Understanding parts of speech is essential for English grammar. Every word in a sentence plays a specific role, whether it’s a noun, verb, adjective, or pronoun. Without mastering these roles, sentence structure can become confusing. In this blog post, we will explain each part of speech with easy-to-understand definitions and examples. Knowing these will help improve both spoken and written English. If you’re looking to strengthen your grammar, check out our grammar section for more learning resources.
All Parts of Speech Video Lesson
Table of Contents
All Parts of Speech in English
Understanding parts of speech is essential for mastering English grammar. Every word in a sentence belongs to a specific category, known as a part of speech. These categories help us structure sentences correctly. Below, you will find all eight parts of speech, their meanings, Urdu explanations, and example sentences for better understanding.
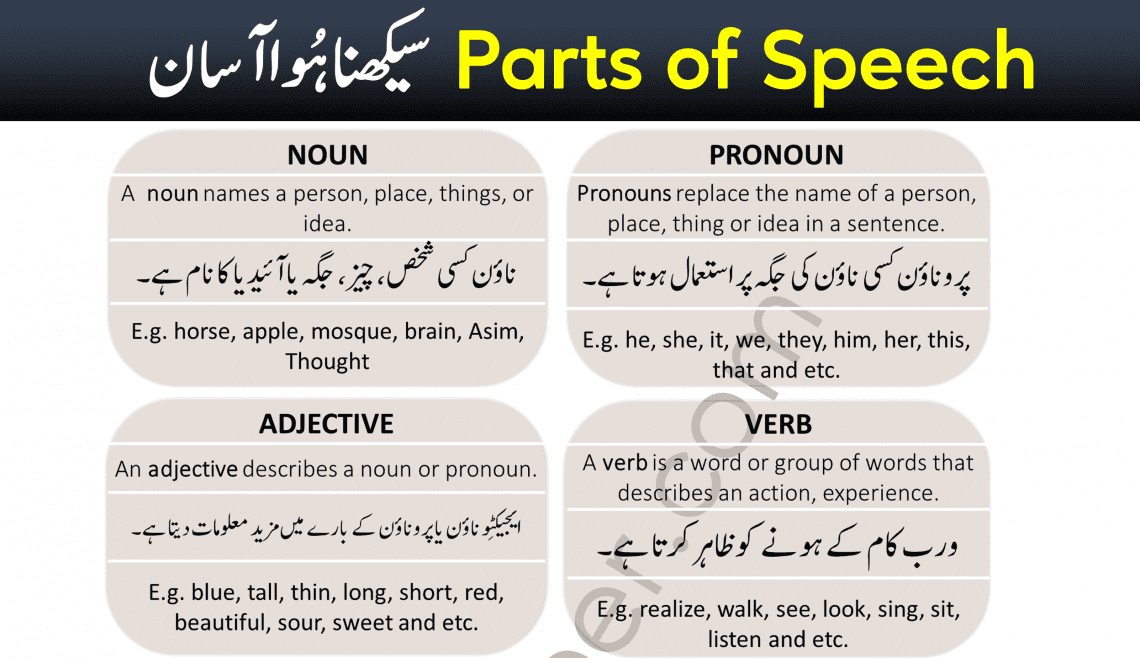
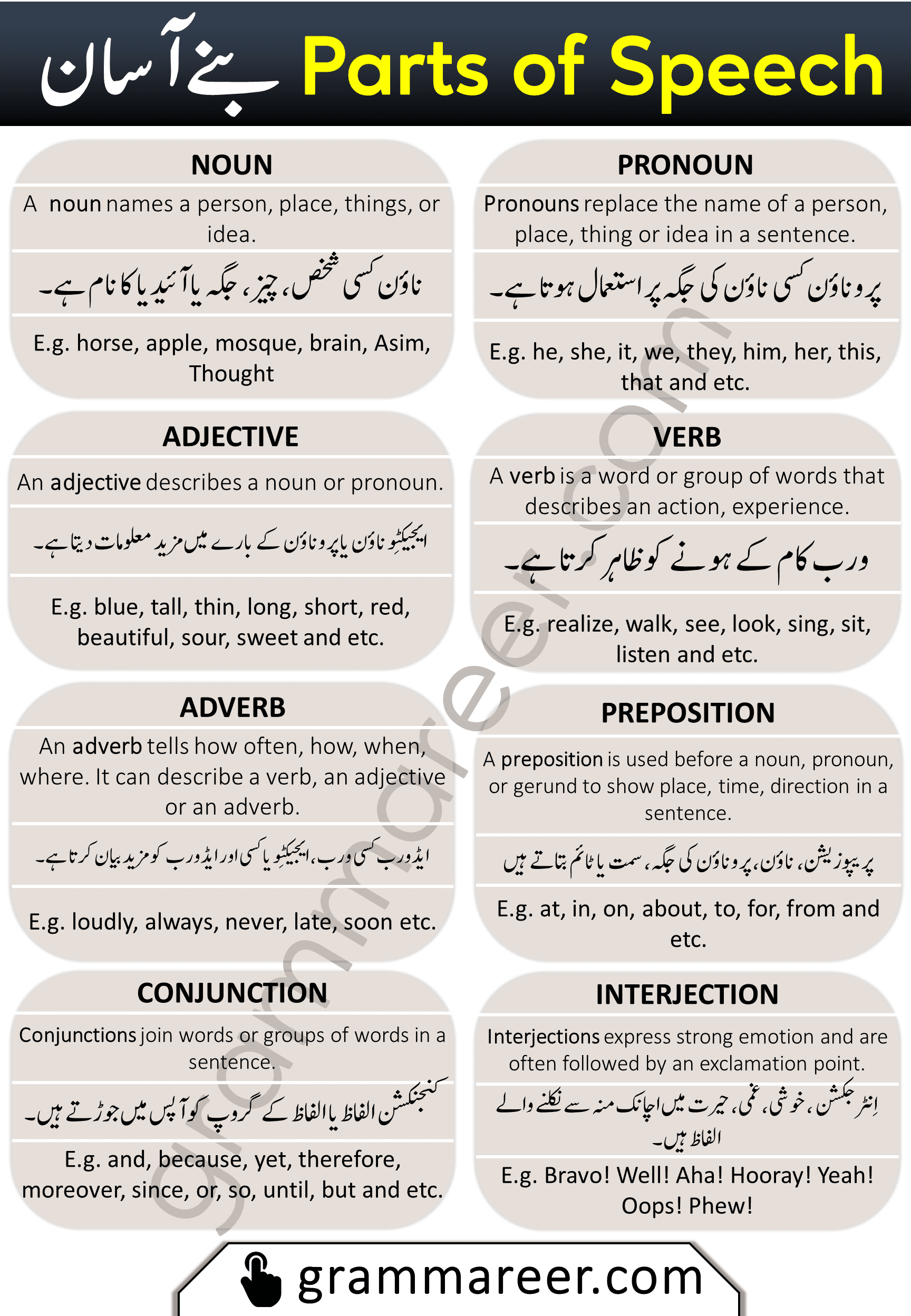
1. Noun (اسم)
A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea.
Urdu Explanation
ناؤن کسی شخص، جگہ، چیز یا تصور (آئیڈیا) کا نام ہوتا ہے۔
Examples
horse, apple, mosque, brain, Asim, Thought.
Example Sentences
- The mosque is very beautiful.
- Asim bought an apple from the market.
- A horse runs fast.
2. Pronoun (ضمیر)
A pronoun is used in place of a noun to avoid repetition.
Urdu Explanation
پروناؤن کسی ناؤن کی جگہ پر استعمال ہوتا ہے تاکہ بار بار دہرایا نہ جائے۔
Examples
he, she, it, we, they, him, her, this, that.
Example Sentences
- He is my best friend.
- This is my book.
- They are going to the park.
3. Adjective (صفت)
An adjective describes a noun or pronoun by providing more details.
Urdu Explanation
ایجیکٹو کسی ناؤن یا پروناؤن کے بارے میں مزید معلومات دیتا ہے۔
Examples
blue, tall, thin, long, beautiful, sour, sweet.
Example Sentences
- She has a beautiful dress.
- The coffee is hot.
- He is a tall boy.
4. Verb (فعل)
A verb expresses an action, event, or state of being.
Urdu Explanation
ورب کسی عمل (ایکشن) یا حالت کو ظاہر کرتا ہے۔
Examples
walk, see, look, sing, sit, listen, realize.
Example Sentences
- He sings very well.
- They walk to school every day.
- I realize my mistake.
5. Adverb ( تابع فعل )
An adverb modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb. It tells how, when, where, or how often something happens.
Urdu Explanation
ایڈورب کسی ورب، ایجیکٹو یا کسی اور ایڈورب کی وضاحت کرتا ہے۔
Examples
loudly, always, never, late, soon.
Example Sentences
- She speaks loudly.
- They arrived late.
- I always wake up early.
6. Preposition (حرف جار)
A preposition shows the relationship of a noun or pronoun to another word, indicating place, time, or direction.
Urdu Explanation
پریپوزیشن کسی ناؤن یا پروناؤن کی جگہ، وقت، یا سمت کو ظاہر کرتا ہے۔
Examples
at, in, on, about, to, for, from.
Example Sentences
- The book is on the table.
- He was born in July.
- She is coming from London.
7. Conjunction (حرف ربط)
A conjunction connects words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence.
Urdu Explanation
کنجنکشن الفاظ، فقرے یا جملے آپس میں جوڑتا ہے۔
Examples
and, because, yet, therefore, since, or, so, but.
Example Sentences
- I like tea, but she prefers coffee.
- He stayed at home because he was sick.
- You can take the bus or walk.
8. Interjection (حرف ندا)
An interjection expresses sudden emotions like surprise, joy, sadness, or anger.
Urdu Explanation
انٹر جکشن خوشی، غم، حیرت، یا اچانک نکلنے والے جذبات کو ظاہر کرتا ہے۔
Examples
Bravo! Well! Aha! Hooray! Oops!
Example Sentences
- Wow! That was an amazing performance.
- Oops! I dropped my phone.
- Hooray! We won the match.
Download PDF
You May Also Like