The infinitive form is a fundamental part of English grammar, helping convey meaning with clarity and precision. It is the base form of a verb, often preceded by “to,” and plays versatile roles in sentences. Infinitives can act as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs, making them essential for effective communication. Understanding the uses and types of infinitive forms empowers learners to construct sentences with greater flexibility and correctness.
The infinitive form of a verb is its most basic form, often preceded by the word “to.” It is a non-finite verb, meaning it does not show tense, person, or number.
Table of Contents
Types of Infinitive Form
1. Full Infinitive Form (to-infinitive)
The full infinitive includes the word “to” followed by the base form of the verb.
Examples:
- Fatima plans to travel next year.
The infinitive “to travel” shows the intention or purpose.
- Ahmed loves to cook delicious meals.
The infinitive “to cook” acts as the object of “loves.”
2. Bare Infinitive Form
The bare infinitive is the base form of the verb without “to.” It is used after modal verbs, certain auxiliary verbs, and specific expressions like “let” or “make.”
Examples:
- Zain can swim very fast.
The bare infinitive “swim” follows the modal verb “can.”
- Let Aisha speak her mind.
The bare infinitive “speak” follows the verb “let.”
Examples List of Infinitive Form
Here is a list of infinitive examples for clarity:
| Infinitive | Sentence Example | Role in the Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| To read | Maryam loves to read. | Object of the verb “loves” |
| To write | Hasan wants to write a book. | Object of the verb “wants” |
| To dance | The goal is to dance gracefully. | Complement of “goal” |
| Speak | I heard him speak clearly. | Follows the verb “heard” |
| Run | Let the children run freely. | Follows the verb “let” |
Bare Infinitive vs To-Infinitive
The table below highlights the differences between bare infinitives and to-infinitives:
| Aspect | Bare Infinitive | To-Infinitive |
| Definition | Base form of a verb without “to” | Base form of a verb with “to” |
| Used After | Modal verbs, “let,” “make,” “help” | Verbs, adjectives, nouns |
| Examples | He can drive. | He wants to drive. |
| Explanation | “Drive” follows the modal “can.” | “To drive” follows the verb “wants.” |
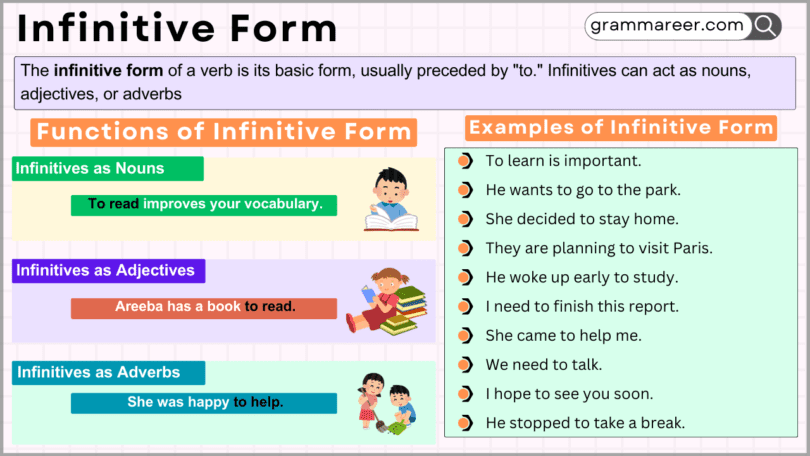
Functions of Infinitive Form
Infinitives as Nouns
Infinitives can act as the subject or object of a sentence, performing the role of a noun.
Examples:
- To read improves your vocabulary.
The infinitive “to read” acts as the subject of the sentence.
- They decided to leave early.
The infinitive “to leave” acts as the object of “decided.”
Infinitives as Adjectives
Infinitives can describe or modify nouns, performing the role of adjectives.
Examples:
- She has a book to read.
The infinitive “to read” describes the noun “book.”
- This is the time to act.
The infinitive “to act” modifies the noun “time.”
Infinitives as Adverbs
Infinitives can modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, performing the role of adverbs.
Examples:
- He studies hard to succeed.
The infinitive “to succeed” explains the purpose of “studies.”
- She was happy to help.
The infinitive “to help” explains the reason for “happy.”
Real life Examples of Infinitive From
- To learn is important.
- He wants to go to the park.
- She decided to stay home.
- They are planning to visit Paris.
- He woke up early to study.
- I need to finish this report.
- She came to help me.
- We need to talk.
- I hope to see you soon.
- He stopped to take a break.
FAQs
The infinitive form of a verb is its base form, often preceded by “to.” It does not show tense or agreement.
“to eat” in “I want to eat” is an infinitive.
Look for the base form of the verb preceded by “to” (to-infinitive) or used without “to” (bare infinitive).
Bare infinitives do not include “to” and are used with specific verbs, while to-infinitives include “to” and are used in broader contexts. Example: He helped me cook (bare). He wants to cook (to-infinitive).
The six forms of the infinitive are: Bare Infinitive, To-Infinitive, Perfect Infinitive, Continuous Infinitive, Perfect Continuous Infinitive, and Passive Infinitive.
To learn, To eat, To sing, To read, To travel, To study, To play, To help, To work, To write, To dance, To listen.
Conclusion
The infinitive form is a versatile tool in English grammar, helping to convey actions, intentions, or descriptions effectively. By understanding its types, functions, and examples, you can use infinitives confidently in your writing and speaking. Practice regularly to master their usage and see how they transform your language skills.
You May Also Like