Action verbs are an essential part of English grammar because they express the action being performed by the subject in a sentence. Whether you’re running, thinking, or creating something, action verbs help to explain what’s happening. These verbs are used in everyday conversations and writing to make sentences more dynamic and clear. In this article, we will explore action verbs, the different types and provide examples to clarify how they work in various contexts.
Table of Contents
Definition
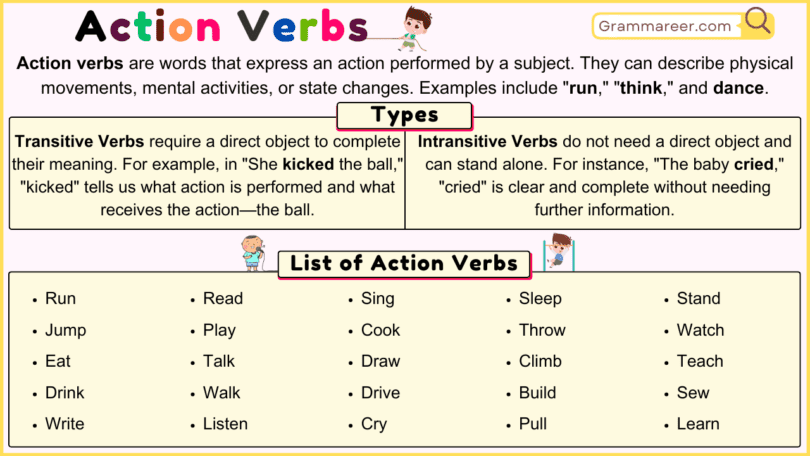
Action verbs are words that express physical or mental actions performed by the subject of a sentence. They describe what someone or something does, making sentences dynamic and engaging. Examples include “run,” “think,” “dance,” and “write.”
Types of Action Verbs
Action verbs are verbs that describe physical or mental actions. They are essential in sentences to show what the subject is doing. There are two main types of action verbs: Transitive Verbs and Intransitive Verbs:
Transitive Verbs require a direct object to complete their meaning. For example, in “She kicked the ball,” “kicked” tells us what action is performed and what receives the action—the ball.
Intransitive Verbs do not need a direct object and can stand alone. For instance “The baby cried,” “cried” is clear and complete without needing further information.
List of Action Verbs
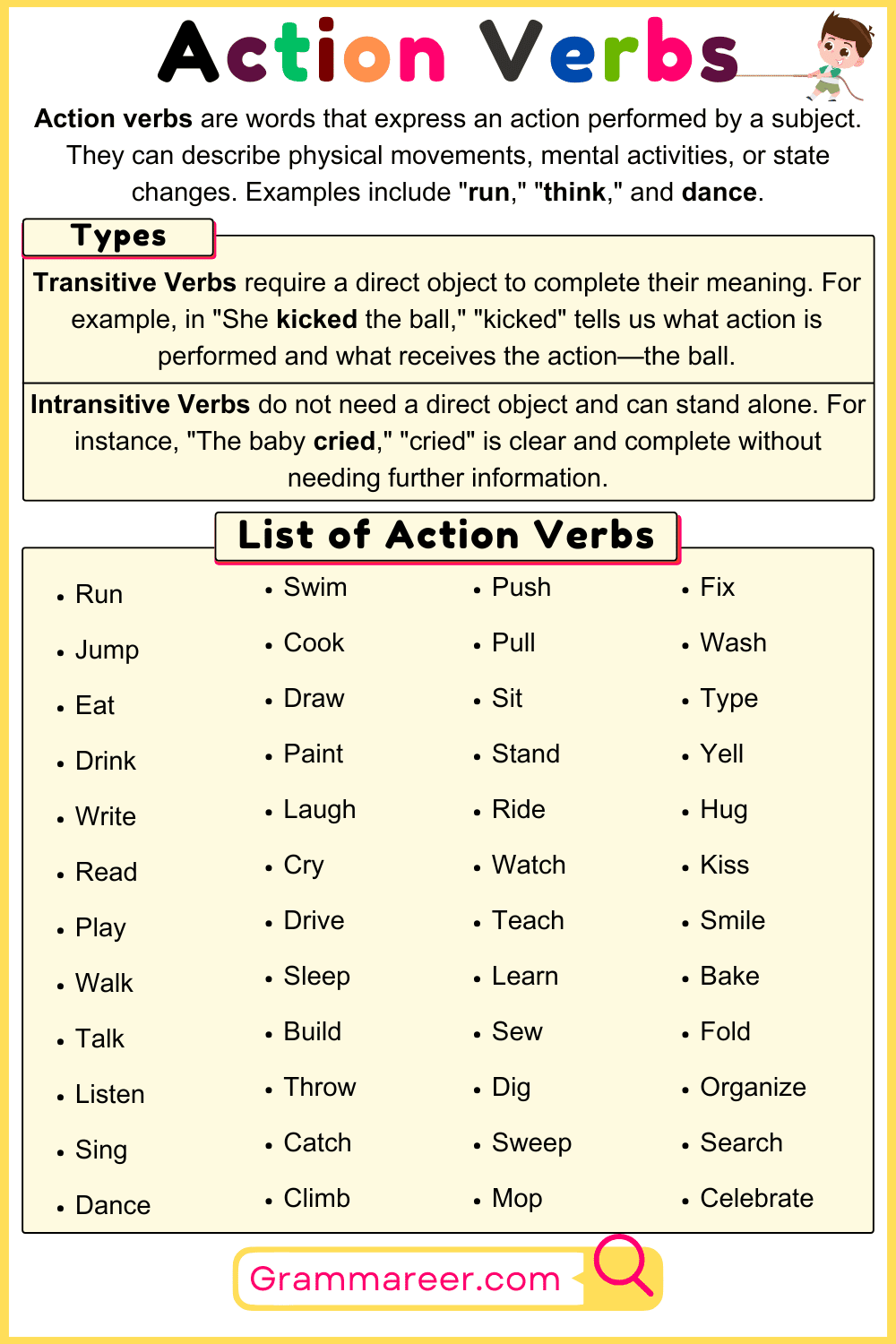
- Run
- Jump
- Eat
- Drink
- Write
- Read
- Play
- Walk
- Talk
- Listen
- Sing
- Dance
- Swim
- Cook
- Draw
- Paint
- Laugh
- Cry
- Drive
- Sleep
- Build
- Throw
- Catch
- Climb
- Push
- Pull
- Sit
- Stand
- Ride
- Watch
- Teach
- Learn
- Sew
- Dig
- Sweep
- Mop
- Fix
- Wash
- Type
- Yell
- Hug
- Kiss
- Smile
- Bake
- Fold
- Organize
- Search
- Celebrate
- Rest
- Travel
Action verbs describe what someone or something does. They show physical or mental actions, and you can use them in sentences to express what’s happening. Here’s how to use them:
Identify the Action
Think about what the subject (person or thing) is doing. For example:
- She runs.
- They study.
Use the Right Verb for the Subject
Make sure the action verb matches the subject in the sentence:
- He jumps. (singular subject)
- They jump. (plural subject)
Choose the Right Form (Tense)
Use the correct verb tense to show when the action happens:
- Past: She walked yesterday.
- Present: She walks now.
- Future: She will walk tomorrow.
Add Details if Needed
You can add more information to the action verb to explain it better:
- He ate a sandwich. (What did he eat?)
- She reads quickly. (How does she read?)
| Aspect | Action Verbs | Stative Verbs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Show actions or activities | Describe states or conditions |
| Examples | run, jump, eat, write, swim | be, know, love, believe, seem |
| Usage | Can be used in all tenses | Usually don’t change form |
| Focus | What someone does | How someone feels or exists |
| Tense Forms | “She runs,” “She ran,” “She is running” | “I am knowing” (incorrect), “I know” |
Read More