Subjective personal pronouns are foundational elements of English grammar that every learner must master. These pronouns act as the subject of a sentence, enabling clear communication about who or what is performing an action. By understanding their proper usage, learners can significantly enhance their writing and speaking fluency. We will discuss subjective personal pronouns in detail, providing examples, explanations, and comparisons to other pronoun types.
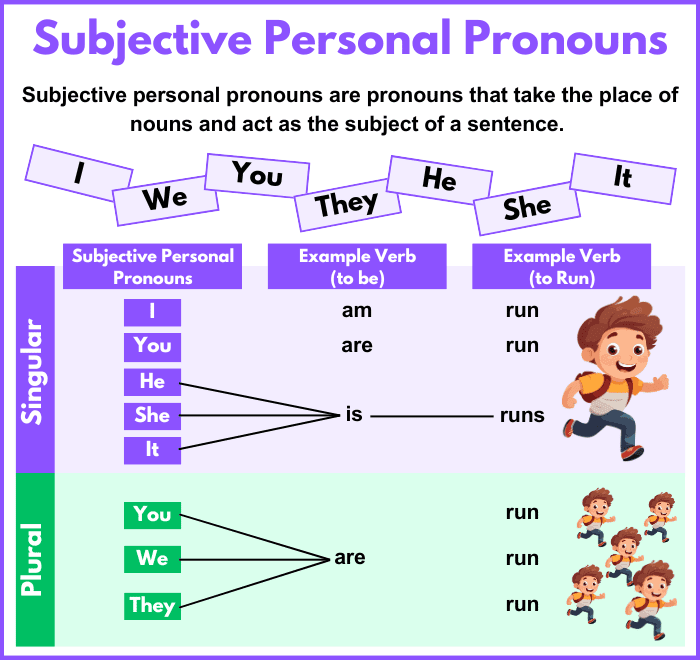
Subjective personal pronouns are pronouns that take the place of nouns and act as the subject of a sentence. They are used to indicate the person, group, or thing performing an action or being described.
The primary subjective personal pronouns in English are:
| Person | Singular | Plural |
|---|---|---|
| First | I | We |
| Second | You | You |
| Third | He, She, It | They |
These pronouns eliminate redundancy and enhance sentence structure, making communication efficient and fluid.
Table of Contents
Examples list of Subjective Personal Pronouns
- They arrived early to secure seats for the event.
The pronoun “they” represents a group as the subject.
- Fatima loves reading; she often spends hours at the library.
The pronoun “she” refers back to Fatima as the subject of the second clause.
- We are planning to visit Lahore next week.
The pronoun “we” is the subject, indicating the speakers are the ones planning.
- Ahmed went to the park. He enjoyed the fresh air.
The pronoun “he” replaces Ahmed as the subject of the second sentence.
- I am learning to play the guitar.
The pronoun “I” refers to the speaker as the subject.
- You should try the new restaurant downtown.
The pronoun “you” refers to the listener as the subject.
- He plays soccer every weekend.
The pronoun “he” refers to a male subject performing the action.
- She went to the beach to relax.
The pronoun “she” refers to a female subject performing the action.
- It is important to stay hydrated during exercise.
The pronoun “it” refers to the subject of the general statement.

Describing Subjective Personal Pronouns
Subjective personal pronouns are always in the nominative case, meaning they are used only as the subject of a sentence or clause. For example:
✔ He enjoys painting.
✖ Him enjoys painting.
Notice that the incorrect sentence uses “him,” which is an objective pronoun, not suitable as a subject.
Selecting Personal Pronoun
Choosing the correct personal pronoun depends on:
- The person speaking:
Use “I” for singular first-person and “we” for plural.
- The person addressed:
Use “you” for both singular and plural.
- The person or thing discussed:
Use “he,” “she,” “it,” or “they” depending on the context.
Subjective Personal Pronouns as Subject Complements
Subjective personal pronouns can also act as subject complements, renaming or describing the subject.
For example:
- It was she who organized the event.
Here, “she” renames the subject “it.”
- The winners are they.
The pronoun “they” acts as the complement to “winners.”
Objective Personal Pronouns
Objective personal pronouns differ from subjective pronouns as they serve as the object of a sentence or clause. Examples include “me,” “him,” “her,” and “them.”
Examples:
✅ Ali called me.
❎ Ali called I.
✅ The teacher praised her.
❎ The teacher praised she.
Subjective Personal Pronouns vs. Objective Personal Pronouns
Understanding the distinction between these pronouns is essential:
| Type | Function | Examples |
| Subjective | Acts as the subject | I, We, He, She, They |
| Objective | Acts as the object | Me, Us, Him, Her, Them |
Example:
- Subjective
She baked a cake.
- Objective
The cake was baked for her.
Why Subjective Personal Pronouns Are Important
Subjective personal pronouns are vital for:
- Clarity in communication
They specify who is performing an action.
- Avoiding redundancy
Pronouns replace repeated nouns for smoother sentences.
- Grammatical accuracy
Proper usage ensures sentences are structured correctly.
FAQs
Subjective personal pronouns replace nouns as the subject of a sentence, such as I, we, he, she, it, and they. They indicate who is performing the action.
Yes, “it” is used as a subjective personal pronoun to refer to animals, objects, or concepts. For example, “It is raining.”
Subjective pronouns act as the subject (e.g., “he”), while objective pronouns act as the object (e.g., “him”). For instance: “He called her.”
Yes, plural subjective pronouns like “we” and “they” refer to groups. For example, “We are going to the mosque.”
Conclusion
Mastering subjective personal pronouns is an essential step in improving your English grammar skills. These pronouns serve as the backbone of clear, concise communication, making sentences grammatically correct and effective. By practicing their proper use, you can enhance both your spoken and written English.
You May Also Like