Understanding direct and indirect speech is essential for improving English communication and grammar. Direct speech quotes the exact words of a speaker, while indirect speech conveys the message without quotation marks. The verb tense, pronouns, and time expressions often change when converting from direct to indirect speech. In this blog post, we’ll cover the key rules in both English and Urdu, helping you master sentence transformations with ease.
Learn more about grammar here.
Table of Contents
Direct and Indirect Speech Rules in English
What is Direct Speech?
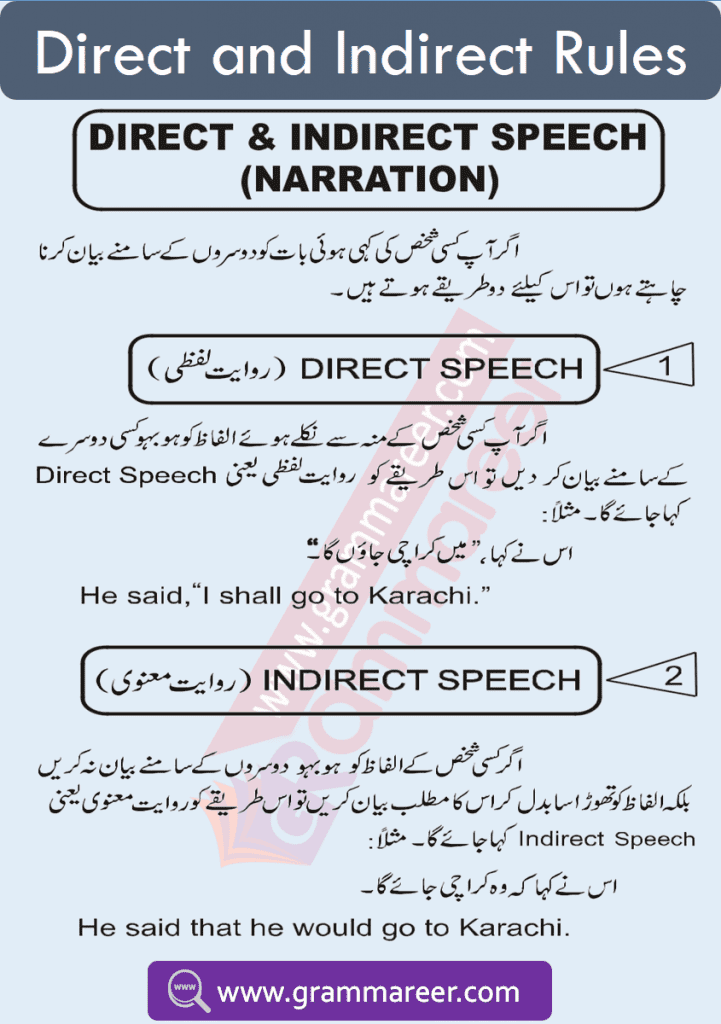
Direct speech is a report of the exact words used by a speaker or writer. for example She said, “I am watching a movie”.
What is Indirect Speech?
A report on what someone else said or wrote without using that person’s exact words. for example She said that she was watching a movie.
Direct Speech Example Sentence
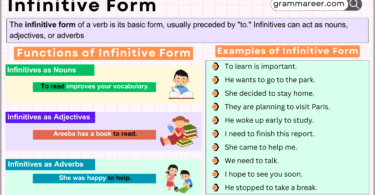
✅ Direct Speech:
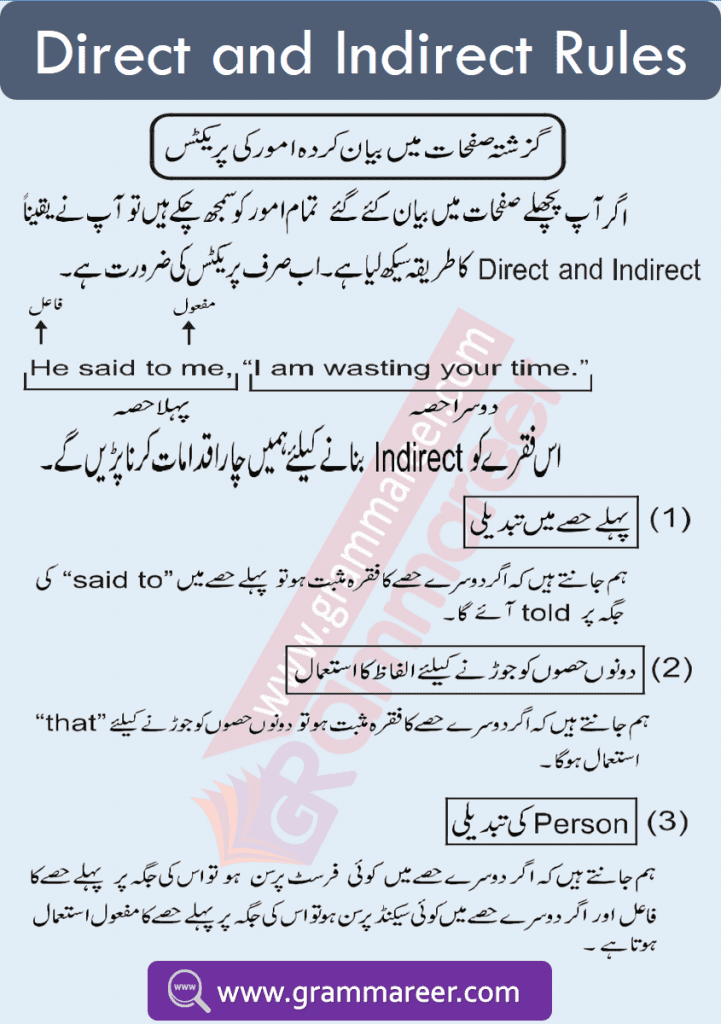
He said to me, “I am going to Karachi.”
A direct speech sentence consists of two parts:
1️⃣ Reporting Speech (Part 1):
👉 He said to me.
- This part contains the subject (He), object (me), and a comma (,) before the quotation.
2️⃣ Reported Speech (Part 2):
👉 “I am going to Karachi.”
- This part is enclosed in inverted commas (” “) and contains the speaker’s exact words.

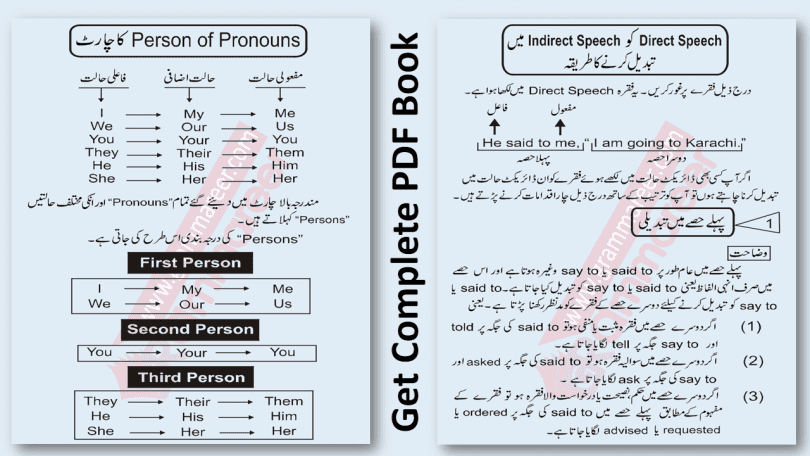
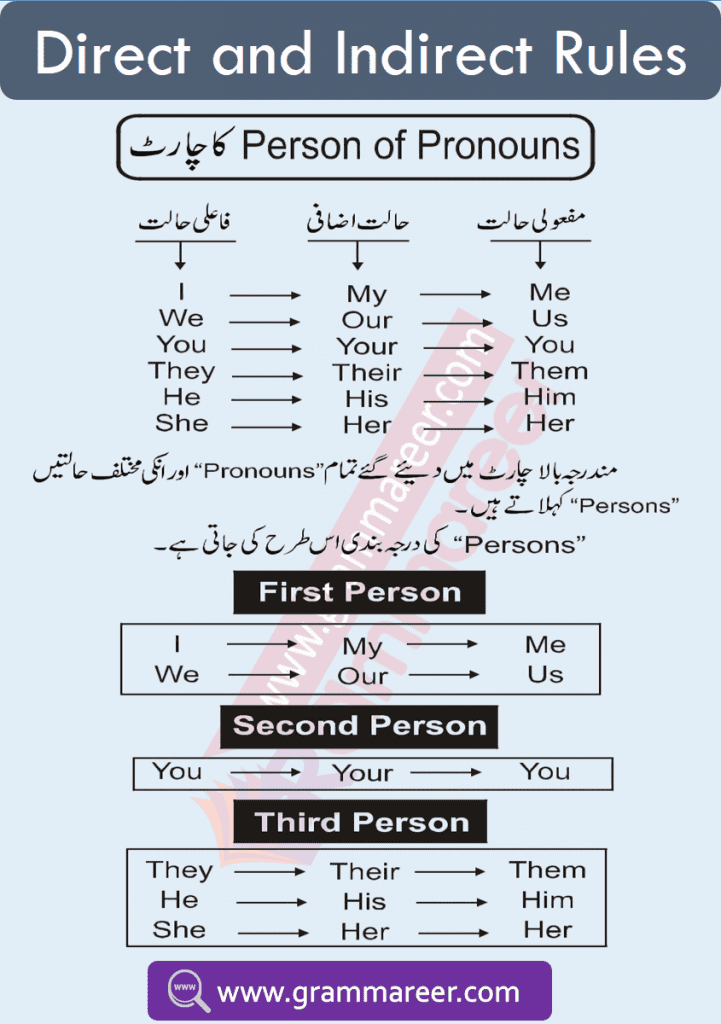
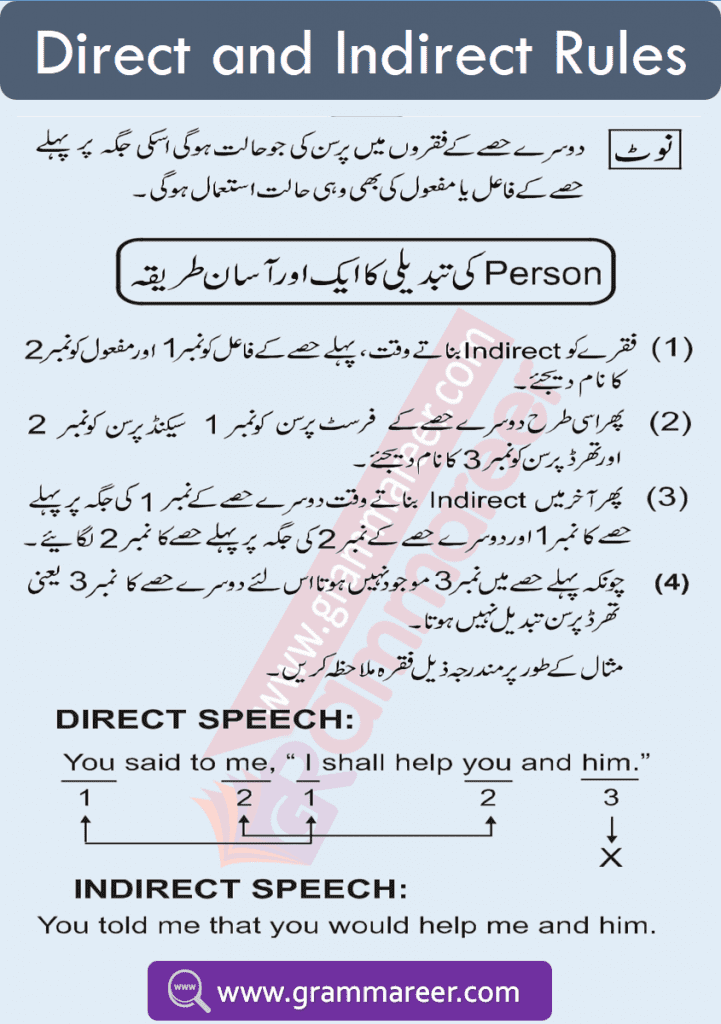
Persons of Pronouns
| I | My | Me |
| You | Your | You |
| They | Their | Them |
| He | His | Him |
| She | Her | Her |
| We | Our | Us |
1st Person
| I | My | Me |
| We | Our | Us |
2nd Person
| You | Your | You |
3rd Person:
| They | Their | Them |
| He | His | Him |
| She | Her | Her |
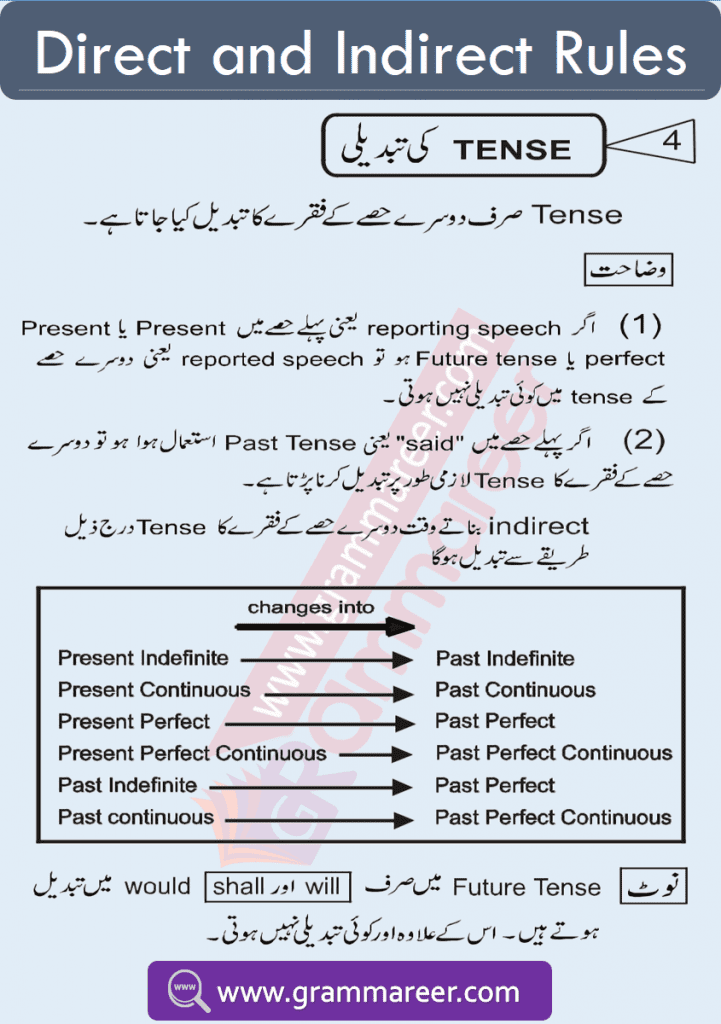
Rules for Changing Direct Speech to Indirect Speech
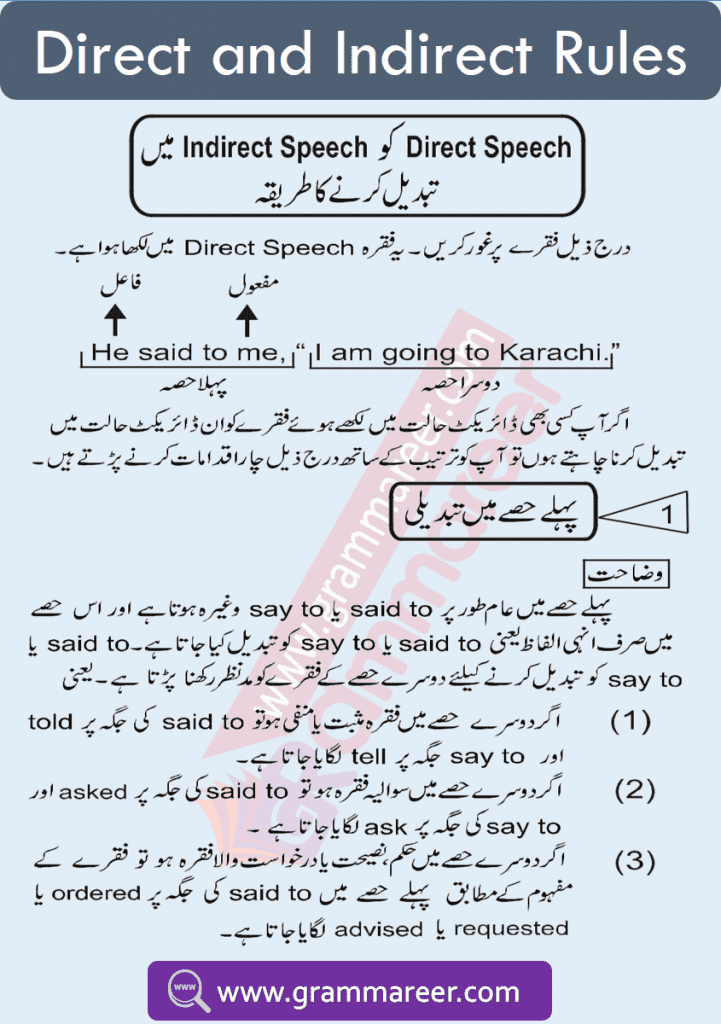
1️⃣ Simple & Negative Sentences
- “Said to” → “Told”
- “Say to” → “Tell”
✅ Example:
🔹 Direct: He said to me, “I am busy.”
🔹 Indirect: He told me that he was busy.
2️⃣ Interrogative Sentences (Questions)
- “Said to” → “Asked”
- “Say to” → “Ask”
✅ Example:
🔹 Direct: She said to him, “Where are you going?”
🔹 Indirect: She asked him where he was going.
3️⃣ Commands, Advice, and Requests
- “Said to” → “Ordered,” “Advised,” or “Requested” (based on context)
✅ Example (Order):
🔹 Direct: The teacher said to the student, “Sit down.”
🔹 Indirect: The teacher ordered the student to sit down.
✅ Example (Advice):
🔹 Direct: The doctor said to him, “Take your medicine on time.”
🔹 Indirect: The doctor advised him to take his medicine on time.
✅ Example (Request):
🔹 Direct: She said to me, “Please help me.”
🔹 Indirect: She requested me to help her.
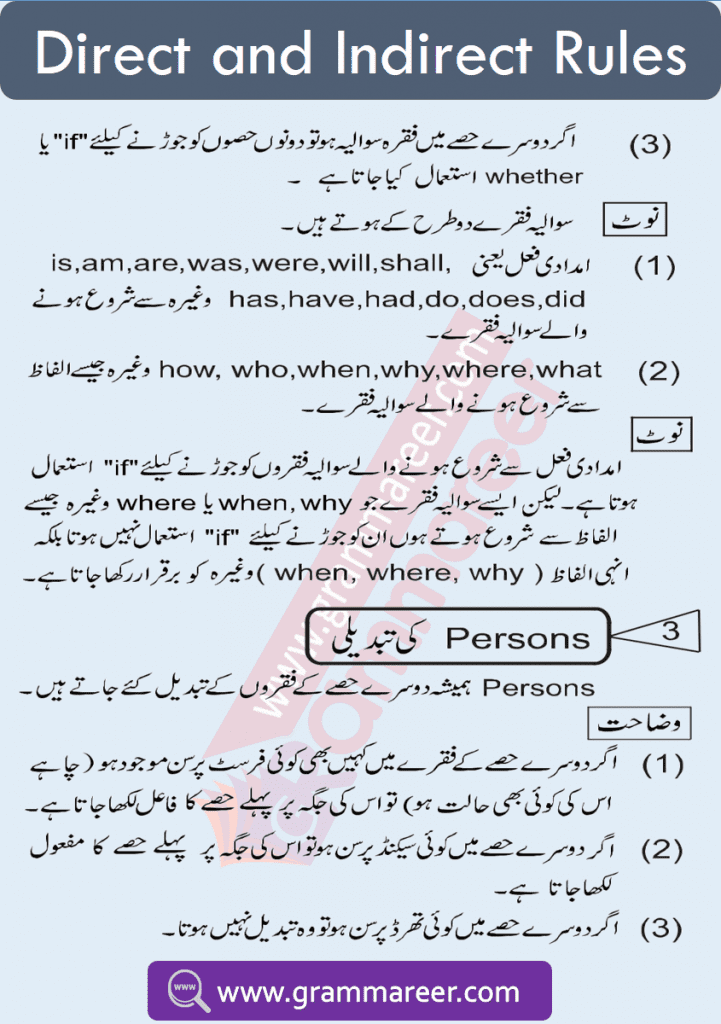
4️⃣ Sentences Expressing a Proposal or Suggestion
- “Said to” → “Proposed”
✅ Example:
🔹 Direct: He said to me, “Let’s go for a walk.”
🔹 Indirect: He proposed to me that we should go for a walk.
5️⃣ Sentences Expressing Joy, Sorrow, or Wonder
- “Said to” → “Exclaimed with joy” (خوشی)
- “Said to” → “Exclaimed with sorrow” (افسوس)
- “Said to” → “Exclaimed with wonder” (حیرت)
✅ Example (Joy):
🔹 Direct: She said, “Hurray! We won the match!”
🔹 Indirect: She exclaimed with joy that they had won the match.
✅ Example (Sorrow):
🔹 Direct: He said, “Alas! I lost my wallet.”
🔹 Indirect: He exclaimed with sorrow that he had lost his wallet.
✅ Example (Wonder):
🔹 Direct: They said, “Wow! What a beautiful place!”
🔹 Indirect: They exclaimed with wonder that it was a beautiful place.



You May Also Like