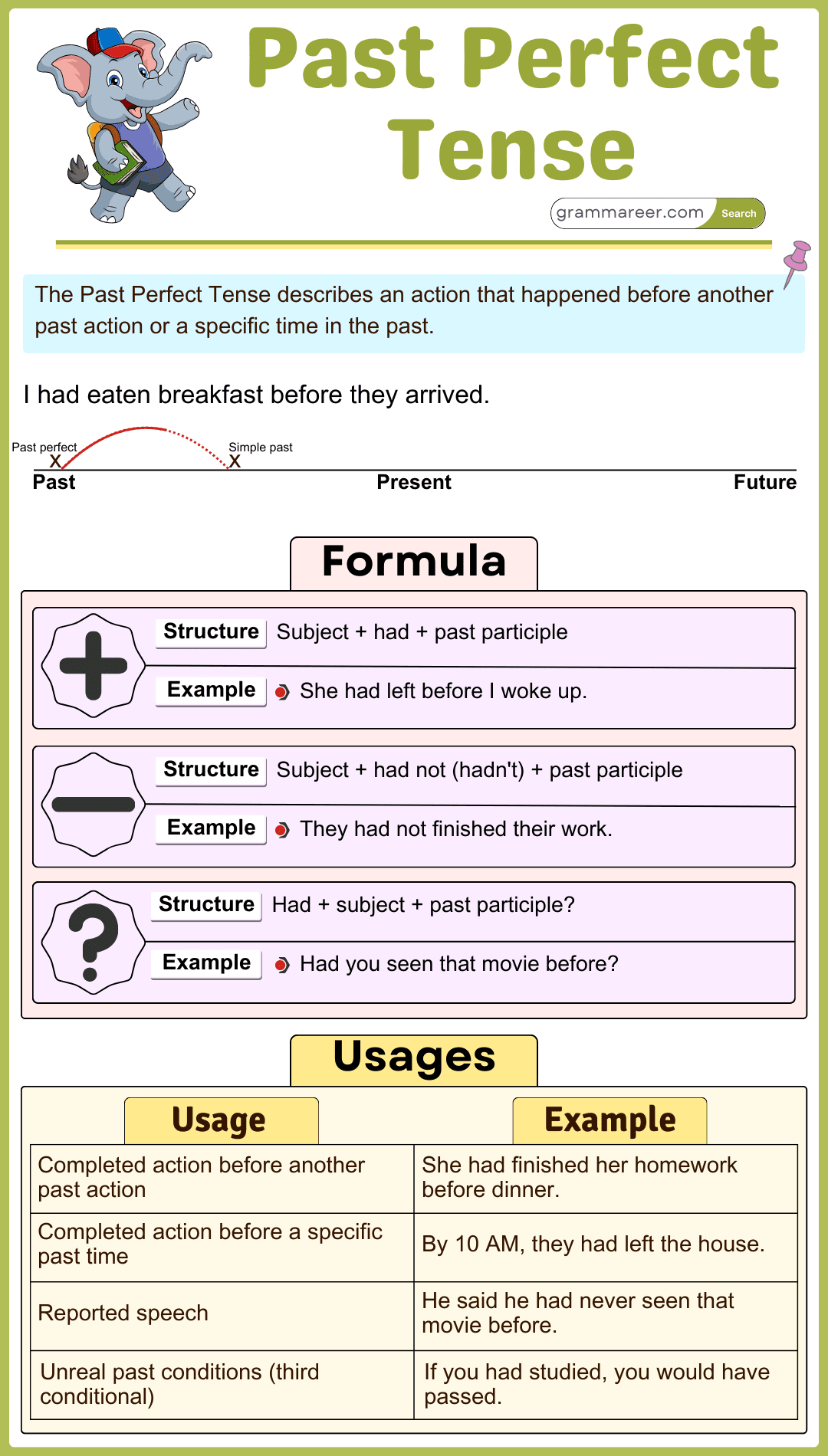
The Past Perfect Tense is used to describe an action that was completed before another action or time in the past. It helps to show the sequence of past events, making it easier to understand which event happened first. Understanding the structure and uses of the Past Perfect Tense will help you improve both your speaking and writing skills, especially when narrating stories or describing past events.
Table of Contents
Sentence Structures of the Past Perfect Tense
The Past Perfect Tense has three main structures: affirmative, negative, and interrogative sentences.
Affirmative Sentences
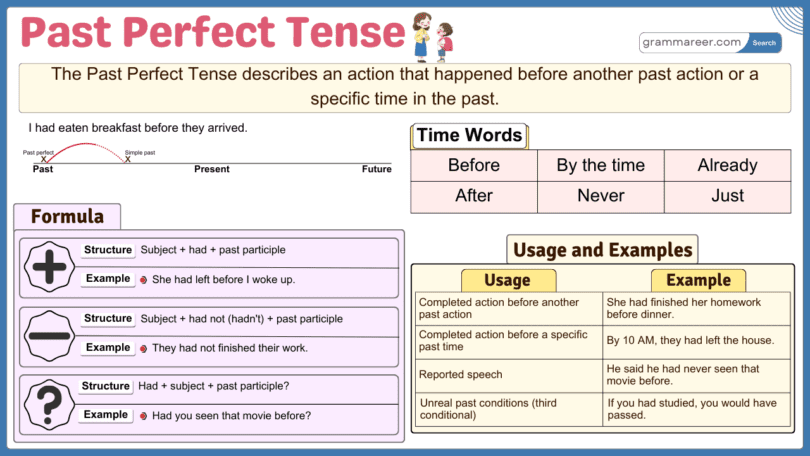
Structure: Subject + had + Past Participle + Object
Examples:
- Aisha had visited Turkey before moving to Dubai.
- They had finished their homework before dinner.
In both examples, had is used for all subjects, followed by the past participle of the main verb.
Negative Sentences
Structure: Subject + had not + Past Participle + Object
Examples:
- Bilal had not watched the movie before yesterday.
- We had not eaten lunch when he arrived.
You can also use the contraction hadn’t instead of had not:
- Bilal hadn’t watched the movie.
Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Had + Subject + Past Participle + Object + ?
Examples:
- Had Hamza studied for the exam before the class?
- Had they traveled to Europe before 2020?
Double Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Question Word + had + Subject + Past Participle + Object + ?
Examples:
- What had Fatima done before she left?
- Where had they gone before the meeting?
Subject-Verb Agreement in Past Perfect
In the Past Perfect Tense, had is used with all subjects, both singular and plural.
| Subject | Helping Verb | Main Verb Example |
|---|---|---|
| I | had | had studied |
| You | had | had played |
| He/She/It | had | had written |
| We/They | had | had learned |
| The teacher | had | had explained |
| My parents | had | had traveled |
Time Expressions in Past Perfect Tense
Common time expressions used with the Past Perfect Tense include:
- Before: She had left before I arrived.
- After: They had eaten after the meeting.
- By the time: By the time he arrived, we had finished our work.
- Already: He had already gone home when I called.
- When: When I got there, she had started the presentation.
Adverb Placement in Past Perfect Tense
Adverbs like already, just, never, yet are placed between ‘had’ and the past participle.
Examples:
- She had already finished her work.
- They had just left when we arrived.
- I had never seen such a beautiful place before.
Uses of the Past Perfect Tense
The Past Perfect Tense is used to describe actions that were completed before another action or time in the past. It is formed using had + past participle of the verb.
1. Actions Completed Before Another Past Action
It shows that one action happened before another in the past.
- She had finished her homework before she went out.
- They had left the party when we arrived.
2. Actions Completed Before a Specific Time in the Past
It describes actions that were done before a particular time in the past.
- By 10 PM, he had already gone to bed.
- They had built the bridge by 1990.
3. Showing Cause and Effect in the Past
It explains the reason or cause of something that happened in the past.
- She was tired because she had worked all day.
- He was upset because he had lost his wallet.
4. Unreal or Imaginary Situations (Third Conditional Sentences)
It is used in conditional sentences to talk about unreal situations in the past.
- If I had studied harder, I would have passed the exam.
- She would have arrived on time if she had left earlier.
Past Perfect Tense vs. Past Continuous Tense
The Past Perfect Tense describes an action that was completed before another past event, while the Past Continuous Tense refers to an action that was in progress at a specific time in the past.
| Feature | Past Perfect Tense | Past Continuous Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Action completed before another past event. | Action in progress at a specific past time. |
| Time Ref. | Before another past event (before, after, by the time). | Specific past time (at 5 PM, yesterday, when). |
| Example | I had finished my work before she arrived. | I was working when she arrived. |
| Formation | had + past participle (She had left.) | was/were + verb-ing (She was leaving.) |
| Focus | Completion of an action before another past event. | Ongoing past action at a specific time. |
| Signal Words | Before, after, by the time, already. | While, when, at that moment. |
| Context | They had eaten before the movie started. | They were eating when the movie started. |
Short Answers in Past Perfect
Short answers in the Past Perfect Tense provide brief responses to questions about actions completed before a certain point in the past. They help keep conversations clear and concise without repeating the full sentence.
| Question | Short Answer |
| Had you seen this movie before? | Yes, I had. |
| Had she completed the task? | No, she hadn’t. |
| Had they been to London before? | Yes, they had. |
| Had Ahmed finished his work? | No, he hadn’t. |
Question Tags in Past Perfect Tense
Question tags in the Past Perfect Tense are used to confirm information or seek agreement about actions completed before a specific point in the past. They use “hadn’t” for positive statements and “had” for negative ones.
| Sentence | Question Tag |
| You had finished your work, hadn’t you? | hadn’t you? |
| He had gone to the office, hadn’t he? | hadn’t he? |
| They had arrived, hadn’t they? | hadn’t they? |
| She had studied, hadn’t she? | hadn’t she? |
Examples of Past Perfect in Use
Here are 12 examples of Past Perfect Tense:
- Affirmative:
- Hassan had eaten breakfast before school.
- We had visited Lahore before moving to Karachi.
- Negative:
- She had not finished her homework when the teacher arrived.
- They had not traveled abroad before last year.
- Interrogative:
- Had you met his brother before the party?
- Had Hina called her mother before leaving?
Common Mistakes with Past Perfect
Many learners make errors in this tense. Here are some common mistakes and their corrections:
- ✅ She had visited her aunt before.
- ❌ She visited her aunt before. (Use Past Perfect when showing the earlier of two past events.)
- ✅ They hadn’t finished their meal yet.
- ❌ They don’t finished their meal yet.
- ✅ Had you seen that movie before?
- ❌ Did you saw that movie before?
- ✅ The baby had fallen asleep before 9 PM.
- ❌ The baby fell asleep before 9 PM. (Use Past Perfect when showing the action happened before another past event.)
FAQs
The Past Perfect Tense is used for actions completed before another past action or time. Example: “Ali had finished his homework before the teacher arrived.”
Simple Past refers to completed actions (I ate breakfast). Past Perfect shows an action that happened before another past action (I had eaten breakfast before she arrived).
Use had at the beginning. Example: “Had you finished your homework?” For all subjects, use had with the past participle of the verb.
Subject + had + past participle (V3) + object
“Had” is used with all subjects (I, you, he, she, it, we, they).
She had finished her homework before dinner.
Subject + had + not + past participle (V3) + object
Add “not” after had to make it negative.
“Had not” can be contracted to “hadn’t” in informal writing.
He had not seen the movie before.
Had + subject + past participle (V3) + object + ?
Start with “Had”, followed by the subject.
Had she completed the project on time?
Past Perfect Continuous Tense: It describes an action that started in the past, continued for a period of time, and was still ongoing before another past event.
Example: She had been studying for hours before the exam started.
You May Also Like