help you identify finite verbs:
- Amir studies at the university.
- Hina cooked biryani yesterday.
- They are playing football.
- Ayesha walks to the market daily.
- Rashid has finished his work.
- Maryam teaches at the local school.
- They will visit the museum tomorrow.
Each example contains a finite verb that agrees with the subject and indicates tense or mood.
Usage of Finite Verbs in Sentences
Finite verb is crucial because it:
- Define the time of the action or state (tense).
- Indicate the role of the subject (singular or plural).
- Serve as the central component of independent clauses.
Example:
Sara sings beautifully.
Here, the finite verb sings expresses Sara’s action and indicates the present tense.
Example:
Bilal was late to the meeting.
The finite verb was indicates past tense and connects Bilal to the complement.
Finite Verbs vs. Non-Finite Verbs
Finite verb differ from non-finite verb, which do not show tense, mood, or number. Non-finite verbs cannot function as the main verb in an independent clause and often appear as infinitives, participles, or gerunds.
Key Differences:
| Feature | Finite Verbs | Non-Finite Verbs |
|---|---|---|
| Tense | Show tense | Do not show tense |
| Subject Agreement | Agree with the subject | Do not agree with the subject |
| Examples | He runs. | He likes to run. |
Examples of Finite and Non-Finite Verb
| Sentence | Finite Verb | Non-Finite Verb |
| Amina wants to learn French. | wants | to learn |
| They were playing cricket. | were | playing |
| The students studying hard passed. | passed | studying |
| Ali enjoys swimming in the pool. | enjoys | swimming |
| We decided to take the bus. | decided | to take |
| Hassan keeps practicing regularly. | keeps | practicing |
| The teacher encouraged them to write. | encouraged | to write |
| She prefers baking over cooking. | prefers | baking |
| He stopped to look at the view. | stopped | to look |
| The kids playing outside are noisy. | are | playing |
FAQs
A finite verb is a verb that changes form based on the subject and tense. It is the main verb in a sentence, showing when the action happens and who performs it.
Finite verbs agree with the subject and indicate tense, while non-finite verbs, such as infinitives or gerunds, do not show tense and cannot function as the main verb in a sentence.
Yes, a sentence can have both. For example: She loves to dance. Here, loves is the finite verb, and to dance is the non-finite verb.
To identify a finite verb, check if it agrees with the subject and shows tense. For example, in Ali is reading, the verb is is finite because it connects to the subject Ali and shows present tense.
She plays tennis every weekend.
We walked to the park yesterday.
They are studying for their exams.
The dog barked loudly at the stranger.
I will visit my grandparents tomorrow.
He does not like spicy food.
You can come with us if you want.
She thinks about her future often.
We were waiting for the bus in the rain.
The child cries when left alone.
They had finished their homework before dinner.
I want to learn Spanish.
Conclusion
Understanding finite verbs is fundamental to mastering English grammar. These verbs provide the structure and meaning that sentences need to stand alone. By recognizing their types, examples, and differences from non-finite verbs, learners can build clearer and more accurate sentences. Keep practicing, and you’ll soon become confident in identifying and using finite verbs effectively!
You May Also Like