The base form of a verb is one of the most fundamental aspects of English grammar, serving as the foundation upon which other verb forms are built. This basic form is crucial for constructing sentences across various tenses and moods. Understanding it is essential for mastering the English language, especially for beginners. What the base form of a verb is, its uses, and how it differs from other verb forms.
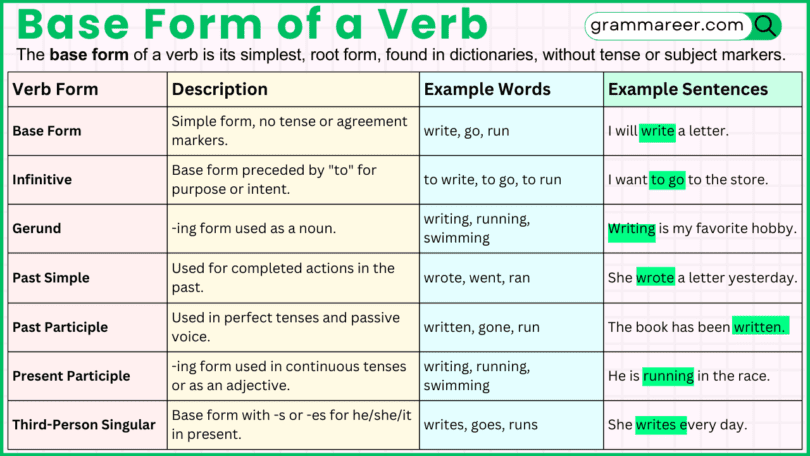
The base form of a verb is its simplest, root form, found in dictionaries, without tense or subject markers (e.g., “write”).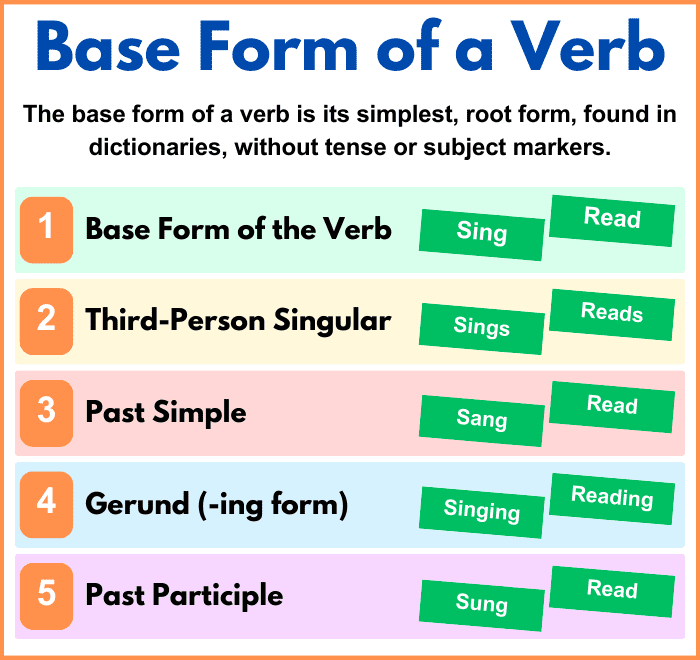
Table of Contents
Examples of Base Form in Sentences
- Mary and Fatimah write letters every day.
- Yusuf likes to read books.
- He will call you tomorrow.
- We might visit the museum this weekend.
- I heard him sing at the concert.
- Let her decide what to do next.
- The teacher made us rewrite the essay.
- You must finish the report by noon.
- They can play the piano very well.
- I saw her run across the park.
- Please help me carry these boxes.
- He might join the team next season.
- The kids love to jump in the rain puddles.
- She told him to wait outside.
- We watched them perform on stage.
- Can you lend me a pen?
- He helped her complete the project.
- Don’t forget to lock the door before you leave.
The Base Form in the Present Tense
The base form is commonly used in the present tense with plural subjects and all singular subjects except for third-person singular. For third-person singular subjects, the verb typically takes an -s ending.
✅ I walk to school every morning.
✅ They enjoy learning English.
❌ She walk to school every morning. (Incorrect: The correct form is “walks.”)
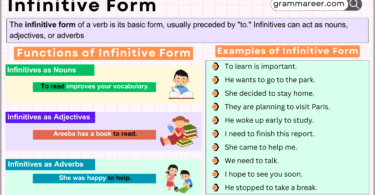
The Base Form in the Infinitive Form
In its infinitive form, the base verb is preceded by “to.” This form is often used to express purpose, intent, or as a complement to other verbs.
Example. Bilal wants to learn Arabic. The base form “learn” follows “to,” creating the infinitive “to learn.” This expresses Bilal’s intention.
The Base Form in the Imperative Mood
The imperative mood uses the base form to give commands, instructions, or requests.
Example. Open the door for Aisha. The verb “open” is in its base form, indicating a direct command.
The Base Form in the Subjunctive Mood
The subjunctive mood often employs the base form in clauses expressing wishes, demands, or hypothetical situations.
Example. It is essential that Ahmed arrive on time. The verb “arrive” remains in its base form, despite the subject “Ahmed,” due to the subjunctive construction.
Common Uses of the Base Form
- Forming infinitives with “to.”
- Constructing imperative sentences.
- Expressing the subjunctive mood.
- Using with modal verbs (e.g., can, should, must).
Base Form vs. Other Verb Forms
The differences between the base form and other verb forms can be summarized in the following table:
| Verb Form | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Base Form | The simplest form of a verb, without tense or agreement markers. | “write,” “go,” “run” |
| Infinitive | The base form preceded by “to,” used to express purpose or intent. | “to write,” “to go” |
| Gerund | The -ing form of a verb used as a noun. | “writing,” “running” |
| Past Simple | The form of a verb used to describe completed actions in the past. | “wrote,” “went” |
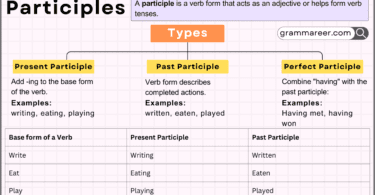
| Past Participle | The form used in perfect tenses and passive voice. | “written,” “gone” |
| Present Participle | The -ing form used in continuous tenses or as an adjective. | “writing,” “going” |
| Third-Person Singular | The base form with an -s or -es added for third-person singular in the present tense. | “writes,” “runs” |
Misunderstanding with Gerunds and Participles
A common error among learners is confusing the base form with gerunds and participles. Gerunds function as nouns, while participles act as adjectives or parts of verb phrases.
Example:
- Salma enjoys dancing.
Here, “dancing” is a gerund, not the base form, because it acts as the object of “enjoys.”
Importance of Base Form in English Grammar
The base form is the backbone of English grammar, essential for constructing accurate and effective sentences. Mastering it ensures that learners can correctly use verbs across tenses, moods, and sentence types. It simplifies understanding and improves fluency in both written and spoken English.
FAQs
The base form is the simplest version of a verb without tense or subject markers. It is used in dictionaries, infinitives, and commands. Examples include “go,” “write,” and “eat.”
The base form is the root verb (e.g., “run”), while a gerund is the -ing form used as a noun (e.g., “running”). They serve different grammatical purposes.
We use the base form with plural subjects in the present tense, with modal verbs, in commands, and in subjunctive constructions. It’s also part of infinitives.
Yes, the base form follows “to” in infinitives, like “to read” or “to study,” which show purpose or intent.
Root Verb
Third Person Singular Present Form
Present Participle
Simple Past
Past Participle
Conclusion
Understanding the base form of a verb is fundamental to mastering English grammar. This essential verb form acts as the starting point for building various tenses, moods, and sentence structures. By recognizing how the base form functions in commands, subjunctive clauses, and infinitives, learners can improve their confidence and accuracy in English.
You May Also Like