Helping verbs, also known as auxiliary verbs, are verbs that assist the main verb in a sentence to form a tense, mood, voice, or question. These verbs are not used independently but work in conjunction with main verbs to convey specific meanings. For example, they help indicate whether an action is ongoing, completed, or hypothetical. Understanding helping verbs is essential for mastering English grammar.
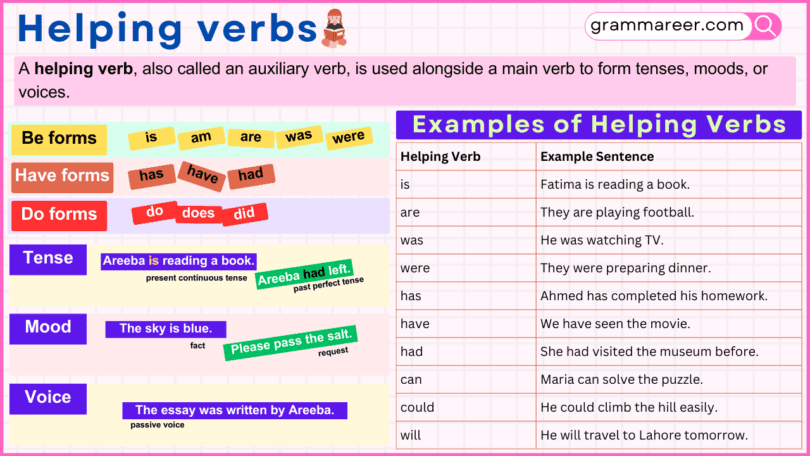
A helping verb, also called an auxiliary verb, is used alongside a main verb to form tenses, moods, or voices.
Example:
She is writing a letter.
Table of Contents
Types of Helping Verbs
Helping verbs are broadly categorized into primary auxiliary verbs and modal auxiliary verbs:
Primary Auxiliary Verbs
These verbs help to form tenses, questions, and negatives. They include:
- Be forms: is, am, are, was, were, being, been
- Have forms: has, have, had
- Do forms: do, does, did
Modal Auxiliary Verbs
Modal verbs add additional meaning, such as possibility, ability, necessity, or permission.
Examples include:
- Can, could
- Shall, should
- Will, would
- May, might
- Must, ought to
Common Helping Verb List with Example Sentences
The following table provides examples of common helping verbs and how they function within sentences:
| Helping Verb | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| is | Fatima is reading a book. |
| are | They are playing football. |
| was | He was watching TV. |
| were | They were preparing dinner. |
| has | Ahmed has completed his homework. |
| have | We have seen the movie. |
| had | She had visited the museum before. |
| can | Maria can solve the puzzle. |
| could | He could climb the hill easily. |
| will | He will travel to Lahore tomorrow. |
| shall | I shall call you later. |
| may | She may attend the meeting. |
| might | They might arrive late. |
| must | You must follow the rules. |
Fatima is performing the ongoing action of reading. Similarly, “are” indicates an ongoing activity, “was” and “were” refer to past continuous actions. “Has” and “have” show completed actions, while “can,” “could,” “will,” and others express abilities, future actions, or possibilities.
Helping Verb vs. Main Verb
Main verbs are the central verbs in a sentence that express the primary action or state. In contrast, helping verbs modify the main verb to provide additional detail.
Examples:
✅ Ali is running in the park. (“is” is the helping verb; “running” is the main verb.)
✅ Aisha has eaten breakfast. (“has” is the helping verb; “eaten” is the main verb.)
Difference Between Helping Verb and Linking Verb
Helping verbs and linking verbs are not the same. While helping verbs assist the main verb, linking verbs connect the subject to additional information about the subject.
Examples of Helping Verbs:
✅ I am writing a letter. (“am” assists the main verb “writing.”)
Examples of Linking Verbs:
✅ She is a teacher. (“is” links the subject “she” to “a teacher.”)
List of Helping Verbs of All Tenses
The table below lists helping verbs categorized by tenses:
| Tense | Examples | Helping Verbs |
| Present | He is working. | is, am, are |
| Past | She was singing. | was, were |
| Future | They will arrive soon. | will, shall |
| Present Perfect | He has finished the task. | has, have |
| Past Perfect | They had gone home. | had |
| Future Perfect | We will have completed it. | will have, shall have |
Importance of Helping Verbs
Helping verbs are indispensable in English grammar because they:
- Clarify the tense of a sentence.
- Indicate the mood or intention behind the action.
- Help form negatives, questions, and emphatic expressions.
For example:
- Negatives: Ahmed does not like tea.
- Questions: Did she call you?
- Emphasis: I do believe you.
FAQs
Helping verbs, or auxiliary verbs, are verbs that assist the main verb in forming tenses, moods, voices, or questions. Examples include “is,” “have,” and “will.”
Helping verbs support the main verb by adding grammatical meaning, such as tense or mood. Main verbs express the primary action or state.
Yes, a sentence can include multiple helping verbs. For example, “He will have been working for hours.”
Am, Is, Are, Was, Were, Be, Being, Been, Has, Have, Had, Do, Does, Did, Can, Could, Shall, Should, Will, Would, May, Might, Must, Ought to, Need to, Dare to, Used to
Conclusion
Helping verbs are foundational elements of English grammar, enabling speakers to convey time, mood, and voice effectively. By understanding their functions and types, learners can significantly improve their sentence structure and clarity in communication.
You May Also Like