Pronouns are essential in English, replacing nouns to prevent repetition and enhance sentence flow. Understanding the various types of pronouns is crucial for effective communication. In this blog post, we will delve into 10 kinds of pronouns, providing definitions and examples to clarify their usage. Mastering these will not only improve your writing but also your overall grasp of English grammar.
To deepen your understanding, explore our comprehensive resources on grammar.
Table of Contents
What is a Pronoun?
A pronoun is a word that replaces or refers to a noun (a person, place, thing, or idea) mentioned earlier in a sentence or conversation. Pronouns help avoid repetition, making speech and writing more natural and efficient.
For example:
- She is going to the store.
In this sentence, she is a personal pronoun that refers to a female person already mentioned or understood from the context. Instead of repeating the person’s name, we use she to make the sentence concise.
List of Common Pronouns
Personal Pronouns
- Subject Pronouns: I, You, He, She, It, We, They
- Object Pronouns: Me, You, Him, Her, It, Us, Them
Examples of Pronouns in Sentences
- I am going to the park to meet my friends.
- You should finish your homework before dinner.
- He is playing soccer in the backyard.
- She loves to read books in her free time.
- It is a sunny day outside.
- We are going to the beach this weekend.
- They are planning a surprise party for him.
- The teacher asked me to answer the question.
- I gave the ball to him to play with.
- She saw her friend at the park.
Why Are Pronouns Important?
- Avoid Repetition – Pronouns replace nouns, preventing redundancy in sentences.
- Enhance Clarity – They help create smooth and coherent communication.
- Improve Fluency – Pronouns make speech and writing more engaging and natural.
- Maintain Subject-Verb Agreement – Using the correct pronoun ensures grammatical accuracy.
- Increase Flexibility – Pronouns adapt to different grammatical roles (subject, object, possessive).
- Save Time in Communication – They allow for concise expression, especially in conversations.
Noun vs. Pronoun: Key Differences
| Feature | Noun | Pronoun |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Names a person, place, thing, or idea | Replaces a noun to avoid repetition |
| Number | Can be singular or plural | Can be singular or plural |
| Possession | Has possessive forms (e.g., boy’s, house’s) | Uses different forms to show possession (e.g., his, hers, theirs) |
| Examples | boy, house, dog, love | he, she, it, they |
Pronouns are essential for effective communication, helping to make sentences more natural, concise, and engaging. Mastering their usage will improve both writing and speaking skills.

10 Kinds of Pronouns
Pronouns are essential components of English grammar, replacing nouns to prevent redundancy and enhance sentence fluidity. Understanding the various types of pronouns is crucial for effective communication. Below is an overview of different pronoun categories, each serving a unique function in language.
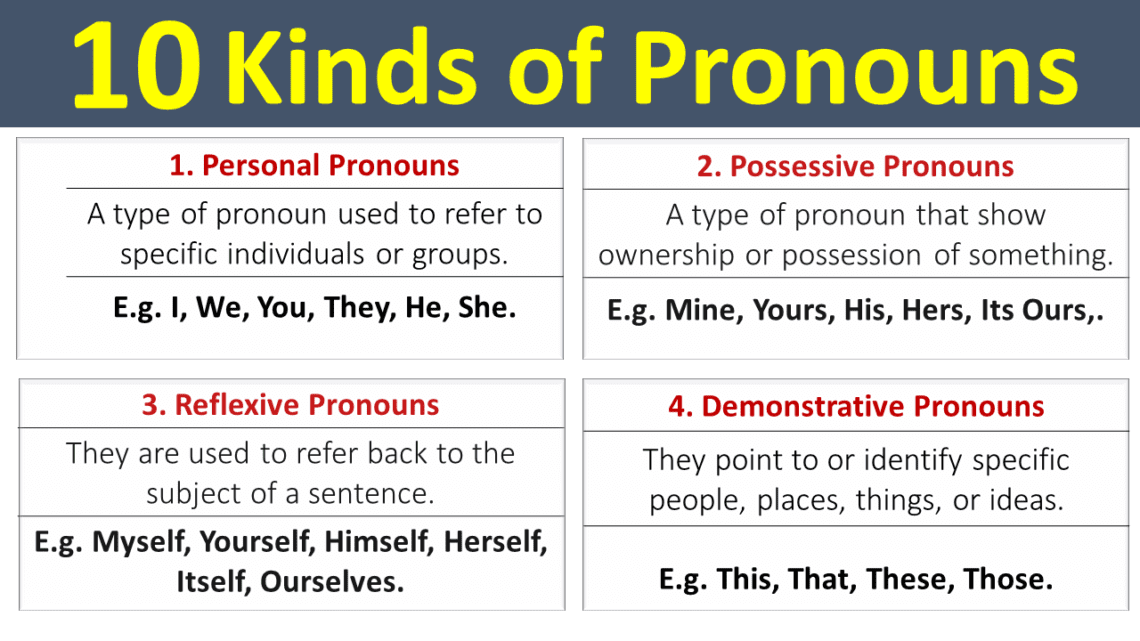
1. Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns substitute specific nouns, indicating person, number, and sometimes gender. They are categorized as follows:
- First Person: I (singular), we (plural)
- Second Person: you (singular and plural)
- Third Person: he (singular masculine), she (singular feminine), it (singular neutral), they (plural)
Examples:
- I am learning English.
- They are attending the workshop.
2. Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns denote ownership or possession, replacing nouns to avoid repetition. They include:
- mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs
Examples:
- This book is mine.
- The decision is theirs.
3. Reflexive Pronouns
Reflexive pronouns refer back to the subject of the sentence, indicating that the subject performs an action on itself. They are:
- myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves
Examples:
- She prepared herself for the presentation.
- We organized the event ourselves.
4. Demonstrative Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns point to specific nouns and indicate their proximity in space or time. The primary demonstrative pronouns are:
- this, that, these, those
Examples:
- This is my favorite mug.
- Those were memorable days.
5. Interrogative Pronouns
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions about people or things. They include:
- who, whom, whose, which, what
Examples:
- Who is leading the meeting?
- Which option do you prefer?
6. Relative Pronouns
Relative pronouns introduce relative clauses, connecting them to the main clause and providing more information about a noun. Common relative pronouns are:
- who, whom, whose, which, that
Examples:
- The author who wrote this novel is renowned.
- The house that we visited is historic.
7. Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite pronouns refer to non-specific persons or things. They include:
- someone, anyone, everyone, no one, somebody, anybody, nobody, everybody, something, anything, nothing, everything
Examples:
- Someone left their umbrella.
- Is there anything we can do?
8. Reciprocal Pronouns
Reciprocal pronouns express mutual actions or relationships between two or more subjects. The primary reciprocal pronouns are:
- each other, one another
Examples:
- The partners trust each other.
- The teammates congratulated one another.
9. Intensive Pronouns
Intensive pronouns emphasize a preceding noun or pronoun, often identical in form to reflexive pronouns. They are:
- myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves
Examples:
- The CEO herself approved the proposal.
- I myself witnessed the event.
10. Possessive Relative Pronouns
Possessive relative pronouns show possession and introduce relative clauses. They include:
- whose, of which
Examples:
- The scientist whose research was groundbreaking received an award.
- The company, of which he is a member, is expanding.

Pronoun Chart
| Pronoun Type | Subject | Object | Possessive Adjective | Possessive Pronoun | Reflexive | Intensive |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Person | I | Me | My | Mine | Myself | Myself |
| 2nd Person | You | You | Your | Yours | Yourself | Yourself |
| 3rd Person | He/She/It | Him/Her/It | His/Her/Its | His/Hers/Its | Himself/Herself/Itself | Himself/Herself/Itself |
| 1st Person (Plural) | We | Us | Our | Ours | Ourselves | Ourselves |
| 2nd Person (Plural) | You | You | Your | Yours | Yourselves | Yourselves |
| 3rd Person (Plural) | They | Them | Their | Theirs | Themselves | Themselves |

A1: Reflexive pronouns indicate that the subject performs an action on itself, essential to the sentence’s meaning. Intensive pronouns, however, merely emphasize a noun or pronoun and can be removed without altering the sentence’s core meaning.
A2: Demonstrative pronouns—this, that, these, those—replace specific nouns and indicate proximity. If the word points to a particular noun and stands alone without a following noun, it’s a demonstrative pronoun.
A3: Yes, “it” functions as a third-person singular neutral personal pronoun, commonly referring to objects, animals, or abstract concepts without specifying gender.
You May Also Like